E x p a n s i o n
3/4 LS/VS550 OWNER’S HANDBOOK
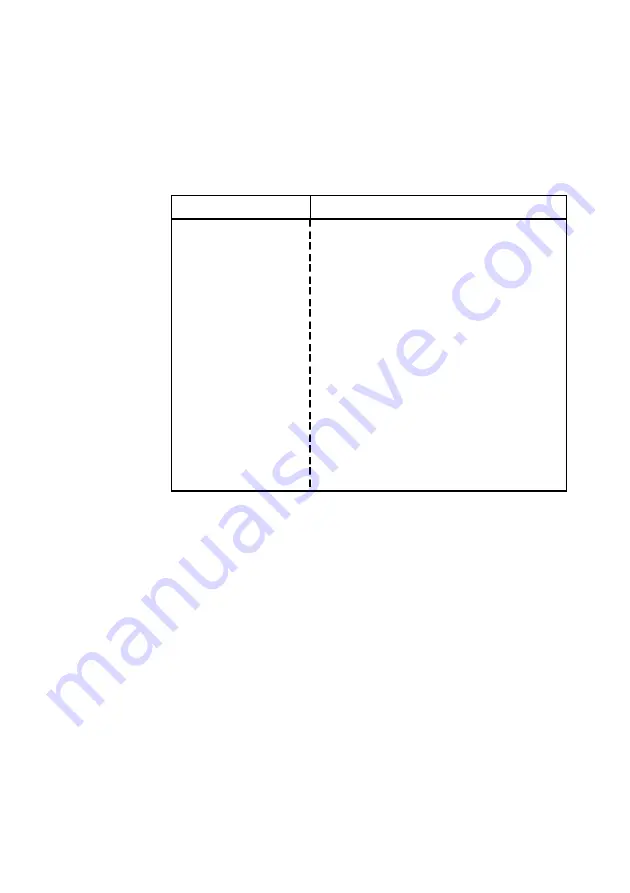
Base input/output (I/O) port address
Some expansion cards are also controlled by I/O ports or ‘address
space’. The base I/O port address specifies where the card’s ports
begin. The following table lists the I/O ports used by devices on the
motherboard.
I/O ports
Default assignment
1F0h-1F7h
Hard disk drive controller
278h-27Fh
Parallel port 2 (optional)
2B0h-2DFh
Alternate VGA
2F8h-2FFh
Serial port 2
378h-37Fh
Parallel port 1
3B0h-3BFh
Monochrome display and printer adapter
3B4h, 3B5h, 3BAh
Video subsystem
3C0h-3C5h
VGA
3C6h-3C9h
Video DAC
3CAh-3DFh
VGA
3F0h-3F7h
Diskette drive controller
3F8h-3FFh
Serial port 1
Any ports not listed are available for expansion cards. All addresses
below 100h are used by the system board for various fixed system
components and chipset controller settings. They are unavailable for use.
Base memory address
Some expansion cards are fitted with memory of their own, usually
read-only memory (ROM) containing functional extensions to the
computer’s BIOS (basic input/output system) ROM. Some cards
also have random-access memory (RAM).
In order that this memory can be recognised by the system
processor, it must be mapped somewhere within the computer’s
own address space. By setting the base memory address you specify
where the card’s memory begins within the address space. Typically,
an expansion card’s memory must be mapped onto the addresses
between C8000h and DFFFF in upper memory. With most
modern expansion cards this is fully automatic.
















































