5
and charge housing with about 10 psi of
air. Be sure air is dry. Do not use air line
where water may be trapped in the line.
Submerge complete unit under water
and check for leaks.
Refill motor chamber with oil. Use high
grade transformer oil or Hydromatic
special submersible oil. Fill chamber until
oil covers top of the windings. Leave
air space in the top for expansion. Use
Permatex on plug threads.
Replace Seals and Bearings:
Drain all oil from motor chamber and seal
chamber as described.
Remove motor housing as described.
Remove bolts that hold seal chamber to
pump housing. Use back-off screws to
break loose. With hardwood block, tape
end of impeller to loosen from shaft.
When free, remove impeller from shaft.
Lift rotating assembly (rotor, shaft and
impeller) from pump case and place
horizontally on bench.
Impeller removal — Hold motor and
remove bolt and washer from impeller
end of shaft. Impeller is threaded to
the shaft, so tap face of impeller with
hardwood block to free threads. Holding
rotor, turn impeller with hardwood block
to free the threads. Holding rotor, turn
impeller counterclockwise as thread is
right-hand.
Remove lower seal spring and pry out
seal with screwdriver.
To remove seal housing, take out socket
head bolts and using bolts in back of
holes, pry plates loose. This will force out
lower seal if not already removed.
Remove snap ring that holds upper seal.
Pull seal if it is free. If not free, it can be
forced off when shaft is removed.
Remove four bolts that hold bearing
housing in place. Set assembly in
upright position and bump end of shaft
on hardwood block. This will push the
bearing from the housing and will force
upper seal from shaft.
Use bearing puller to remove bearings.
Replace with new bearings. Press only
on inner face of bearing when replacing.
Pressing on outer face can damage the
bearing.
IMPORTANT: Do not use any of the old
seal parts. Replace with all new seals.
Thoroughly clean all castings before
replacing seals.
Examine all O-rings for nicks before
using.
Use Loctite
®
on socket head locking
screw into the end of the shaft.
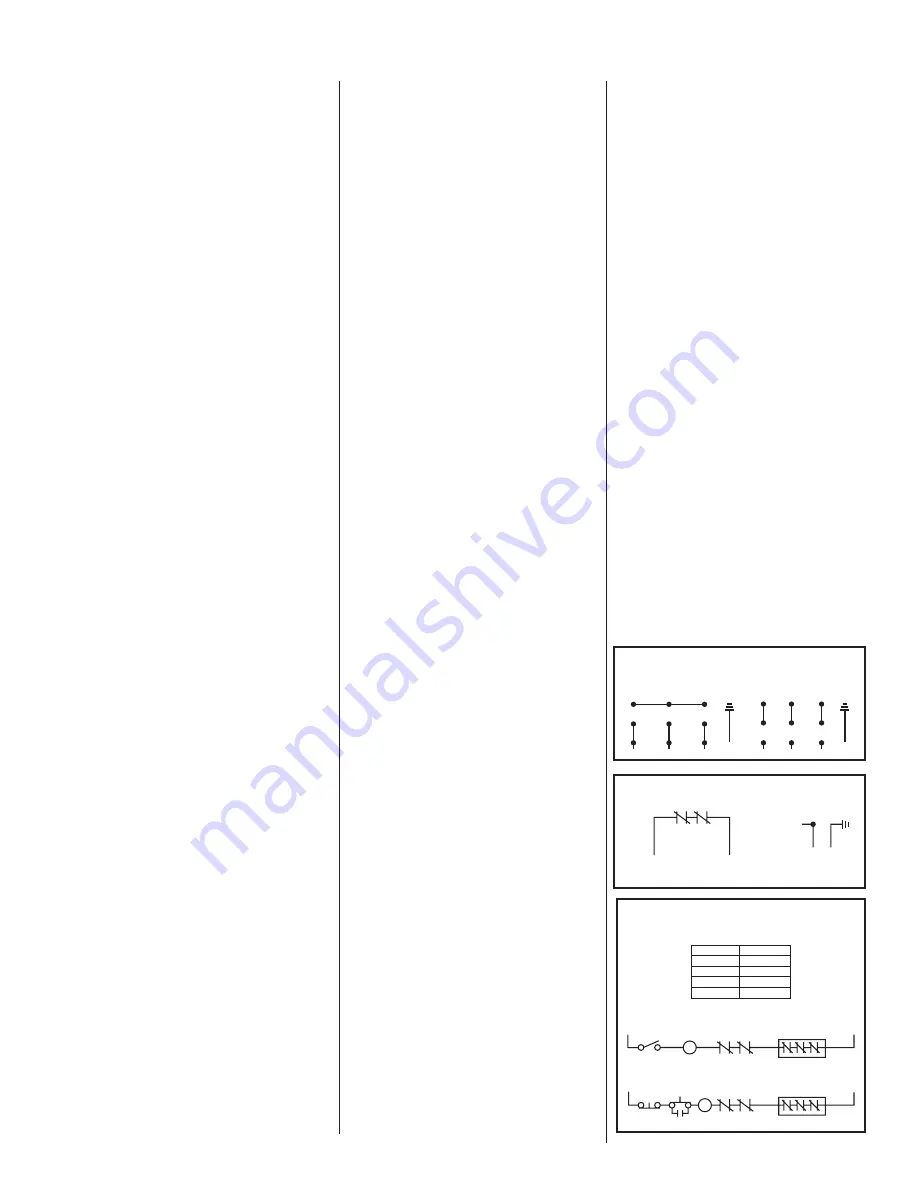
HEAT SENSORS AND SEAL FAILURE CONNECTIONS
FOR ANY VOLTAGE MOTOR
ELECTRODE
HEAT SENSORS
IN MOTOR
WINDINGS
WHITE
BLACK
HEAT SENSORS
SEAL FAILURE
RED
DARK
GREEN
CONNECTION DIAGRAM FOR LEADS IN
MOTOR AND CONNECTION BOX
(Y) WYE MOTOR CONNECTIONS
230 VOLTS
460 VOLTS
GREEN
GREEN
L3
L2
L1
L3
L2
L1
3
2
1
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
9
8
7
6
5
4
WARNING
BLACK
COIL
ON-OFF
SWITCH
L1
THERMOSTATS
IN SERIES
WHITE
L2
TWO WIRE CONTROL OFFERING AUTOMATIC RESET
THERMOSTATS
IN SERIES
WHITE
L2
BLACK
THREE WIRE CONTROL OFFERING AUTOMATIC RESET
L1
COIL
OL
OL
START
IN CERTAIN APPLICATIONS THE NEC MAY REQUIRE THREE OVERLOAD RELAYS
COLOR
PURPOSE
DARK GREEN
SEAL FAILURE
RED
SEAL FAILURE
BLACK
HEAT SENSOR
WHITE
HEAT SENSOR
WARRANTY IS VOID IF HEAT SENSORS ARE NOT
CONNECTED AS SHOWN (IN SERIES WITH CONTACTOR OIL)
Before refilling chamber with oil, air test
as described above. Refill both chambers
with oil as described above.
Always check all leads with high voltage
or with Megger for grounds before
operating the pump.
Troubleshooting
Below is a list of common problems and
the probable causes:
Pump will not start:
No power to the motor. Check for blown
fuse or open circuit breaker.
Selector switch may be in the Off position.
Control circuit transformer fuse may be
blown.
Overload heater on starter may be
tripped. Push to reset.
Pump will not start and overload
heaters trip:
Turn off power and check motor leads
with Megger or ohmmeter for possible
ground.
Check resistance of motor windings.
All three phases should show the same
reading.
If no grounds exist and the motor
windings check OK, remove pump from
sump and check for clogged or blocked
impeller.
Pump operates with selector switch
in Hand position but will not operate
in Auto position:
This indicates trouble in the float level
control or the alternator relay.
To check for a defective float control,
put selector switch in Auto position and
turn off main power. Put a jump wire on
terminal strip. Turn on power and if pump
starts, trouble is in the float control.
Replace control.
Pump runs but will not shut off:
Pump may be air locked. Turn pump off
and let set for several minutes, then
restart.
Lower float control may be hung-up in
the closed position. Check in sump to be
sure control is free.
Selector switch may be in the Hand
position.
Pump does not deliver proper
capacity:
Discharge gate valve may be partially
closed or partially clogged.
Check valve may be partially clogged.
Raise level up and down to clear.
Pump may be running in wrong direction.
Low speed pumps can operate in reverse
direction without much noise or vibration.
Discharge head may be too high.
Check total head with gauge when pump
is operating. Total head is discharge
gauge pressure converted to feet plus
vertical height from water level in sump to
center line of pressure gauge in discharge
line. Gauge should be installed on pump
side of all valves. Multiply gauge pressure
in pounds by 2.31 to get head in feet.
If pump has been in service for some time
and capacity falls off, remove pump and
check for wear or clogged impeller.
Motor stops and then restarts after
short period but overload heaters in
starter do not trip:
This indicates heat sensors in the motor
are tripping due to excessive heat.
Impeller may be partially clogged giving a
sustained overload but not high enough to
trip overload heater switch.
Motor may be operating out of liquid due
to a failed level control. All Hydromatic
submersible motors can operate for
extended periods out of water without
burning up the winding, but the heat
sensors give motor prolonged life by
controlling winding temperature.
Pump may be operating on a short cycle
due to sump being too small or from water
returning to sump due to a leaking check
valve.
Содержание S3HRC
Страница 7: ...7 Wiring Diagrams...






























