36
Glossary
Term
Definition
A
B
C
a-contact
Alternating current type
ionizer (AC method)
Antistatic agent
(process)
Atom
b-contact
Carrying ions through a
tube
CE marking
Charge
Charged device model
(CDM or CPM)
Charging series
(triboelectric series)
Charged plate monitor
Clean room
Cleanliness
Conductor
Contact charging
Contamination
Corona discharge
method ionizer
Coulomb force
A normally open contact that closes when a signal (switch input or sensor input) is given. Also called
NO (Normally Open) contact
⇔
See b-contact.
A type of high-voltage application in corona discharge method ionizers. Devices using alternating high
voltage (AC) are called alternating current method devices.
An agent usually consisting of a surfactant. Coating or blending with an insulation object makes the
surface of the insulation object more hydrophilic, increasing its hygroscopicity and granting it ionic
properties, which increase its surface conductivity and prevent charging.
A particle that cannot chemically be further divided. The atom consists of a nucleus carrying a positive
charge and surrounding electrons carrying a negative charge. The electrons revolve around the
nucleus like satellites.
A normally closed contact that opens when a signal (switch input or sensor input) is given. Also called
NC (Normally Closed) contact.
⇔
See a-contact.
A method where ions generated by the ionizer are carried through a tube to remove charges from an
electrified area. In ionizers with a low frequency of 50/60 Hz, carring ions through a tube is impossible
because the ions are extinguished inside the tube. The DTRY-ELB series and DTRY-ELL series
manufactured by Koganei use a high frequency of 68000 Hz, to achieve an excellent ion balance and
ensure that ions can be carried through a tube with relatively little extinguishing inside the tube.
A safety mark required to be affixed on designated products sold in the European Union (EU) area.
The CE marking is issued as a directive from the European Community Council of Ministers (EC
Directive), and certifies that the product is in compliance with the requisite safety regulations. Koganei
products generally come under the EMC, Low Voltage, and Machinery Directives.
The amount of electricity in a substance or its atoms, electrons, etc., which determines the size of an
electromagnetic interaction. The unit is the Coulomb (C). Charge exists in two states, positive and
negative, which are called positive charge and negative charge, respectively.
A model for when device package leads (terminals) become charged due to friction, etc., causing a
break when the charge is discharged via the device terminal. (CPM: charged package model).
A list of materials that produce a charge when rubbed together arranged in order depending on
whether they have positive or negative charges. In general, rubbing-induced electrification is larger for
materials whose positional relationship is distant than for those that are close together. Even rubbing
between substances of the same material will result in a positive charge on one side and negative
charge on the other.
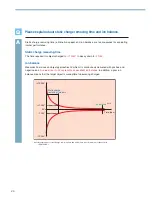
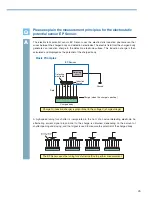
Used for measurement of ionizer performance. High voltage is applied to a
□
150 mm [5.91 in.], 20 pF
metal plate, to measure the time required for an ionizer to decay the voltage (decay time), and the
difference in the amount of ions generated by the ionizer (ion balance).
A space where particles and micro-organisms floating in the air are controlled to be at or below a
certain level of cleanliness, with temperature, humidity, pressure, and other environmental conditions
also controlled as necessary.
An amount showing the state of cleanliness in a target object, expressed in the size or number of
contamination substances incorporated into a certain surface or volume. In addition, the degree of
cleanliness ranked by the amount of contaminated substances or size of particles existing in a
specified location or volume is called the cleanliness level, and the arrangement of cleanliness level
by class is called the cleanliness class.
While standards for clean room cleanliness are independently set in each country, in general,
ISO146441-1 and Fed.Std. 209E are most widely used. Note that the clean room evaluation method
JIS B9920 regulated under the Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS) is based on ISO146441-1.
Substance that easily passes electricity. Gold, silver, copper, iron, aluminum, etc.
Charging caused by contact.
Contaminated by dirt or other foreign material. Particles adhering to semiconductor wafers are also called
contamination.
Application of high voltage to a needle-tipped electrode forms an unbalanced electric field adjacent to
the electrode, and the discharge that occurs when that electric field locally exceeds the dielectric
breakdown electric field strength is called a corona discharge. In a dark room, this discharge is visible
as a blue-white light near the electrode. The corona discharge method ionizer utilizes this principle to
intentionally induce a corona discharge on the discharging needle, to generate ions.
The force exerted according to Coulomb’s Law, which is defined as one coulomb being equal to the
amount of charge carried by one ampere of current for a period of one second.