BIG 8051 Manual
13
CAN module
Controller Area Network (CAN) is a communication
standard primarily intended for use in the automotive
industry. It is used when microcontrollers and devices
need to communicate with each other in applications
without a host computer. The modern automobile may
have as many as 70 electric control units for various
subsystems. Typically the biggest processor is the en-
gine control unit. Others are used for transmission, air-
bags, ABS, cruise control, electric power steering, audio
systems, power windows, doors, mirrors, etc. Some of
these form independent subsystems, but communica-
tions among others are essential. A subsystem may need
to control actuators or receive feedback from sensors.
The CAN standard was devised to fill this need.
Each CAN node is able to send and receive messages,
but not simultaneously. The devices that are usually
connected by a CAN network are typically sensors, ac-
tuators, and other control devices. The host processor
decides what the received messages mean and what
messages it wants to transmit. Sensors, actuators and
control devices can be connected to the host processor.
CAN controller stores the receives serial bits from the
bus until an entire message is available, which can then
be fetched by the host processer, usually by the CAN
controller triggering an interrupt. For sending, the host
processor sends the transmit messages to a CAN con-
troller, which transmits the bits serially onto the bus
when the bus is free.
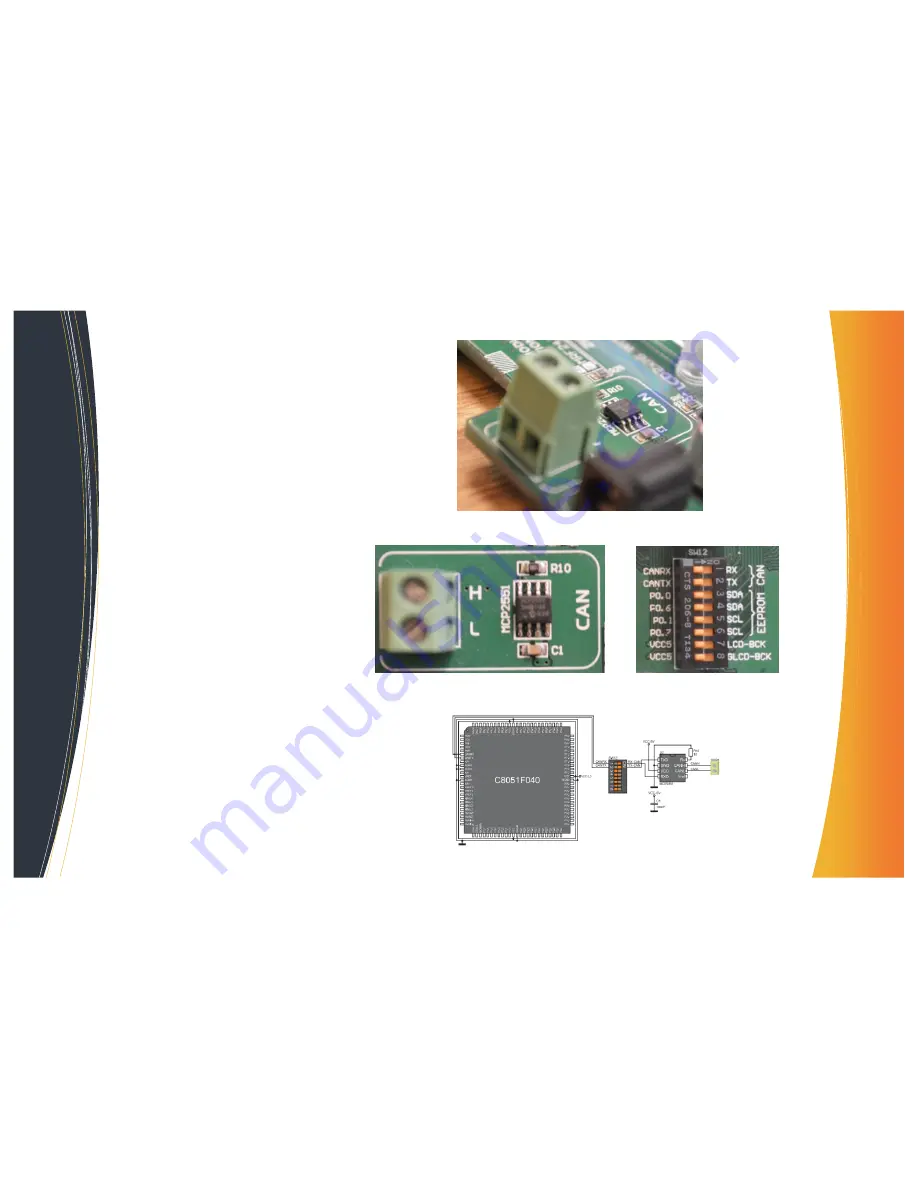
To establish connection between this module and the
microcontroller, it is necessary to set the switches 1 and
2 on the DIP switch SW12 to the ON position.
CAN module connector
CAN module
SW12
CAN module and microcontroller connection schematic [9]