5G Module Series
RM500Q-GL Hardware Design
RM500Q-GL_Hardware_Design 44 / 85
4.3.3. Reference design for PCIe
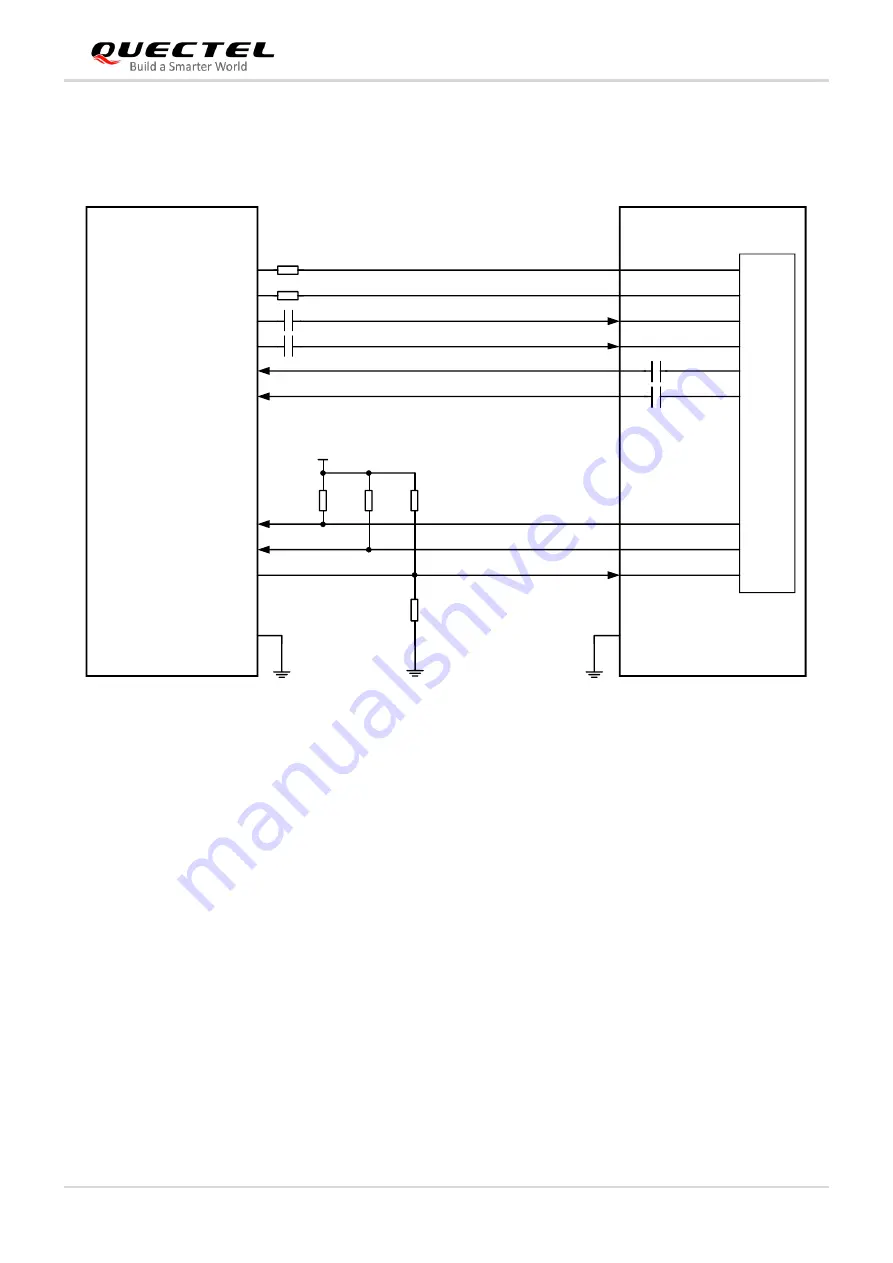
The following figure shows a reference circuit for the PCIe interface.
Host
Module
PCIE_REFCLK_P
PCIE_REFCLK_M
PCIE_RX_P
PCIE_RX_M
PCIE_TX_P
PCIE_TX_M
BB
PCIE_REFCLK_P
PCIE_REFCLK_M
PCIE_RX_P
PCIE_RX_M
PCIE_TX_P
PCIE_TX_M
55
53
49
47
43
41
PCIE_CLKREQ_N
PCIE_RST_N
PCIE_WAKE_N
PCIE_CLKREQ_N
PCIE_RST_N
PCIE_WAKE_N
VCC_IO_HOST
54
52
50
NOTE:
The voltage level VCC_IO_HOST of these three signals depend on the host side due to open drain.
R5 0
Ω
R4 0
Ω
C3 220 nF
C4 220 nF
C1 220 nF
C2 220 nF
R1
10k
R2
10k
R3
NM/10k
R6
10k
Figure 19: PCIe Interface Reference Circuit
To ensure the signal integrity of PCIe interface, AC coupling capacitors C3 and C4 should be placed close
to the host on PCB. C1 and C2 have been integrated inside the module, so do not place these two
capacitors on your schematic and PCB.
The following principles of PCIe interface design should be complied with to meet the PCIe specification.
⚫
Keep the PCIe data and control signals away from sensitive circuits and signals, such as RF, audio,
crystal and oscillator signals.
⚫
Add a capacitor in series on Tx/Rx traces to prevent any DC bias.
⚫
Keep the maximum trace length less than 300 mm.
⚫
Keep the length matching of each differential data pair (Tx/Rx) less than 0.7 mm for PCIe routing
traces.
⚫
Keep the differential impedance of PCIe data trace as 85
Ω ±10 %.
⚫
You must not route PCIe data traces under components or cross them with other traces.
















































