Concept and History of the FG5
1
1. Concept and History of the FG5
1.1. The
FG5
Absolute
Gravimeter
The FG5 absolute gravimeter is a high precision, high accuracy, transportable
instrument that measures the vertical acceleration of gravity (g). The
operation of the FG5 is simple in concept. A test mass is dropped vertically
by a mechanical device inside a vacuum chamber, and then allowed to fall a
distance of about 20cm. The FG5 uses a laser interferometer to accurately
determine the position of the free-falling test mass as it accelerates due to
gravity. The acceleration of the test mass is calculated directly from the
measured trajectory.
The laser interferometer generates optical interference fringes as the test mass
falls. The fringes are counted and timed with an atomic clock to obtain precise
time and distance pairs. These data are fit to a parabolic trajectory to give a
measured value for g. This method of measuring gravity is absolute because
the determination is purely metrological and relies on standards of length
and time. The distance scale is given by a frequency stabilized helium neon
(HeNe) laser used in the interferometer. A rubidium atomic time-base
provides the time scale used for the accurate timing. The value of gravity
obtained with the FG5 can be used without the loop reductions and drift
corrections normally required when using relative instrumentation.
1.2. HISTORY
1-1
The FG5 is a new generation of absolute gravimeter based on technology
developed over the last thirty years by Dr. James Faller of the National
Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), and his colleagues. Beginning
with a white-light-fringe interferometric system built in 1962, Faller and
coworkers have continuously improved the designs of the instruments. The
most recent predecessors of the FG5 was the series of six JILAg gravimeters,
built in 1985 at the Joint Institute of Laboratory Astrophysics (JILA), with
support from NIST, the Defense Mapping Agency (DMA), the National
Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), the Canadian
Содержание FG5
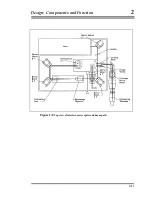
Страница 19: ...Design Components and Function 2 Figure 2 8 Top view of interferometer optics and beam path 2 11 ...
Страница 20: ...Design Components and Function 2 Figure 2 9 Side view of interferometer optics and beam path 2 12 ...
Страница 22: ...Design Components and Function 2 Figure 2 10 The Superspring 2 14 ...
Страница 31: ...Design Components and Function 2 Figure 2 13 Rotation Monitor 2 23 ...
Страница 32: ......
Страница 42: ...How to Set Up and Run the FG5 3 3 10 ...
Страница 44: ...How to Set Up and Run the FG5 3 Figure 3 2 V Post 3 12 ...
Страница 53: ...How to Set Up and Run the FG5 3 1 Backup the data 2 Shut off computer power 3 21 ...
Страница 87: ...Adjustment and Maintenance 4 4 29 ...
Страница 91: ...Adjustment and Maintenance 4 4 33 ...
Страница 104: ...Troubleshooting 5 5 2 ...
Страница 117: ...Troubleshooting 5 5 15 ...
Страница 131: ...Checklists and Logs Appendix D 9 3 ...
Страница 140: ...Checklists and Logs Appendix D Table 9 6 Replacing Drive Belt 9 12 ...
Страница 145: ...Checklists and Logs Appendix D Table 9 10 Replace Linear Bearings 9 17 ...
Страница 149: ...Checklists and Logs Appendix D Table 9 13 Replace Shaft Encoder 9 21 ...