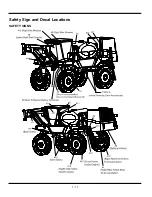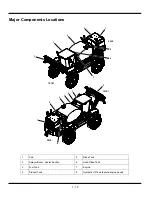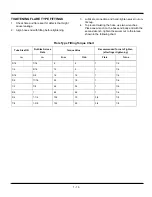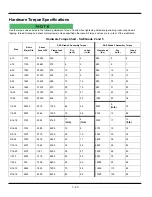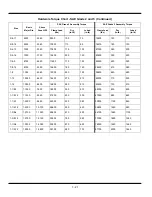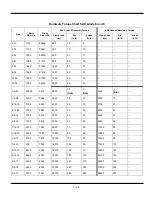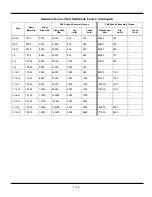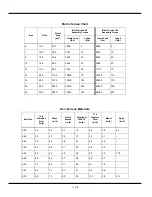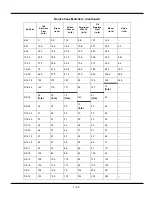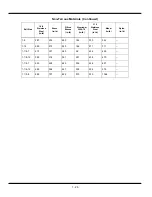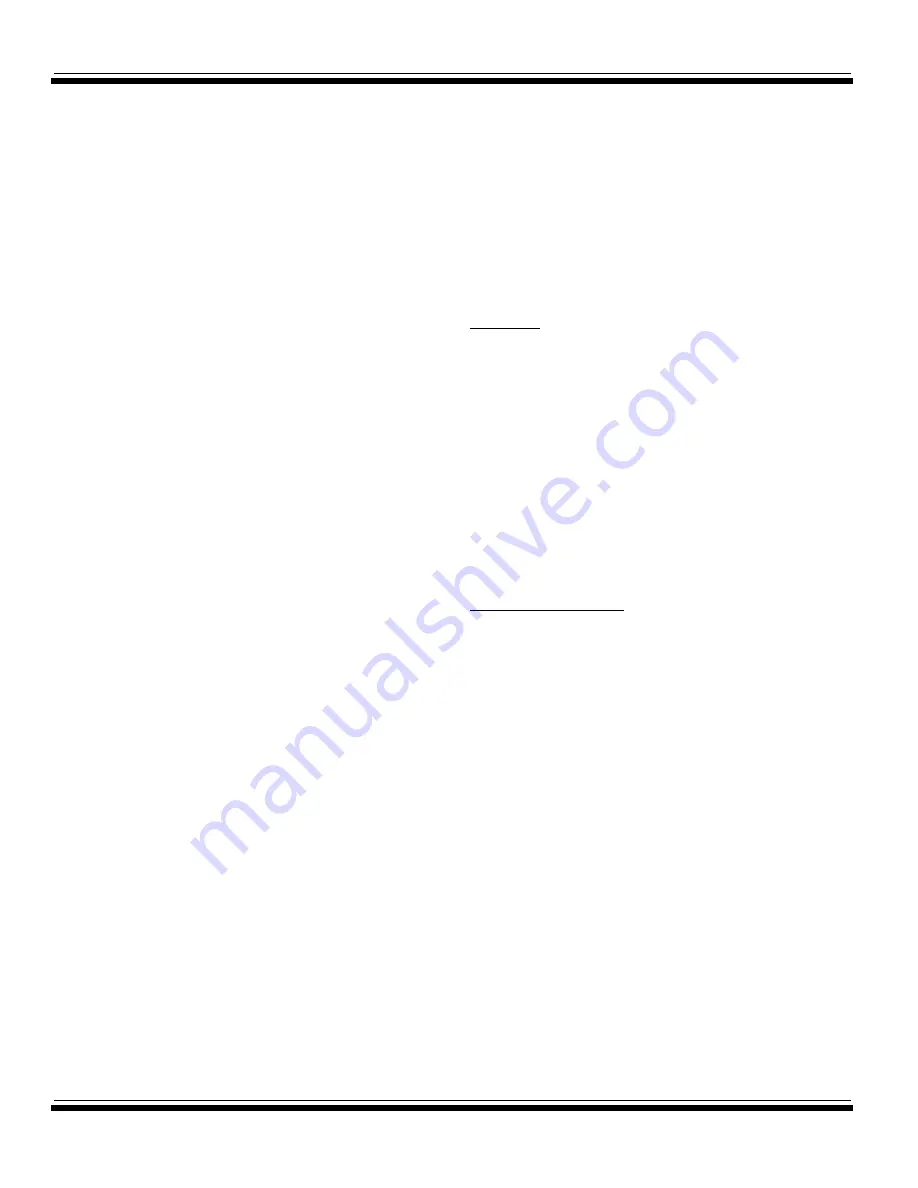
1 - 16
Hoses/Fittings - General
Application Basics
Hydraulic hoses, fittings, and hose assemblies connect
hydraulic motors to the pump and transmit high-pres-
sure hydraulic fluids. These high-pressure fluids transfer
energy and do useful work.
Hydraulic hose is flexible and is used primarily to allow
motion between components at either end of the hose
assembly, and to simplify routing/installation.
Bending, Motion, Routing
Hose assemblies should be long enough and routed in
such a way that prevents exceeding manufacturers min-
imum bend radius recommendations.
To prevent excessive strain at hose-to-coupling interfac-
es, make hoses long enough to allow for contraction
and expansion. Depending on size and application, hy-
draulic hoses can elongate up to 2 percent when pres-
surized, but more importantly, can contract as much as
4 percent which can especially stress hose-to-coupling
interfaces.
Twisting a high-pressure hose only 5 degrees can re-
duce service life by 70 percent and a 7-percent twist can
reduce service life up to 90 percent. When this kind of
motion cannot be avoided, hose clamps between bends,
with ample hose length on both sides of clamp, can re-
lax torsion and help compensate for hose contraction.
Hose clamps can also provide protection from abrasion
against adjacent surfaces. Additionally, metal or fabric
sleeves can be installed to help keep abrasive particles
away from hoses, and assist in the bundling of multiple
hoses.
Hoses that do not properly accommodate equipment dy-
namics, such as hoses connected to cylinders that un-
dergo pivoting motions, can create an undesirable situa-
tion. A swivel joint can provide a solution to this situation
by permitting pivoting motions that reduce the bending
transmitted to the hose assembly and by reducing the
length of hose required.
Hose and Fitting Care
The hose manufacturers’ guidance should be followed
on the selection of hose fittings, hose types, and instal-
lation, as well as compatibility with the pressure rating of
the system within which they will be used.
Many variables can affect compatibility of system fluids
with hose materials, including type of fluid, fluid pres-
sure, temperature, concentration, and duration of expo-
sure.
Inspection
A careful examination of the hoses and fittings should
be performed prior to assembly, checking for correct
type, size, and length. Also inspect for cleanliness, ob-
structions, burrs, blisters, kinks, cracks, cuts, or any oth-
er visible defects. If any of these conditions are found,
immediately shut down the vehicle and replace the hose
assembly.
The fitting and sealing surfaces need to be inspected for
burns, nicks, corrosion, or other imperfections. No sub-
standard or defective components should be used in an
assembly.
Repairs/Replacements
If any of the previously mentioned undesirable or defec-
tive hoses or fittings are found, including leaking fittings,
worn clamps, guards, or shields, then these items must
be tightened, repaired, corrected, or replaced as re-
quired.
Before performing any repairs/replacements, be sure to
follow these precautions:
•
Always shut the engine off and release all hydrau-
lic pressure.
•
Beware of any hydraulic pressure that may be
stored in pressure vessels or accumulators.
•
Always use supports, jacks, stands, or blocks to
prevent movement of hydraulic implements or
components.