AHB Bus Matrix
UG0331 User Guide Revision 15.0
220
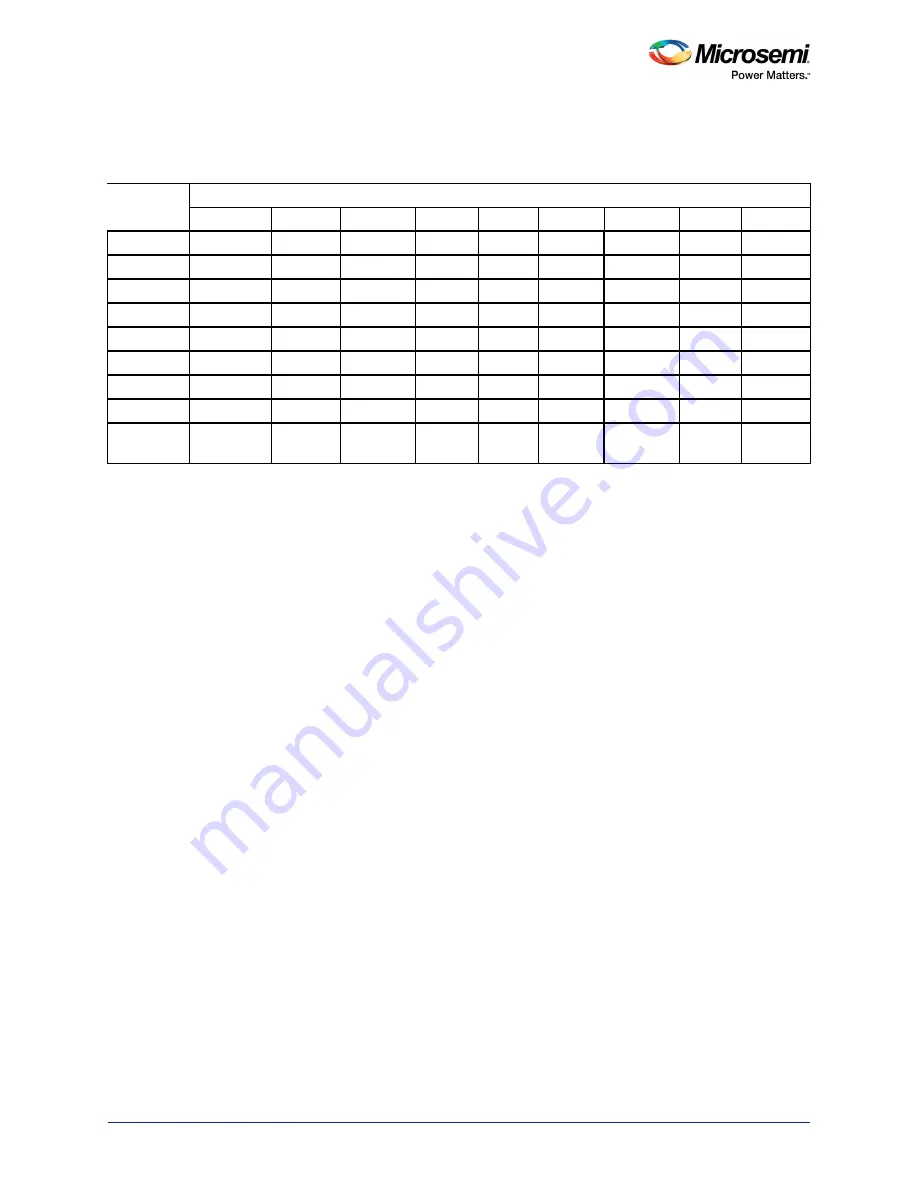
The following table gives an example of a pure round robin and fixed priority arbitration scenario for
eSRAM1. This example illustrates default AHB bus matrix behavior.
In the preceding table, WRR masters and fixed priority masters arbitrate for the S1 (eSRAM1) slave
during HCLK cycle 1. The last row in the table, labeled eSRAM1: S1, shows which of the masters obtains
access to the slave according to the arbitration in that clock cycle. In the first cycle, master M3 (HPDMA)
is granted access, since it is the first master in the round robin scheme. In the second cycle, even though
master M4 is scheduled to get access to the slave as per the round robin scheme, the M2 master
(Cortex-M3 processor SBus) is granted access since it has a higher priority. In the third cycle, the master
M4 (FIC_0) in the round robin scheme is granted access. In the fourth cycle, both M0 (Cortex-M3
processor ICode bus) and M1 (Cortex-M3 processor DCode bus) are trying for access. Since M1 has the
highest priority among the fixed priority masters, it is granted access, followed by the M0 master. WRR
masters are delayed while the fixed priority masters get access to the slave. The remaining cycles are
consumed by the WRR masters in order.
7.1.3.1.3
WRR Arbitration
In this mode, the slave arbitration parameters, programmable weight (SW_WEIGHT_<master>) and
eSRAM slave maximum latency (SW_MAX_LAT_ESRAM<0/1> of ESRAM_MAX_LAT) can be
configured to operate as WRR arbitration. The slave arbiter operates on a round robin basis, with each
master having a maximum of N consecutive access opportunities to the slave in each round of
arbitration. The value of N is determined by the programmed weight for the master and eSRAM slave
maximum latency. Programmable weight values can be changed dynamically. The following figure
depicts the WRR slave arbitration scheme. At each stage, the arbiter checks whether that master is
requesting access. If so, the master performs N transfers equal to its programmed weight and then has
to re-arbitrate for the bus. For a WRR master, the WRR priority in the round robin sequence changes
after the programmed number of transfers. Due to its highest priority, the Cortex-M3 processor DCode
bus master is allowed to perform transfers as long as there are transfers to complete. However, if a
locked transaction occurs, the master issuing the lock (HMASTLOCK = 1) maintains ownership of the
slave until the locked transaction completes.
Table 142 •
Pure Round Robin and Fixed Priority Arbitration Scenario for eSRAM1
Master
HCLK
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
M3-I: M0
eSRAM1
M3-D: M1
eSRAM1
M3-S: M2
eSRAM1
eSRAM1
HPDMA: M3 eSRAM1
FIC_0: M4
eSRAM1
FIC_1: M5
eSRAM1
GIGE: M6
eSRAM1
PDMA: M7
eSRAM1
eSRAM1:
S1
HPDMA M3 M3-S M2 FIC_0 M4
M3-D M1 M3-I M0 M3-S M2 FIC_1 M5
TSE M6 PDMA M7
Содержание SmartFusion2 MSS
Страница 1: ...UG0331 User Guide SmartFusion2 Microcontroller Subsystem ...
Страница 166: ...Cortex M3 Processor Reference Material UG0331 User Guide Revision 15 0 132 ...
Страница 200: ...Embedded NVM eNVM Controllers UG0331 User Guide Revision 15 0 166 Figure 87 System Builder Window ...
Страница 407: ...Universal Serial Bus OTG Controller UG0331 User Guide Revision 15 0 373 ...
Страница 806: ...Fabric Interface Controller UG0331 User Guide Revision 15 0 772 Figure 345 FIC Master AHB Lite Subsystem ...
















































