19
LTC1624
where
I
V
V
V
V
OUT MAX
IN
OUT
D
IN
:
I
SW MAX
( )
( )
=
+
+
δ
is the temperature dependency of R
DS(ON)
and k is a
constant inversely related to the gate drive current. The
maximum switch current occurs at V
IN(MIN)
and the peak
switch current is I
SW(MAX)
+
∆
I
L
/2. The maximum voltage
across the switch is V
IN(MAX)
+
V
OUT
.
MOSFETs have I
2
R losses plus the P
MAIN
equation
includes an additional term for transition losses that are
highest at high total input plus output voltages. For
(
V
OUT
+ V
IN
) < 20V the high current efficiency generally
improves with larger MOSFETs, while for (
V
OUT
+ V
IN
)
> 20V the transition losses rapidly increase to the point
that the use of a higher R
DS(ON)
device with lower C
RSS
actual provides higher efficiency. For additional informa-
tion refer to the Step-Down Converter: Power MOSFET
Selection in the Applications Information section.
Positive-to-Negative Converter: Inductor Selection
For most applications the inductor will fall in the range of
10
µ
H to 100
µ
H. Higher values reduce the input and output
ripple voltage (although not as much as step-down con-
verters) and also reduce core loss. Lower inductor values
are chosen to reduce physical size and improve transient
response but do increase output ripple.
Like the boost converter, the input current of the positive-
to-negative converter is calculated at full load current.
Peak inductor current can be significantly higher than
output current, especially with smaller inductors (with
high
∆
I
L
values). The following formula assumes continu-
ous mode operation and calculates maximum peak induc-
tor current at minimum V
IN
:
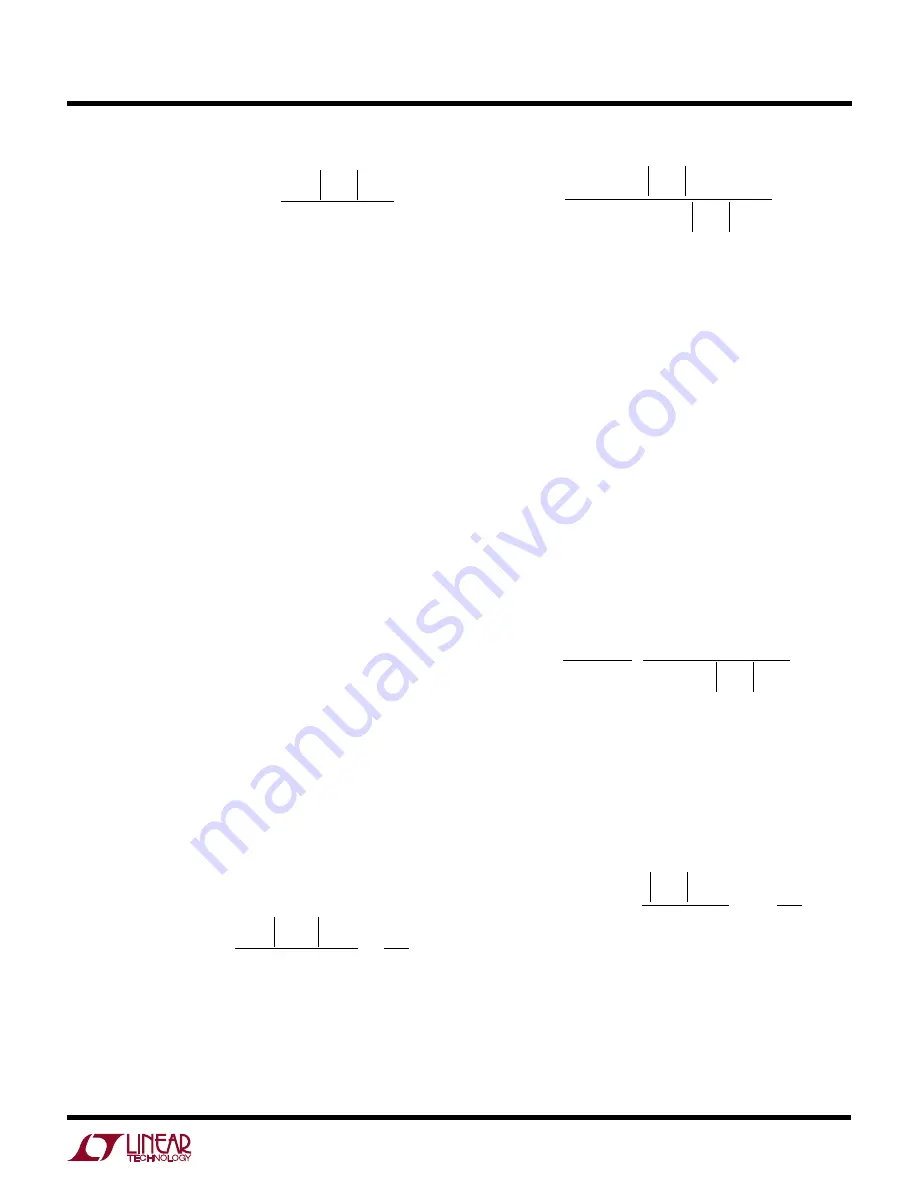
I
I
V
V
V
V
I
L PEAK
OUT MAX
IN
OUT
D
IN
L
( )
( )
=
+
+
+
∆
2
The ripple current in the inductor (
∆
I
L
) is typically 20% to
50% of the peak inductor current occuring at V
IN(MIN)
and
I
OUT(MAX)
to minimize output ripple. Maximum
∆
I
L
occurs
at minimum V
IN
.
APPLICATIO
N
S I
N
FOR
M
ATIO
N
W
U
U
U
∆
I
V
V
V
kHz L V
V
V
L
IN
OUT
D
IN
OUT
D
P-P
( )
=
( )
+
(
)
(
)( )
+
+
(
)
200
Specify the maximum inductor current to safely handle
I
L(PEAK)
. Make sure the inductor’s saturation current rat-
ing (current when inductance begins to fall) exceeds the
maximum current rating set by R
SENSE
.
Positive-to-Negative Converter: R
SENSE
Selection for
Maximum Output Current
R
SENSE
is chosen based on the required output current.
Remember the LTC1624 current comparator has a maxi-
mum threshold of 160mV/R
SENSE
. The current compara-
tor threshold sets the peak of the inductor current, yielding
a maximum average output current I
OUT(MAX)
equal to
I
L(PEAK)
less half the peak-to-peak ripple current with the
remainder divided by the duty cycle.
Allowing a margin for variations in the LTC1624 (without
considering variation in R
SENSE
) and assuming 30% ripple
current in the inductor, yields:
R
mV
I
V
V
V
V
SENSE
OUT MAX
IN MIN
IN MIN
OUT
D
=
+
+
( )
( )
( )
100
Positive-to-Negative Converter: Output Diode
The output diode conducts current only during the switch
off-time. Peak reverse voltage for positive-to-negative
converters is equal to
V
OUT
+ V
IN
. Average forward
current in normal operation is equal to I
D(PEAK)
–
∆
I
L
/2.
Peak diode current (occurring at V
IN(MIN)
) is:
I
I
V
V
V
I
D PEAK
OUT MAX
OUT
D
IN
L
( )
( )
=
+
(
)
+
+
1
2
∆
Positive-to-Negative Converter: Input and
Output Capacitors
The output capacitor is normally chosen by its effective
series resistance (ESR), because this is what determines
output ripple voltage. Both input and output capacitors
need to be sized to handle the ripple current safely.
























