16 - PVD3627-August 2011
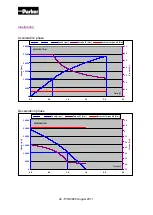
3.1.4.2. Constant Torque Phase – t
2
calculation
Method #1
This method is simple and provides an estimation of
t
2
sufficient in most situations:
:
- when the resistant torque
M
resistant
is small compared to
M
motor
- when the resistant torque
M
resistant
is equal to 0.
Procedure to follow:
We calculate firstly an estimation
2
)
(
*
max
tan
tan
base
t
resis
t
resis
M
P
Ω
+
Ω
≈
of the resistant power
P
resistant
as follows:
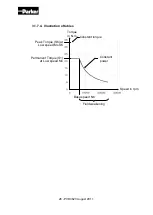
The power available for the acceleration is equal to:
Acceleration time t
2
“at constant Power” from
Base speed
to
Maximal speed
:
t
resis
mot
P
P
P
tan
−
=
So the estimated
P
J
t
base
²)
²
(
*
2
1
max
2
Ω
−
Ω
Σ
=
duration
t
2
is given by the formula:
The power available for the deceleration is equal to:
Deceleration time t
2
“at constant Power” from
Maximal speed
to
Base speed
:
t
resis
mot
P
P
P
tan
+
=
So the estimated
P
J
t
base
²)
²
(
*
2
1
max
2
Ω
−
Ω
Σ
=
duration
t
2
is given by the formula:
2
1
t
t
t
+
=
Λ
Total acceleration (resp. deceleration) time
∆
t
will be given by the sum of t
1
and t
2
: