1. Be sure air is in "OFF" position when connecting tool to air supply.
2. Always wear approved eye protection when using air tools. If raising dust, wear a
suitable mask.
WARNING: Some dust created by power sanding, sawing, grinding, drilling, and other construction activities, contain chemicals known [to
the State of California] to cause cancer, birth defects or other reproductive harm. Some examples of these chemicals are:
1. Lead from lead-based paints;
2. Crystalline silica from bricks and cement or other masonry products;
3. Arsenic and chromium from chemically treated lumber.
Your risk from these exposures varies, depending on how often you do this type of work. To reduce your exposure to these chemicals:
work in a well ventilated area, and work with approved safety equipment, such as those dust masks that are specially designed to filter out
microscopic particles.
3. Use only those accessories that are designed for use with air tools. For example, with
impact wrenches do not use ordinary sockets. Use impact sockets for all- air tools.
4. Be sure to disconnect tool from air supply before changing accessories, performing
service on tool and when not in use.
5. As with any tool, use common sense when operating. Do not wear loose clothing or
jewelry that could become caught by moving parts, causing injury. Operate tool a safe
distance from yourself and others in the work area.
6. To ensure long life of the air tool be sure to oil the tool daily before using. See below for
instructions.
7. Follow air source manufacturers directions for connection of regulators, filters, and
other accessories to air source. Do not install quick couplers directly on tool as they put
unnecessary strain on the air inlet threads possibly causing them to wear out
prematurely. Instead, install them on a short length of air hose attached to the tool.
1. Use of a center punch to mark the starting point of a hole is recommended when
drilling metals with this tool. Place drill against work before starting motor. Do not apply
too much pressure to the drill as this can cause the bit to overheat and break. When the
hole is drilled, do not stop the drill until it is withdrawn from work.
2. If the drill should bind and stop inside the work, release the trigger immediately and
determine the cause. If removal of bit from the drill is necessary, disconnect the drill from
the air source before removing. Do not attempt to free the bit by forcing it with the drill.
3. A forward and reverse lever permits the tool to run in a forward (clockwise) rotation or in
reverse (Counter-clockwise) rotation. Do not attempt to change direction while tool is running.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
OPERATION
Clean air of correct air pressure is recommended for the power supply for this tool. A
maximum of 90 PSI at the tool is recommended for most air tools of this class. Check
specifications section for recommended pressure. (Depending on length of air hose and
other circumstances, air pressure at compressor may need to be increased to 100 PSI to
ensure 90 PSI at the tool.)
Water in the air hose and compressor tank contributes to reduced performance and
damage of the air tool. Drain the air tank and filters before each use and as necessary to
keep the air supply dry.
Hose length over 25’ causes loss in line pressure. Increase hose I.D. or increase
compressor pressure to compensate for the pressure loss. Use an in-line pressure
regulator with gauge if air inlet pressure is critical.
AIR SOURCE
Oil tool before each use. 4 to 5 drops of a good grade Air Tool Oil placed in the air inlet
is sufficient. Use proper air pressure and CFM rating listed for this tool.
Drain water from hoses and compressor tank. Water in the air supply line will cause
gumming and loss of power. Clean the air filter on the supply line and flush the tool with
gum solvent or a 50/50 mix of air tool oil and kerosene. It may be necessary to
disassemble the tool to properly clean and re-lubricate.
LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE
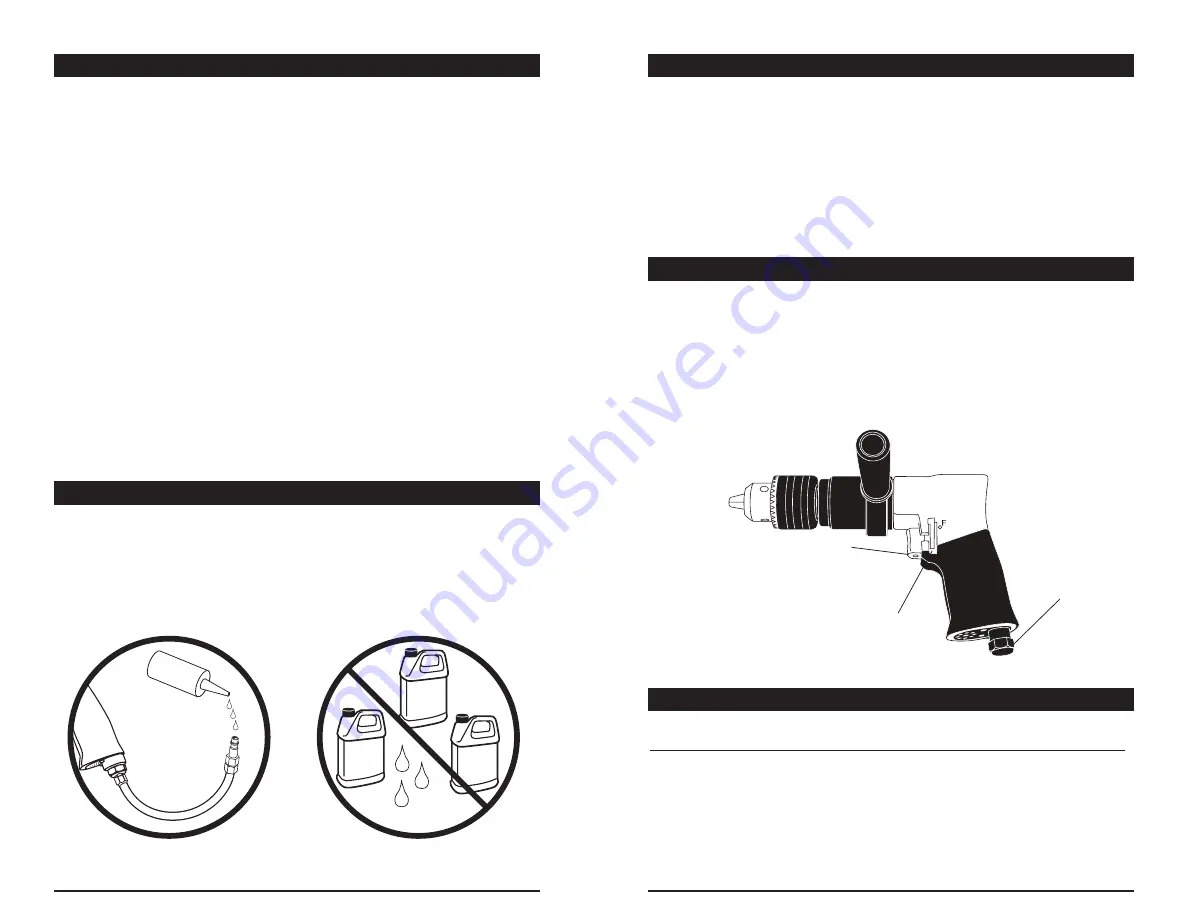
Forward/Reverse Lever
Air Inlet
Trigger
INSUFFICIENT POWER:
Probable Cause
Solution
Dirty or clogged air passages......... Flush and lubricate tool, drain air tank and supply line
Insufficient air supply ...................... Increase line pressure, Make sure compressor
matches tool's air pressure and consumption needs
Air leakage ...................................... Use Teflon tape at all fittings and joints. Check tool for
worn or damaged O-rings & seals.
Worn/damaged wear & tear parts .. Replace as necessary.
Tool matching ................................. Be sure you are using a tool suited for the torque
requirements of the job at hand.
TROUBLESHOOTING
Motor
Oil
Trans.
Fluid
Brake
Fluid
Water
Whip
hose
Air Tool
Oil
Yes
No
1
2