PT4208 Service Manual
14
Table 6.2), and press the PTT key. Then measure the voltage
of PD by DMM. The resulting voltage should be lower than
4.5V.
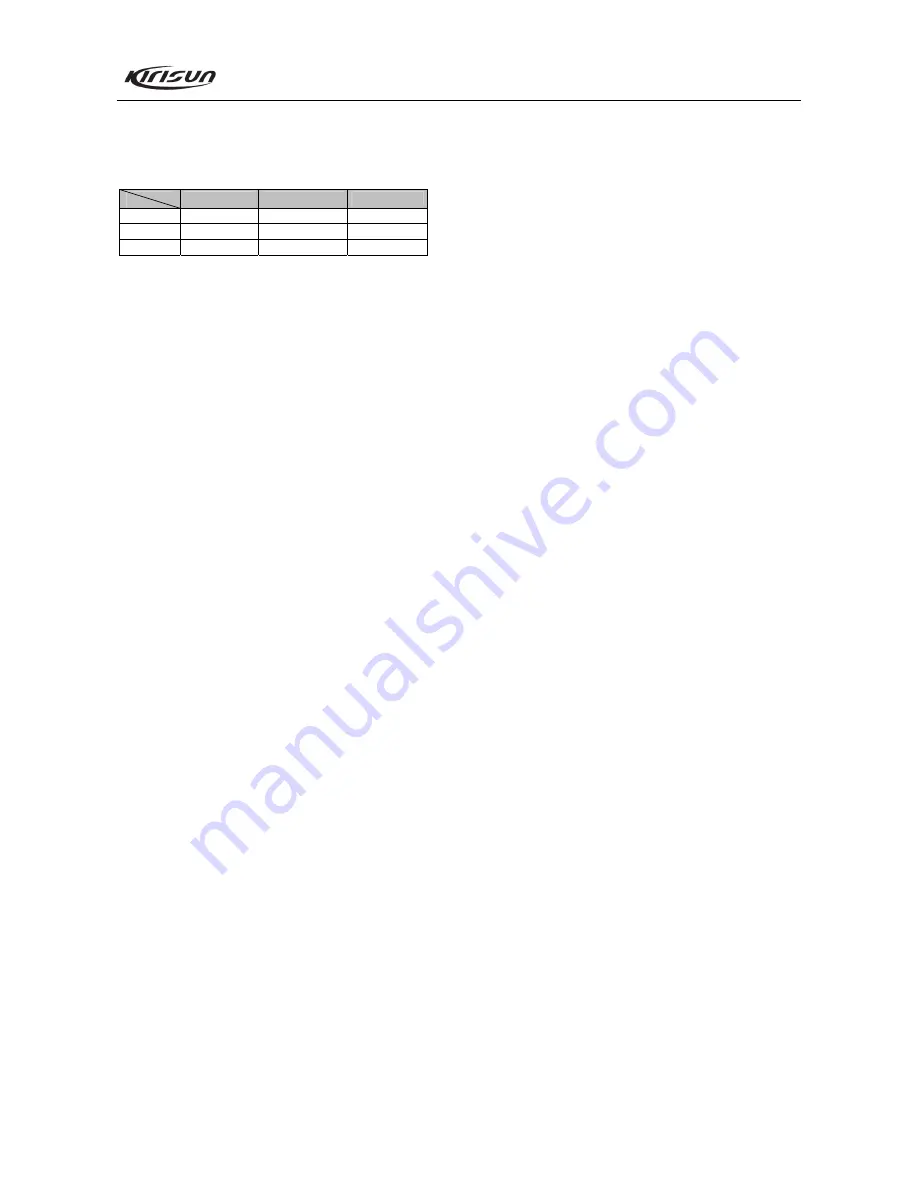
Table 6.2 High/Center/Low Frequency Point for PT4208
Low Freq Point Center Freq Point High Freq Point
PT4208(1)
136.125 MHz
145.125 MHz
173.975 MHz
PT4208(2) 400.125MHz 425.125MHz 449.975MHz
PT4208(3) 420.125MHz 445.125MHz 469.975MHz
6.3.2 PLL frequency
In the Tuning Mode, double click the “6250Hz
stability/2500Hz stability” item to enter. Adjust the
parameter within the adjusting range of 0-255 to make the
Tx frequency be the rated value (with error within
±200Hz).
6.3.3 Tx power
In the Tuning Mode, double click the Tx “High power”
item to enter. Adjust the five frequency points of “Lowest”,
“Low”, “Mid”, “High” and “Highest” within the adjusting
range of 0-255 to make the Tx power be higher than 4W.
Meanwhile, observe the operating current, and make sure
that the current is no larger than 1.7A.
In the Tuning Mode, double click the Tx “Low power”
item to enter. Adjust the five frequency points of “Lowest”,
“Low”, “Mid”, “High” and “Highest” within the adjusting
range of 0-255 to make the Tx power be higher than 1W.
See Table 6.5 for detailed parameters.
6.3.4 Tx low voltage/Rx low voltage for BATT
Firstly, adjust the power voltage to be 6.8V. Double click
the “Tx low voltage/Rx low voltage” in the Tuning Mode.
Click “Begin” to let the software test automatically. When
the value changes no more or only changes a little, click
SAVE to exit.
6.3.5 Max. deviation
Input audio signal (100mV, 1000Hz) to the MIC jack of
the radio. Adjust the potentiometer VR2 to make the Max.
deviation be
±4.5kHz.
6.3.6 DCS Tx signal waveform and deviation
In the Tuning Mode, double click the “DCS DEV” item
to enter. Adjust the potentiometer VR1 and observe the
demodulation signal (the waveform should be smooth and
similar to square wave). Click wideband, and adjust the five
frequency points of “Lowest”, “Low”, “Mid”, “High”, and
“Highest” to make the deviation be 0.8kHz. Then click
narrowband, and adjust the five frequency points to make the
deviation be 0.4kHz.
6.3.7 CTCSS deviation
In the Tuning Mode, double click the “QT(67.0) DEV”
item to enter. Click wideband, and adjust the five frequency
points of “Lowest”, “Low”, “Mid”, “High”, and “Highest” to
make the deviation be 0.75kHz. Then click narrowband, and
adjust the value to make the deviation be 0.35kHz.
In the Tuning Mode, double click the “QT(151.4) DEV”
item to enter. The tuning method is the same as that of
“QT(67.0) DEV”.
In the Tuning Mode, double click the “QT(254.1) DEV”
item to enter. The tuning method is the same as that of
“QT(67.0) DEV”.
6.3.8 Rx sensitivity
In the Tuning Mode, double click the “Sensitivity” item
to enter. Adjust the five frequency points of “Lowest”,
“Low”, “Mid”, “High”, and “Highest” within the adjusting
range of 0-255 to make the sensitivity be the highest.
See Table 6.4 for detailed parameters.
6.3.9 Rx squelch
In the Tuning Mode, double click the “SQL9 On” item to
enter. Click wideband and use the following method to
adjust the five frequency points of “Lowest”, “Low”, “Mid”,
“High”, and “Highest” respectively. Firstly, click one of the
frequency points, and adjust the RF signal frequency of the
test equipment to be the same with the receiving frequency
of that frequency point, and adjust the signal level to be
-116dBm. Then adjust the frequency of the modulation
signal to be 1kHz and the deviation to be 3kHz. Click
“Begin”, the programming software will adjust the value
automatically. When the value keeps stable, click “OK”, the
adjustment of that frequency point is completed. Then click
the next frequency point to do the adjustment. After all of the
five frequency points are adjusted, use the same method to
adjust the five frequency points of the narrowband. The only
difference is that the frequency of the modulation signal
should be 1kHz, and the deviation should be 1.5kHz.
In the Tuning Mode, double click the “SQL9 Off” item
to enter. Click wideband and use the following method to
adjust the five frequency points of “Lowest”, “Low”, “Mid”,
Содержание PT4208
Страница 1: ......
Страница 35: ......
Страница 36: ......
Страница 37: ...PT4208 Service Manual 36 Figure 5 PT4208 Main Board Top Layer Position Value Diagram 420 470MHz ...
Страница 38: ...PT4208 Service Manual 37 Figure 6 PT4208 Main Board Bottom Layer Position Value Diagram 420 470MHz ...
Страница 39: ...PT4208 Service Manual 38 Figure 7 PT4208 Main Board Top Layer Layout 420 470MHz ...
Страница 40: ...PT4208 Service Manual 39 Figure 8 PT4208 Main Board Bottom Layer Layout 420 470MHz ...
Страница 42: ...PT4208 Service Manual 41 Figure 10 PT4208 Main Board Top Layer Position Mark Diagram 136 174MHz ...
Страница 43: ...PT4208 Service Manual 42 Figure 11 PT4208 Main Board Bottom Layer Position Mark Diagram 136 174MHz ...
Страница 44: ...PT4208 Service Manual 43 Figure 12 PT4208 Main Board Top Layer Position Value Diagram 136 174MHz ...
Страница 45: ...PT4208 Service Manual 44 Figure 13 PT4208 Main Board Bottom Layer Position Value Diagram 136 174MHz ...
Страница 46: ...PT4208 Service Manual 45 Figure 14 PT4208 Main Board Top Layer Layout 136 174MHz ...
Страница 47: ...PT4208 Service Manual 46 Figure 15 PT4208 Main Board Bottom Layer Layout 136 174MHz ...
Страница 48: ...PT4208 Service Manual 47 Figure 16 KBC 70C Schematic Circuit Diagram ...
Страница 49: ...PT4208 Service Manual 48 Figure 17 KBC 70C Top Layer Position Value Diagram ...
Страница 50: ...PT4208 Service Manual 49 Figure 18 KBC 70C Top Layer Position Mark Diagram ...
Страница 51: ...PT4208 Service Manual 50 Figure 19 KBC 70C Bottom Layer Position Value Diagram ...
Страница 52: ...PT4208 Service Manual 51 Figure 20 KBC 70C Bottom Layer Position Mark Diagram ...
Страница 53: ...PT4208 Service Manual 52 Figure 21 KBC 70C Layout ...






























