User’s Manual
141
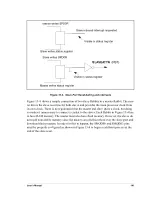
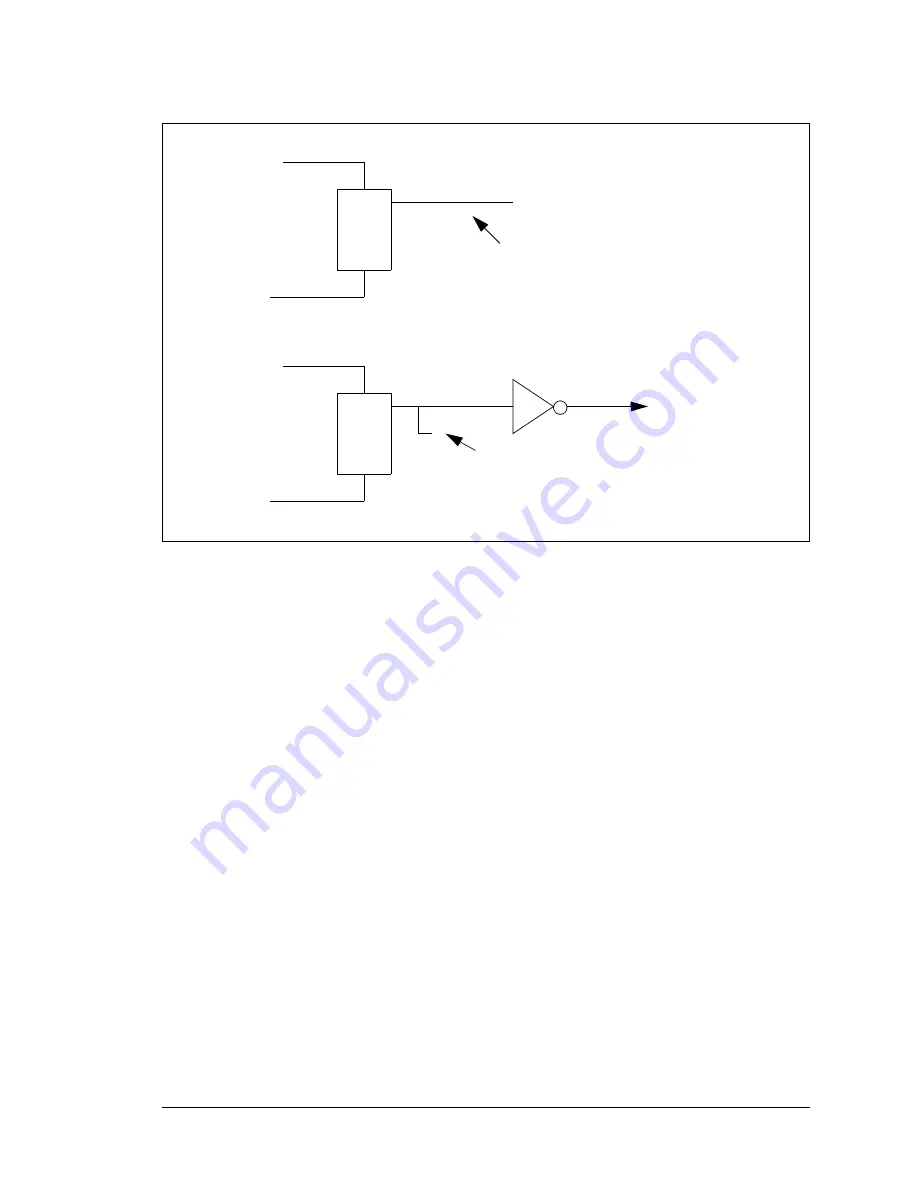
Figure 13-3. Slave Port Handshaking and Interrupts
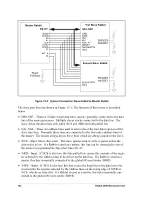
Figure 13-4 shows a sample connection of two slave Rabbits to a master Rabbit. The mas-
ter drives the slave reset line for both slaves and provides the main processor clock from
its own clock. There is no requirement that the master and slave share a clock, but doing
so makes it unnecessary to connect a crystal to the slaves. Each Rabbit in Figure 13-4 has
to have RAM memory. The master must also have flash memory. However, the slaves do
not need nonvolatile memory since the master can cold boot them over the slave port and
download their program. In order for this to happen, the SMODE0 and SMODE1 pins
must be properly configured as shown in Figure 13-4 to begin a cold boot process at the
end of the slave reset.
Master writes SPD0R
Slave writes status register
Slave inbound interrupt requested
Visible in status register
Slave writes SPD0R
Master writes status register
/SLAVEATTN
(PB7)
Visible in status register
Содержание 2000
Страница 1: ...Rabbit 2000 Microprocessor User s Manual 019 0069 041018 M...
Страница 12: ...6 Rabbit 2000 Microprocessor...
Страница 46: ...40 Rabbit 2000 Microprocessor...
Страница 54: ...48 Rabbit 2000 Microprocessor...
Страница 76: ...70 Rabbit 2000 Microprocessor...
Страница 96: ...90 Rabbit 2000 Microprocessor...
Страница 142: ...136 Rabbit 2000 Microprocessor...
Страница 154: ...148 Rabbit 2000 Microprocessor...
Страница 170: ...164 Rabbit 2000 Microprocessor...
Страница 174: ...168 Rabbit 2000 Microprocessor...
Страница 180: ...174 Rabbit 2000 Microprocessor...
Страница 202: ...196 Rabbit 2000 Microprocessor...
Страница 206: ...200 Rabbit 2000 Microprocessor...
Страница 226: ......
Страница 230: ...224 Rabbit 2000 Microprocessor...