Evaluates: MAX1455
MAX1455 Evaluation Kit
_______________________________________________________________________________________
5
Computer Requirements
and Connections
The next logical step after checking the module perfor-
mance is to actually edit and reprogram the module
using the same sensor. To do so, configure the EV kit
for digital operation and connect the digital interface to
the computer first. Below is a list of the computer
requirements:
•
IBM-compatible PC
•
Windows 95/98/2000/XP
•
One unused serial port
Detailed Hardware Description
The MAX1455 (U1) performs analog temperature com-
pensation on piezo-resistive sensors. The MAX1455
contains the temperature compensation coefficients in
its internal EEPROM.
Figure 2 shows the circuit diagram of the EV board.
Figures 3–6 illustrate the PCB component placement
and wiring details.
The MAX1455 has a single-wire digital interface that can
be connected to the output to maintain a true 3-wire sys-
tem. The MAX1452KEY interface adapter converts and
buffers the outputs from the computer serial port to com-
municate with the ASIC. The adapter also controls power
to the EV board when in digital mode. This configuration
allows power resets to be performed under software
control.
The adapter operates internally at 5V. The ratiometricity
tests of the evaluation board should be limited to 4.5V
to 5.5V while the digital connector is in place. This
requirement is to prevent logic-level mismatch and the
activation of any biasing protection diodes in the front
end of the digital circuits.
Figure 7 shows the adapter circuit diagram and Figures
8, 9, and 10 provide PCB component placement and
wiring information.
Replacing the Sensor
(MAX1455EVKIT-CS)
The factory-calibrated sensor can be replaced by a
user-provided sensor. It is recommended to become
fully familiarized with the basic operation of the ASIC
and the software before attempting to remove the sen-
sor supplied with the board and replacing it with the
user sensor. The MAX1455 works with 4-wire closed
Wheatstone bridge-configured sensors. An 8-pin DIL
socket is provided for alternative sensor mounting. The
pinout for this connector is given in Table 1.
Alternatively, the user can test the ASIC using an artifi-
cial bridge consisting of four discrete resistors. Some
general knowledge of the user’s sensor parameters
must be known in order to set the initial coefficients.
This way, the ASIC is not overloaded (i.e., output satu-
rated). It is recommended that the sensor wires be kept
as short as possible to minimize system noise. At this
point, refer to the
Compensation Procedure section in
the MAX1455 user manual for a step-by-step procedure
for compensating the sensor.
Calibrate the new sensor in a temperature-controlled
environmental chamber.
EV Kit Software
An unused serial port on the host PC is required to
allow software control of the MAX1455 EV board.
The MAX1455 EV kit software is an executable file
developed using National Instrument’s LabVIEW soft-
ware. LabVIEW application is not required to run the EV
kit software. The software is a high-level interface that
calls a low-level serial.dll.
Note:
The MAX1455 software tools can be down-
loaded and installed from the Maxim website at
www.maxim-ic.com.
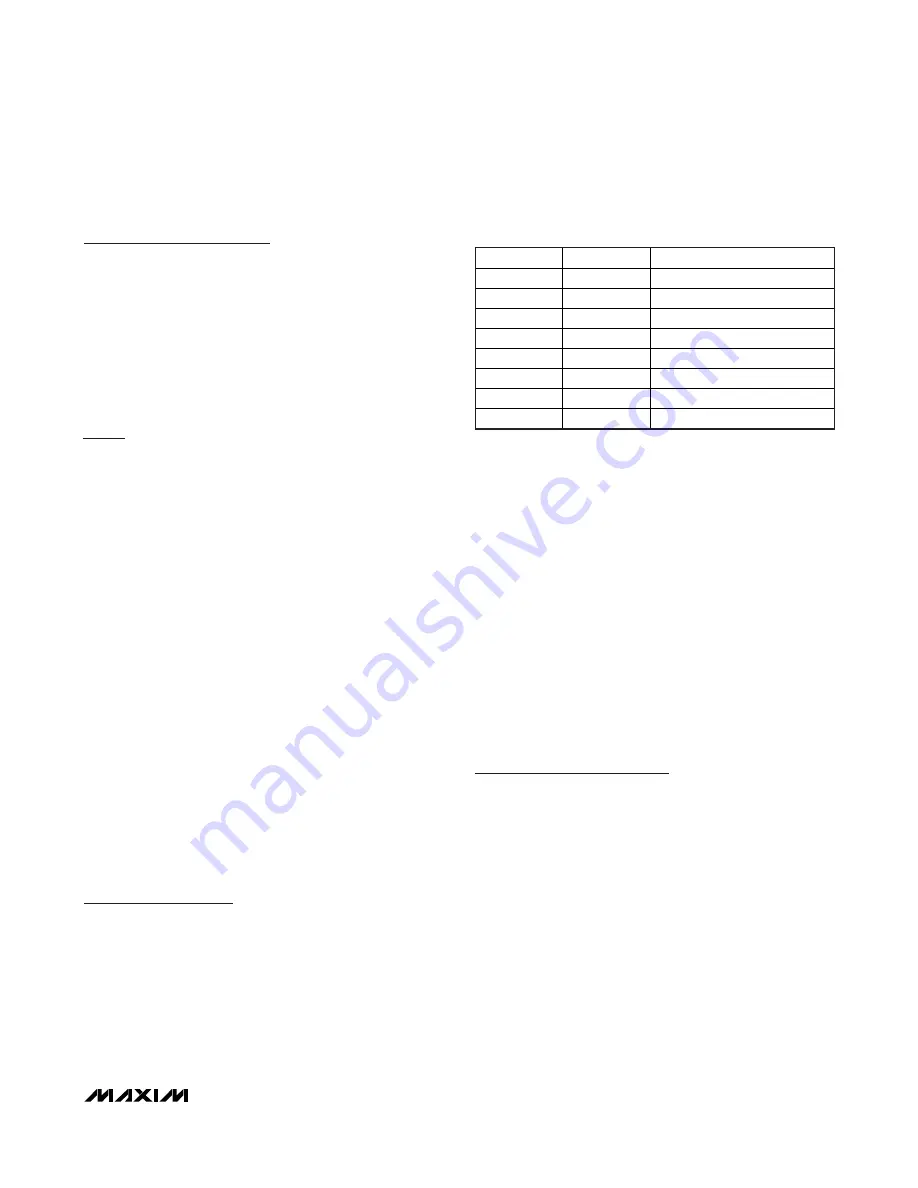
Table 1. I/O Connector S3 Signals Sensor
Interface
PIN
SIGNAL
DESCRIPTION
1
OUT+
Positive output sensor
2
IN+
Top of Wheatstone bridge
3
OUT+
Positive output sensor
4
IN-
Bottom of Wheatstone bridge
5
OUT-
Negative sensor output
6
IN-
Bottom of Wheatstone bridge
7
OUT-
Negative sensor output
8
IN+
Top of Wheatstone bridge










