Side 2
Install the Operating System Drivers
5
Create Installation Media
To manage a RAID array, install Intel
®
RAID Web Console 2
Install the Intel® RAID Web Console 2 package from the Resource CD.
Choose one of four installation modes: Complete (installs all features), Client (administrative machine only), Server (can be managed remotely), or StandAlone (only manages itself).
To start Intel® RAID Web Console 2 from within the OS: Choose Start | Programs | RAID WebConsole | RAID WebConsole 2. For additional details, see the Intel® RAID Software User’s Guide.
Create installation media (floppy disk required for Microsoft Windows 2003*; removable
media, such as a floppy disk, USB device, or CD/DVD-ROM, required for Microsoft
Windows 2008*). See the instructions at the right.
2
3
Boot the server and start the OS installation.
Press the <F6> key as soon as the first
screen appears.
When prompted to specify a mass
storage controller:
4
5
Extract the contents of the ZIP file and run Setup.exe from the Disk1 folder.
Unpack Linux_rwc2_**tar.gz.
Remove any line breaks and allow permissions by typing
$> tr -d ‘\15\32’ < existing_file_name > new_file_name
$> chmod a+x new_file_name
Run ./install.sh
1
4
5
When you see: “Where do you want to
install windows?”, select
Load Driver
,
and then click Next.
Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the Windows installation.
Extract the files from the zip file to your
hard drive. Copy the appropriate files to a
floppy disk (for Microsoft Windows 2003*)
or removable media (for Microsoft
Windows 2008*).
Copy the matching .sys, .cat,
.oem, and .inf driver files to a floppy disk
or removable media.
Extract the driver update disk (DUD) image (file
extension .img) from the zip file to your hard drive.
If you have a system with Microsoft Windows*, you
will need a third-party utlity such as ‘rawrite’ to
extract the DUD image to a floppy disk. For a system
under Linux or Sun Solaris*, use the ‘dd’ command
as follows:
Microsoft Windows*
Linux*
Obtain the drivers either from the resource CD or the Intel web site.
1
If using the Resource CD, insert the resource CD. Browse to \Drivers and then the matching OS folder.
Go to http://downloadcenter.intel.com and locate your product under Server Products in the left menu.
OR
2
3
When prompted by the Load Driver dialog:
a. Insert the removable installation media
that you created in step 1 above.
b. Press the <Enter> key to select the
“Installation Driver” and continue with
the Windows installation.
b. Insert the installation driver disk that
you created in step 1 above.
c. Press the <Enter> key to select the
“Installation Driver” and continue with
the Windows installation.
a. Press <S> to specify additional storage
devices.
Create installation media (removable media, such as a floppy disk, USB device,
or CD/DVD-ROM, required). See the instructions at the right.
1
2
3
At the boot prompt, insert the
Linux installation disk that you created
in step 1.
Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation. The RAID controller
driver is automatically detected and installed.
Boot the system with Red Hat*
Enterprise Linux CD-ROM.
Boot the system with SuSE* Linux
Enterprise Server (SLES) CD-ROM.
When the first screen displays, insert the
Linux installation disk that you created
step 1.
Press the <F5> key for SLES 10 or the
<F6> key for SLES 11 to load the driver,
and then select an installation menu
option.
Type
Linux dd
, and press the
<Enter>
key.
dd if=<image_file_name> of=<path-to-media>
‘path-to-media’ is usually /dev/fd0, but may
differ if you are using a USB floppy drive.
Install the Intel® RAID Web Console 2 package from the Resource CD.
Note: Below section lists the general driver loading process for frequently used operating systems. For more details, and for other supported operating systems, refer to the
corresponding driver release notes to get latest information.
Microsoft
Windows 2003*
OR
OR
Microsoft
Windows 2008*/2012*
OR
Red Hat*
Enterprise Linux
SuSE* Linux
Enterprise Server
RAID 1E (IME)
RAID 1 (IM)
RAID 0 (IS)
Minimum Disks:
2
Read performance:
Excellent
Write performance:
Excellent
Fault tolerance:
None
Number of Disks:
2
Read performance:
Excellent
Write performance:
Good
Fault tolerance:
Excellent
Minimum Disks:
3
Read performance:
Excellent
Write performance:
Good
Fault tolerance:
Excellent
Striping of data across multiple drives in an array. This
provides high performance, but no data protection.
Disk mirroring, meaning that all data on one disk is
duplicated on another disk. This is a high availability
solution, but only half the total disk space is usable.
Enhanced disk mirroring, meaning that all data on one
disk is duplicated on other disks. This is a high availability
solution, but only half the total disk space is usable.
D2
Disk 2
D1
Disk 1
D1
Disk 2
D1
Disk 1
D2
D2
Choosing the Right RAID Level
Disk 1
D6
D4
D1
D3
Disk 2
D4
D5
D2
D1
Disk 3
D5
D6
D3
D2
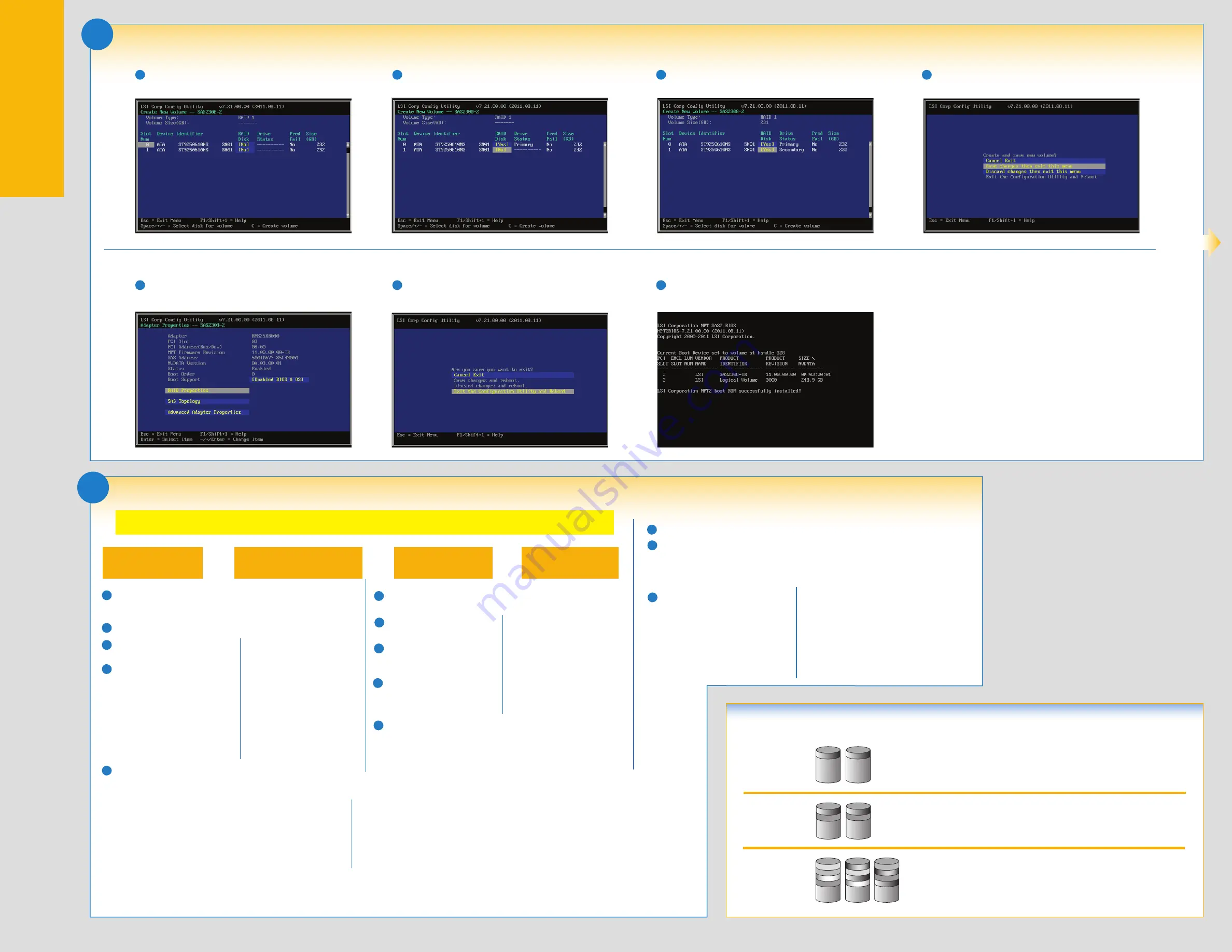
Creation of a RAID volume is now complete.
After the RAID array is created, the following screen will appear. Press <
Esc
> to
return to the main menu.
9
Choose
Exit the Configuration Utility and Reboot
and press <
Enter
> to
reboot the system.
10
During system reboot, verify that Logical Volume is displayed in the Product
column.
11
4
In the RAID Disk column highlight
No
and press <
Space
>.
6
When the RAID Disk status is listed as shown below, press <
C
> to create an array.
7
In the RAID Disk column highlight
No
and press <
Space
>.
5
(Cont.) Use the LSI MPT SAS BIOS Configuration Utility* to Create a RAID Virtual Drive
Select
Save changes then exit this menu
, then press <
Enter
>.
8


