MP1584 – 3A, 1.5MHz, 28V STEP-DOWN CONVERTER
MP1584 Rev. 1.0
www.MonolithicPower.com
14
8/8/2011
MPS Proprietary Information. Unauthorized Photocopy and Duplication Prohibited.
© 2011 MPS. All Rights Reserved.
High Frequency Operation
The switching frequency of MP1584 can be
programmed up to 1.5MHz with an external
resistor.
With higher switching frequencies, the inductive
reactance (X
L
) of capacitor comes to dominate,
so that the ESL of input/output capacitor
determines the input/output ripple voltage at
higher switching frequency. As a result of that,
high frequency ceramic capacitor is strongly
recommended as input decoupling capacitor
and output filtering capacitor for such high
frequency operation.
Layout becomes more important when the
device switches at higher frequency. It is
essential to place the input decoupling
capacitor, catch diode and the MP1584 (Vin pin,
SW pin and PGND) as close as possible, with
traces that are very short and fairly wide. This
can help to greatly reduce the voltage spike on
SW node, and lower the EMI noise level as well.
Try to run the feedback trace as far from the
inductor and noisy power traces as possible. It
is often a good idea to run the feedback trace
on the side of the PCB opposite of the inductor
with a ground plane separating the two. The
compensation components should be placed
closed to the MP1584. Do not place the
compensation components close to or under
high dv/dt SW node, or inside the high di/dt
power loop. If you have to do so, the proper
ground plane must be in place to isolate those.
Switching loss is expected to be increased at
high switching frequency. To help to improve
the thermal conduction, a grid of thermal vias
can be created right under the exposed pad. It
is recommended that they be small (15mil
barrel diameter) so that the hole is essentially
filled up during the plating process, thus aiding
conduction to the other side. Too large a hole
can cause ‘solder wicking’ problems during the
reflow soldering process. The pitch (distance
between the centers) of several such thermal
vias in an area is typically 40mil.
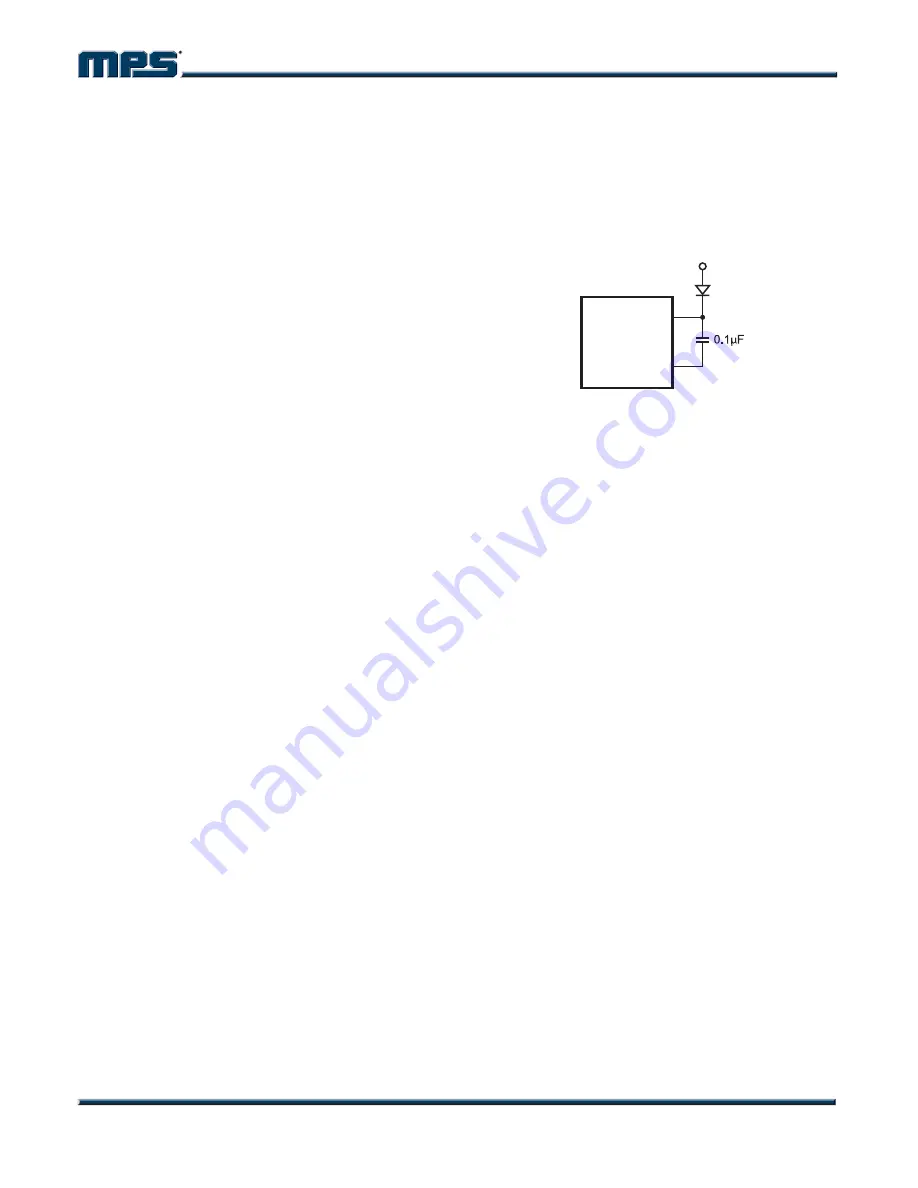
External Bootstrap Diode
It is recommended that an external bootstrap
diode be added when the input voltage is no
greater than 5V or the 5V rail is available in the
system. This helps improve the efficiency of the
regulator. The bootstrap diode can be a low
cost one such as IN4148 or BAT54.
MP1584
SW
BS
5V
Figure 2—External Bootstrap Diode
This diode is also recommended for high duty
cycle operation (when V
OUT
/V
IN
>65%) or low
V
IN
(<5Vin) applications.
At no load or light load, the converter may
operate in pulse skipping mode in order to
maintain the output voltage in regulation. Thus
there is less time to refresh the BS voltage. In
order to have enough gate voltage under such
operating conditions, the difference of V
IN
–V
OUT
should be greater than 3V. For example, if the
V
OUT
is set to 3.3V, the V
IN
needs to be higher
than 3.3V+3V=6.3V to maintain enough BS
voltage at no load or light load. To meet this
requirement, EN pin can be used to program
the input UVLO voltage to Vout+3V.

















