Chapter 5
Advanced Configuration
Wireless-G Access Point with Power Over Ethernet
Access Point address, the Broadcast destination addresses,
a time stamp, Delivery Traffic Indicator Maps, and the
Traffic Indicator Message (TIM). The default is
00 ms
.
DTIM Interval
This value indicates how often the Access
Point sends out a Delivery Traffic Indication Message
(DTIM). Lower settings result in more efficient networking,
while preventing your PC from dropping into power-
saving sleep mode. Higher settings allow your PC to
enter sleep mode, thus saving power, but interferes with
wireless transmissions. The default is
ms
.
RTS Threshold
This setting determines how large a packet
can be before the Access Point coordinates transmission
and reception to ensure efficient communication. This
value should remain at its default setting of
4
. If you
encounter inconsistent data flow, only minor modifications
are recommended.
Fragmentation Threshold
This specifies the maximum
size a data packet can be before splitting and creating a
new packet. It should remain at its default setting of
46
.
A smaller setting means smaller packets, which will create
more packets for each transmission. If you experience
high packet error rates, you can decrease this value, but
it will likely decrease overall network performance. Only
minor modifications of this value are recommended.
Change these settings as described here and click
Apply
to save your changes. Help information is available on the
right side of the screen.
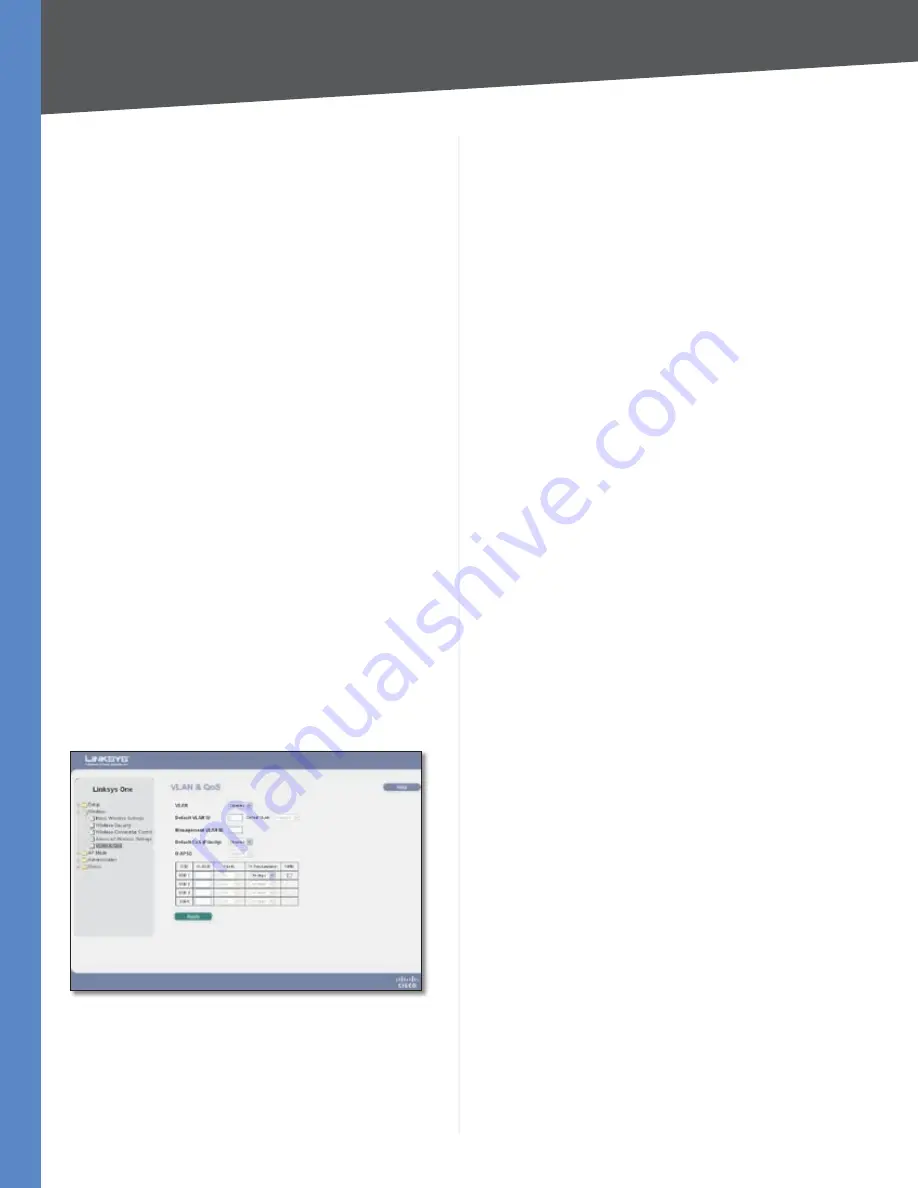
Wireless > VLAN & QoS
This screen allows you to configure the VLAN and QoS
related settings for the Access Point.
Wireless > VLAN & QoS
VLAN
Select Enabled if you want to pass 802.1q VLAN
tagged traffic between the wired LAN and wireless LAN.
Your Access Point will map the VLAN tag (wired side) to
different SSIDs (wireless side) according to your specified
settings. Select Disabled and your Access Point will drop all
tagged traffic coming in from the wired LAN. The default
is
Disabled
.
Default VLAN ID
Enter the default VLAN ID number (1
- 4094), the default value is
. The default VLAN number
should match with your Switch’s settings. For example,
the SRW2024 has Trunk port mode which set default VLAN
(PVID) to 1 untagged, while General port mode can set
PVID to any VLAN either tagged or untagged.
Default VLAN
Set the tagging option for the default
VLAN ID. This has to match your Switch’s settings. The
default is
untagged
.
Management VLAN ID
When the VLAN option is enabled,
the value entered (VLAN ID) in this field defines the VLAN
that connects to the Access Point. The default value is
. The VLAN should be accessible from the wired side in
order to use web-based utility. To access the web-based
utility from wireless side, the SSID needs to map to the
same VLAN ID. Remember to enable wireless web access
on the
Administration > Management
tab.
The following options are VLAN global settings for the
Access Point.
Default CoS (Priority)
Select Enabled if you want to
assign a default CoS value to each SSID. This option is
automatically enabled when the VLAN option is enabled.
The default is
Disabled
.
U-APSD (Unscheduled Automatic Power Save
Delivery)
This option is only available when WMM is
enabled on any of the SSIDs. Select Enabled if you want
client devices with U-APSD capability to take advantage
of the power save mode. The default is
Disabled
.
SSID Name
Displays the SSIDs defined on the
Basic
Wireless Settings
screen. If an SSID has been disabled, the
options cannot be configured.
VLAN ID
Select a VLAN ID (1 - 4094) for the SSID where
you want to map the traffic to on the wired side. The
wireless traffic will not carry VLAN information. Multiple
SSIDs can map to the same VLAN on the wired side.
Priority
You can assign the default priority (802.1p CoS
bits) for packets coming in from each wireless network by
selecting a value from the drop-down menu. The default
is
Low
.
Tx Rate Limitation
You can limit the maximum data
rate used in your network to save bandwidth and power
consumption on client devices. The actual data rate is
determined by the Auto-Fallback mechanism between
your Access Point and a client device. The default is
54
Mbps
.
WMM
Wi-Fi Multimedia is a QoS feature defined by the
WiFi Alliance before IEEE 802.11e was finalized. Now it is
part of IEEE 802.11e. When this is enabled, it provides four






























