PortSIP Solutions, Inc
4
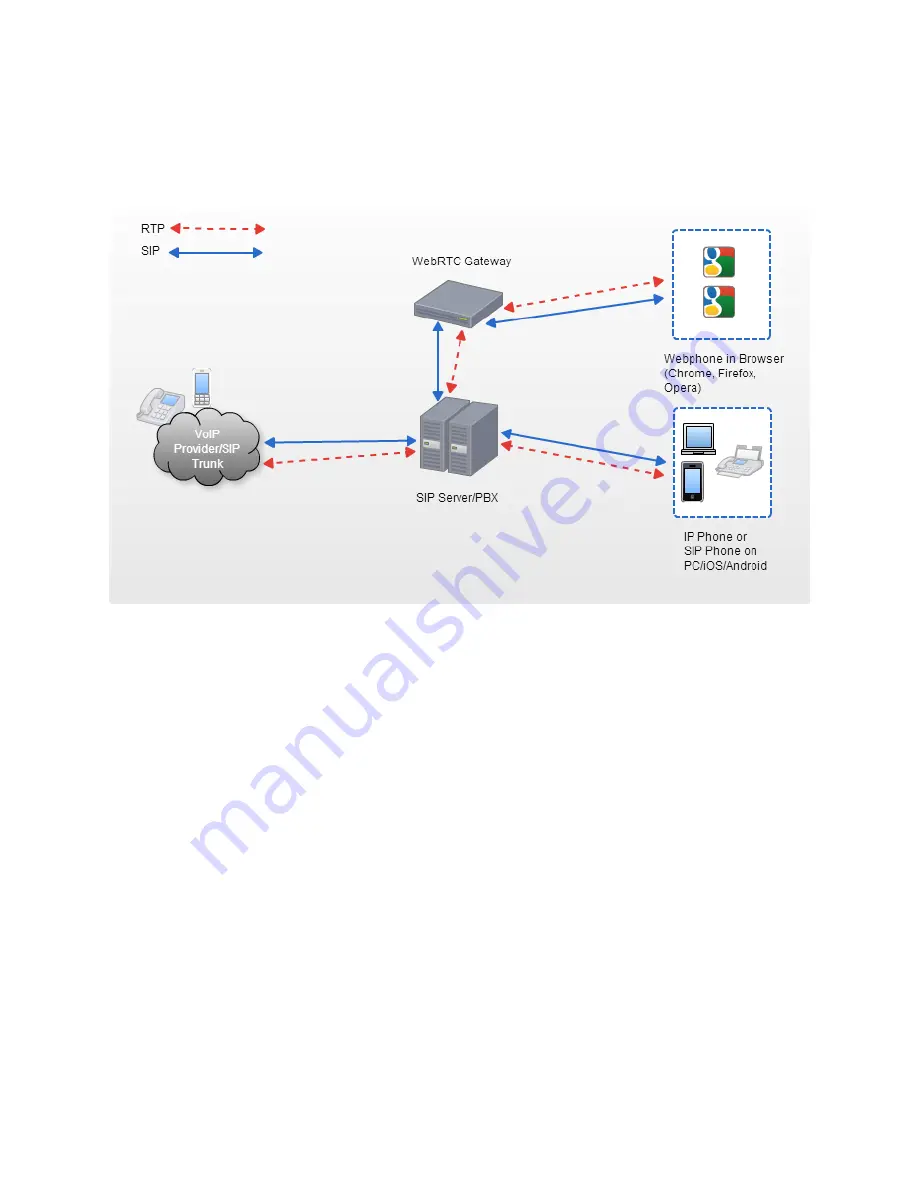
1. The WebRTC Gateway Architecture
Typically, the WebRTC Gateway architecture as below:
This document assumes that the Windows OS are already deployed and that Microsoft administrators
are available to administrators PortSIP WebRTC Gateway.
2. How it works?
PortSIP WebRTC Gateway sits at the network edge to bridge the traditional operator network
(PSTN/VoIP Provider/SIP Trunking/IP PBX) with the Web Browser, letting carriers build Web services
on top of it. The gateway essentially turns any Web page into a telephone that the network can dialogue
with as it would a phone.
Since the traditional operator network (PSTN/VoIP Provider/SIP Trunking) and SIP devices (IP Phone,
Softphone) don’t support the newest WebRTC standards such as TURN, DTLS-RTP, RTC-FB, ICE,
therefor we need the WebRTC Gateway to transform the signaling and RTP streams. That’s why the
Gateway is works like a bridge.
When the user make calls in Web Browser, the WebRTC Gateway will transform the Signaling to
standard SIP message and route calls to PSTN/VoIP Provider/SIP Trunking/IP PBX. After the call
established, the WebRTC Gateway receive RTP stream from browser and transcode it then send to
PSTN/VoIP Provider/SIP Trunking/IP PBX and vice versa.












