42
RQTV0057
Glossary
Audio channel for DVD (ch)
Sound is divided into channels based on the sound’s role.
Example: 5.1 channel
≥
Front speakers— 1 left channel and 1 right channel
≥
Center speaker— 1 channel
≥
Surround speakers— 1 left channel and 1 right channel
≥
Subwoofer— 1 channel
a
0.1
(the ratio of bass to the total amount
of sound output)
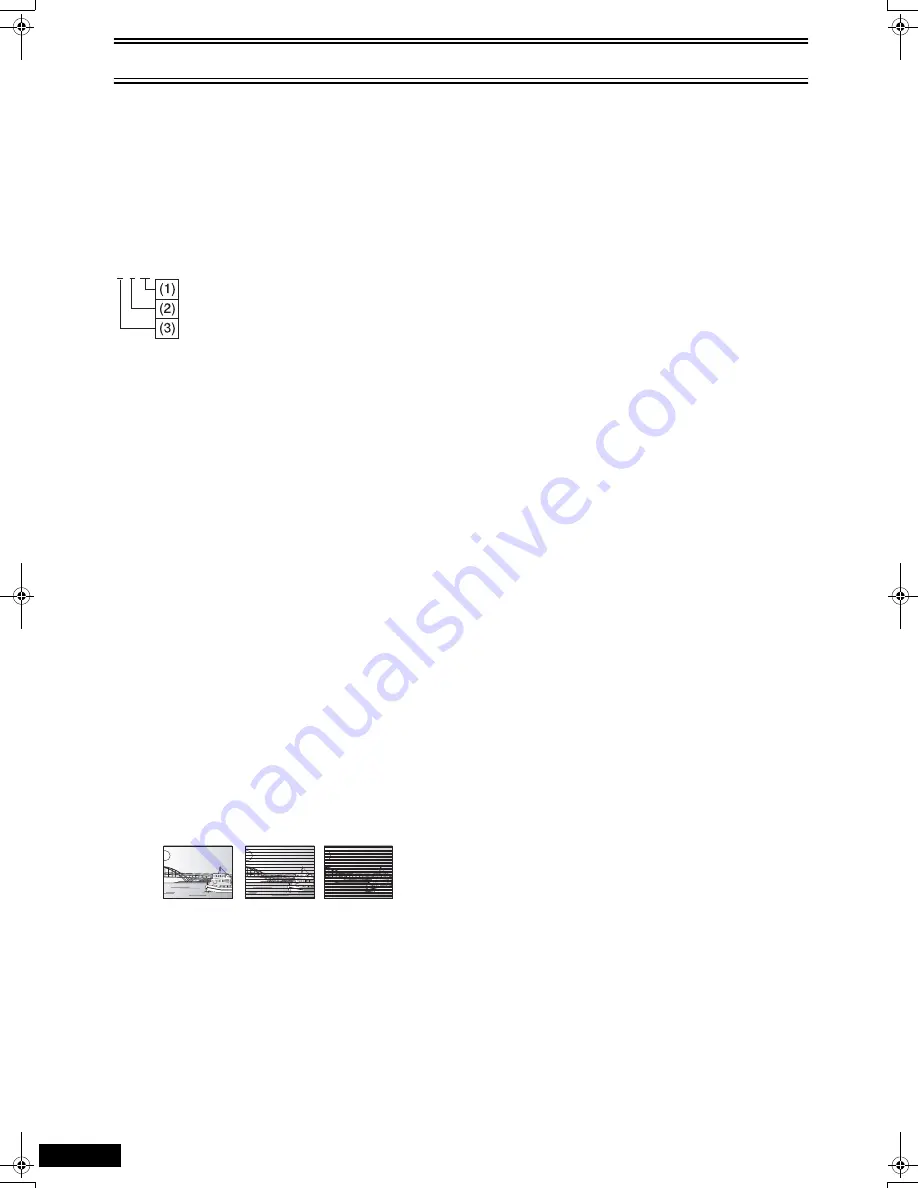
The following are indicated on the On-Screen Menu Icons.
Example:
(1) .1: Subwoofer signal
(not displayed if there is no subwoofer signal)
(2) 0: No surround
1: Mono surround
2: Stereo surround (left/right)
(3) 1: Center
2: Front left
i
Front right
3: Front left
i
Front right
i
Center
Bitstream
Digitized and compressed audio signal
It is decoded by decoders into multi-channel audio signals, such as
5.1 channels.
Decoder
A device restores the coded audio signals on DVDs to normal. This
is called decoding.
Dolby Digital
This is a method of coding digital signals developed by Dolby
Laboratories. Apart from stereo (2-channel) audio, these signals are
also compatible with 5.1-channel audio. A large amount of audio
information can be recorded on one disc using this method.
Dolby Pro Logic
A surround system where a 4-channel audio track is recorded as 2
channels and then is restored to 4 channels for play.
DTS (Digital Theater Systems)
This surround system is used in many movie theaters around the
world. There is good separation between the channels, so realistic
sound effects are possible.
Film and video
DVD-Videos are recorded using either film or video. Usually, film is
recorded at 24 frames per second, the rate movies are filmed at,
while video is recorded at 30 frames per second.
Frame and field
Frames are the still pictures that go together to make a moving
picture. A frame is made up of 2 fields.
≥
A frame still is made up of two alternating fields, so the picture may
appear blurred, but overall quality is high.
≥
A field still is not blurred, but it has only half the information of a
frame still so picture quality is lower.
ID3 tag
MP3 file that has an area in which the character-based information
referred to as ID3 tag, is stored. The information of the track, such as
the title, artist name, etc. can be stored here. The information can be
displayed on players supporting the ID3 tag when a track is played
back. However, this unit cannot because it does not support the ID3
tag.
Interlace and progressive output
NTSC, the video signal standard, has 480 interlaced (i) scan lines,
whereas progressive scanning uses twice the number of scan lines.
This is called 480p.
I/P/B
The DVD recording system shares the data commonly used by
screens and uses screen-independent data individually for each
screen to store the data on the disc efficiently.
≥
I-picture (Intra coded picture):
A frame recorded independently as reference for commonly used
data.
≥
P-picture (Predictive coded picture):
This picture is calculated based on past I- or P-pictures.
≥
B-picture (Bidirectionally-predictive coded picture):
This picture is calculated by comparing past and future I- and
P-pictures so it has the lowest volume of information.
I-picture has the best quality and is the best to use when adjusting
the picture.
Linear PCM (Pulse Code Modulation)
These are uncompressed digital signals, similar to those found on
CDs.
Multi-session
≥
This means recording data onto a CD-R/CD-RW disc several
times. “Read-in/Programme area/Read-out” of the data on a disc
makes one session.
≥
If data, such as music, is added onto a pre-recorded CD-R/RW
disc, a new session will be added. Such a disc is referred to as a
multisession disc.
≥
Normal audio CD players can play back only the first session. On
the other hand, this unit can play back 2 or more sessions.
Playback control (PBC)
≥
If a Video CD has playback control, you can select scenes and
information with menus.
≥
In this manual, playing back of the contents of a Video CD using
the menu screen is referred to as “Menu play” for Video CD.
3/2 .1 ch
Frame
Field
Field
=
+
VP33GL.book 42 ページ 2005年4月28日 木曜日 午後5時34分