Some Bright Deep-Sky Objects
Even the brightest deep-sky objects may not be
visible in the EZ View finder, so the telescope is
pointed to the object using nearby stars as guides.
Most of the brighter deep-sky objects are mostly
known by their Messier Catalog number. Charles
Messier was a French astronomer around the time
of the American Revolution, and hasd a telescope
with a smaller diameter than the TableTop
Telescope. He was searching for comets, which
when they first appear look like tiny fuzzy blobs.
But comets move. When he found a fuzzy blob
that didn't move against the background of the
sky, he marked it down with a number and
location, so he wouldn't bother with it if he ran
across it again. Many of these objects also have
nicknames.
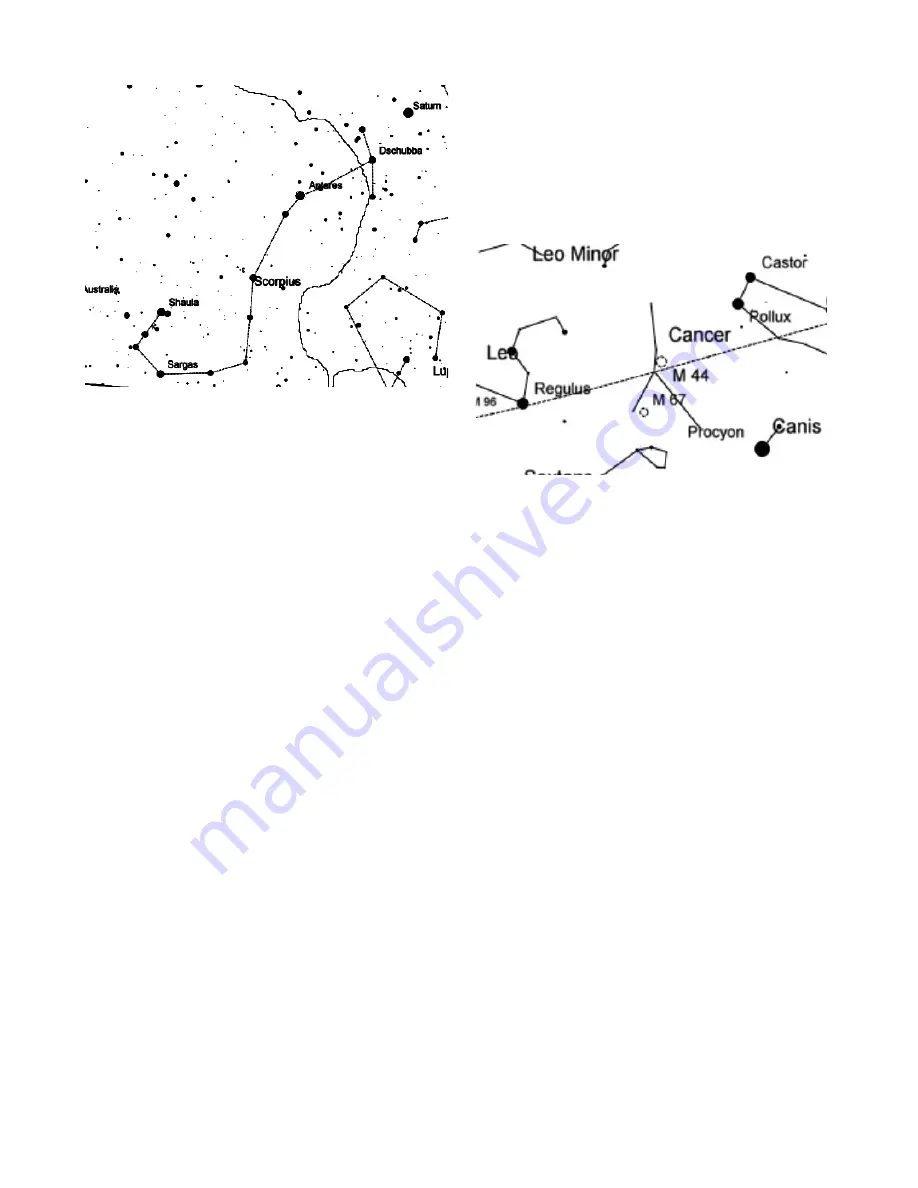
The Beehive Cluster, M44
is a nearby star
cluster easily visible as a star cluster in
binoculars. It is a springtime object. It's a faint
fuzzy spot to the naked eye. It's rather large, so it
will fill the field of the lowest power eyepiece
setting. The Beehive is an open or galactic star
cluster that are generally found in the band of the
Milky Way, unless they are close to us, or very
old. For 2015, the planet Jupiter will be between
Cancer and Leo. It was removed from the chart.
Also distant star cluster M67 in on the chart. It is
small and faint with a lot more stars than the
Beehive and will be a challenge to spot.
The Ring Nebula, M57
is small and cannot be
seen with the naked eye or with binoculars, but it
is still reasonably easy to find. A nebula is a
cloud of gas and/or dust. M57 is in the
constellation of Lyra the harp, a constellation
visible in summer and early autumn. Point the
telescope's finder about half way between the two
southern stars of the parallelogram of stars that's
the harp's body, Sulafat and Sheliak. Move the
telescope in a small spiral enlarging the search
pattern by half the field of view at a time. The
Ring Nebula will appear a ghostly small circular
glow. Once centered, more magnification may be
used. The center will be darker than the edge.
Inside is a very faint invisible star that blew out
its outer layers of gas into a smoke ring near the
end of it's life.
- 13 -
Содержание StarMax 90
Страница 16: ......
















