Remote Access
The IP100 is an IP-based Web solution that provides an Internet communication link to control
and monitor a security system with Web browsers or NEware. This provides the user with the
freedom to access the system from anywhere in the world.
Step 1: Setting up the Router
This step allows you to set up the router so that the IP100 module can function properly.
1.
Ensure that the router is connected properly
as indicated in the router’s instructions.
2.
Access your router’s configuration page.
Refer to your router’s manual for the exact
procedure. In most cases, this is done by
entering the router’s static IP address in the
address bar of your Web browser, see Figure
3. For this manual, we will use 192.168.1.1 as
an example, since it is a commonly used
default router IP address. Your router’s IP
address may be indicated in the router’s
instructions or on a sticker on the router.
3.
In the router’s configuration page, check the
DHCP settings.
If DHCP is enabled
, verify that the IP
address range leaves at least one IP address
available outside of the range. The range
shown in Figure 4, would leave addresses 2
to 4 and 101 to 254 available (all the numbers
in an IP address are between 1 and 254.)
Record one of the addresses outside the
DHCP range as the one you will use for the
IP100.
If DHCP is disabled
, the IP100 will use the
default address of 192.168.1.250. It is
possible to change that address if needed
using the Paradox IP Exploring Tools
software.
4.
In the router’s configuration page, go to the
Port Range Forwarding section (also known
as “port mapping” or “port redirection.”) Add a
service/item, set the Port to 80 and enter the
static IP address selected in the previous
step for the IP module (see Figure 4.) If port
80 is already used, you can use another one,
such as 81 or 82 but you will have to modify
the IP100’s settings in step 2. Some Internet
Service Providers block port 80, therefore the
IP100 may function locally using port 80 but
not over the Internet. If this is the case,
change the port to another number. Repeat
this step for port 10 000.
Step 2: Configuring the IP100
1.
Using a computer connected to the same
network as the IP100, open the Paradox IP
Exploring Tools.
2.
Click
Find It
. Your IP100 appears in the list.
3.
Right-click your IP100 and select
Module
setup
, see Figure 6.
4.
Enter the static IP address you recorded in
Step 1.3 or modify the address so that it
corresponds to the one you have selected for
the IP100. Enter the IP100’s password (default:
paradox) and click
OK
. If it indicates that the IP
address is already used, change it to another
and modify it in the Port Forwarding of the
router (step 1.4) and go back to step 2.1.
5.
Set any additional information such as port, subnet
mask, etc. To find this information, click Start >
Programs > Accessories > Command Prompt.
Enter command: IPCONFIG /ALL (with space after
IPCONFIG).
NOTE: For increased communication security, please
change the default PC password and Panel ID in the
control panel.
NOTE: The IP100 supports SMTP and ESMTP
protocols (TLS/SSL not supported).
Step 3: Setting up ParadoxMyHome
(optional)
This step is not needed if the IP address provided
by the Internet Service Provider is static.
Using the ParadoxMyHome service will allow you to
access your system over the Internet with a dynamic IP
address. The IP100 will then poll the ParadoxMyHome
server to keep the information updated. By default, the
ParadoxMyHome service is disabled.
To set up the ParadoxMyHome service:
1.
Go to www.paradoxmyhome.com, click
Request
Login
and provide the requested information.
2.
Start the Paradox IP Exploring Tools software and
right-click the IP100.
3.
Select
Register to ParadoxMyHome
.
4.
Enter the requested information. Enter a unique
SiteID
for the module.
5.
When registration is complete, you can access the
IP100 page by going to:
www.paradoxmyhome.com/[SiteID]
If there are issues with connecting to the IP100, try
making the polling delay shorter (configured on the
IP100’s webpage interface), so that the IP information available for the ParadoxMyHome
connection is up to date. However, a shorter delay for the polls will increase the traffic on the
internet (WAN).
Step 4: Using a Web Browser to Access the System
Once the module is configured, it can be accessed either from the local network or through the
internet using the user code or user IP100 password.
On-Site Access:
1.
Enter the IP address assigned to the IP100 in the address bar of your Web browser. If you
have used a port other than port 80, you must add [: port number] at the end. (For
example, if the port used is 81, the IP address entered should look like this: http://
192.168.1.250:81).
or
Use the Paradox IP Exploring Tools software, click
Refresh
and double-click on your
IP100
in the list.
2.
Enter your alarm system’s User Code and IP100 password (default: paradox).
Off-Site Access:
1.
Go to www.paradoxmyhome.com/siteID (replace ‘siteID’ by the ‘siteID’ you used to
register with the ParadoxMyHome service)
2.
Enter your alarm system’s
User Code
and
IP100 password
(default: paradox).
Firmware and
Language Update
To update an IP100 using IP Exploring:
1.
Open IP Exploring Tools.
2.
Click the
Language / Update
tab (see
Figure 9).
3.
Select your preferred language in the
Language drop-down list.
4.
Select the correct Connection Mode from
the following three types:
Locally
- Select your IP100 from the Site
Name list
Remotely
- Enter your module's IP
Address (as shown in the Exploring Mode
tab) and NEware Port (default =
10000). Click the Exploring Mode tab,
right-click the IP100 and select More
Details.
ParadoxMyHome
- Enter your IP module
site ID.
5.
Enter the module password.
6.
Click
Update Module
. A Web update
progress box appears (see Figure 10).
If a new firmware version is found, you are
informed of the old version number and you
will have to confirm the installation of the new
version. The update process begins. If it is
interrupted, the IP100 will not be functional
until the firmware is properly installed.
Glossary
IP Reporting
Using IP reporting, system events are transmitted
to the monitoring station via the Internet. This
method provides increased security due to frequent polling by the monitoring station.
IP Addresses (Static/Fixed or Dynamic)
(Internet Protocol address) The address of a device connected to an IP network. This is
equivalent to a phone number in the sense that they are all unique and are used to establish
communication to a particular network. In an IP network, addresses can either be fixed or
dynamic. Fixed addresses are established by the network administrator while dynamic
addresses are decided through DHCP protocols and change over time.
DHCP
(Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) This protocol automatically assigns temporary IP
addresses to devices connected to an IP network. It eliminates the need to set static IP
addresses every time a device is added to a network. This is done automatically in servers
and routers.
Port Forwarding
Port Forwarding allows a router in a private network to let a party outside the network to
connect a device in the network. Once port forwarding is set, requests from the internet
(outside users) will be forwarded to the proper device. If you were to set the port number 80
(HTTP) to be forwarded to IP address 192.168.1.101, then all HTTP requests from outside
users to this port would be forwarded to the device with that address.
Table 1: Technical Specifications
Warranty
For complete warranty information on this product please refer to the Limited Warranty Statement found on the Website www.paradox.com/
terms. Your use of the Paradox product signifies your acceptance of all warranty terms and conditions. EVO, Digiplex EVO, Magellan,
Spectra SP, Esprit and Esprit E55 are trademarks or registered trademarks of Paradox Security Systems Ltd. or its affiliates in Canada, the
United States and/or other countries. For the latest information on products approvals, such as UL and CE, please visit www.paradox.com.
© 2009 Paradox Security Systems Ltd. All rights reserved. Specifications may change without prior notice. One or more of the following US
patents may apply: 7046142, 6215399, 6111256, 6104319, 5920259, 5886632, 5721542, 5287111, 5119069, 5077549
and RE39406 and
other pending patents may apply. Canadian and international patents may also apply.
This product includes software developed by Viola Systems (http://www.violasystems.com/) Copyright © 2002-2002 Viola Systems
Ltd. All rights reserved
.
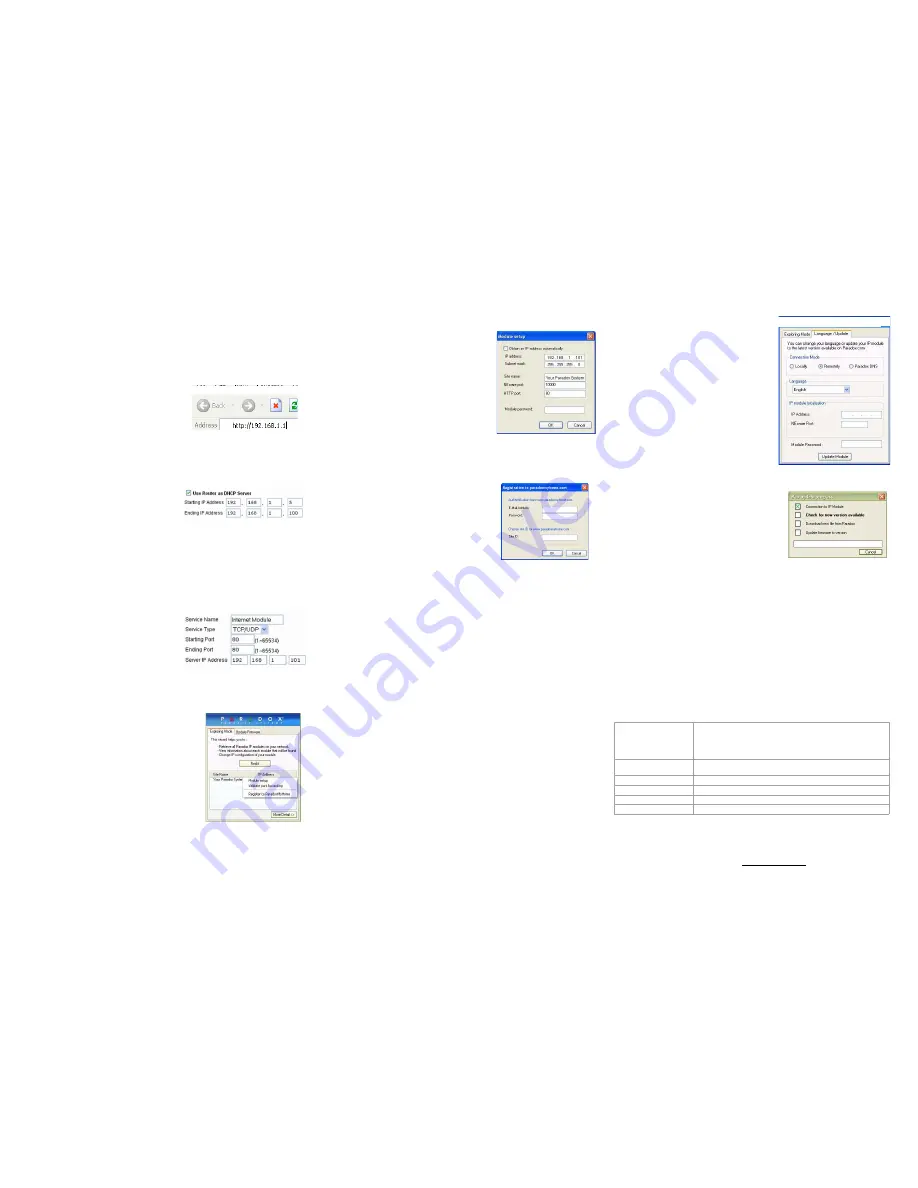
Figure 3: Router Configuration Page
*
* Screenshot may differ depending
on type of router used
Figure 4: DHCP Settings*
* Screenshot may differ depending
on type of router used
Figure 5: Port Forwarding*
* Screenshot may differ depending
on type of router used
Figure 6: IP100 Configuration Access
Figure 7: IP Address Assignment
Figure 8: Module Registration
Panel Compatibility
Any Digiplex EVO panel (V2.02 for IP reporting)
Any Spectra SP series panel (V3.42 for IP reporting)
Any MG5000 / MG5050 panel (V4.0 for IP reporting)
Any Esprit E55 (does not support IP reporting)
Esprit E65 V2.10 or higher
Browser Requirements
Optimized for Internet Explorer 6 or higher and Mozilla 1.5 or
higher 1024 x 768 resolution minimum
Encryption
AES 256-bit, MD5 and RC4
Current Consumption
110 mA
Input Voltage
Powered by the serial port
Enclosure Dimensions
9.9cm x 7.2cm x 1.8cm (3.9in x 2.8in x 0.7in)
Figure 9: Firmware and Language Update
Figure 10: Web update progress


