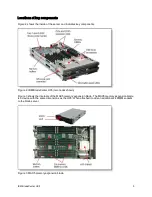
IBM BladeCenter HX5
2
Key features
The IBM BladeCenter HX5 is a scalable 2-to-4-socket blade server optimized for virtualization,
consolidation, database, and ERP. It offers outstanding performance, and superior reliability and
fault-tolerant memory characteristics.
IBM® has been designing and implementing servers under the X-Architecture® name since 2001. IBM
eX5 technology represents the fifth generation of enterprise servers based on the same design principle
IBM began with in 1997: to offer systems that are expandable, offer “big iron” reliability, availability, and
serviceability (RAS) features, with extremely competitive price/performance on an Intel Xeon
processor-based system.
Scalability and performance
The BladeCenter HX5 offers numerous features to boost performance, improve scalability, and reduce
costs:
The HX5 supports up to two high-performance Intel Xeon E7 family allowing you to upgrade as
business needs require.
The server can be scaled to four processors by connecting two HX5 servers together to form a single
system image; alternatively, extra memory can be added with the addition of the MAX5 memory
expansion blade
Supports the Intel Xeon E7-2800, E7-4800 and E7-8800 families of high performance processors, up
to 10 cores each, offering superior system performance
Each HX5 scalable to 512 GB of memory internally or 1.25 TB of memory with the addition of the
MAX5 memory expansion blade.
Intel Turbo Boost Technology dynamically turns off unused processor cores and increases the clock
speed of the cores in use, by up to three model frequencies. For example, with 7-10 cores active, a
2.4 GHz E7-2870 10-core processor can run the cores at up to 2.53 GHz. With 5-6 cores active, it can
run those cores at 2.67 GHz; with only 1-4 cores active, it can run those cores at 2.8 GHz
Each processor includes an integrated memory controller, to reduce memory bottlenecks and improve
performance. Memory access is at up to 1066 MHz frequency, depending on the processor model
and memory used.
The MAX5 adds an additional memory controller to maximize memory parallelism and performance.
In processors implementing Hyper-Threading technology, each core has two threads capable of
running an independent process. Thus, a 10-core processor can run 20 threads concurrently.
Intel’s Virtualization Technology (VT) integrates hardware-level virtualization hooks that allow
operating system vendors to better utilize the hardware for virtualization workloads.
Intel QuickPath Interconnect (QPI) technology for processor-to-processor connectivity and Intel
Scalable Memory Interconnect (SMI) processor-to-memory connectivity:
Intel QPI link topology at up to 6.4 Gbps with four QPI links per CPU
Intel SMI link topology at up to 6.4 Gbps with four SMI links per CPU
The server has 16 DIMM sockets, plus an additional 24 DIMMs with an optional MAX5 memory
expansion blade, for a total of 40 DIMM sockets.
The use of solid-state drives (SSDs) instead of, or along with, traditional spinning drives (HDDs) can
significantly improve I/O performance. An SSD can support up to 100 times more I/O operations per
second (IOPS) than a typical HDD.
Two optional 1.8-inch SSD bays for local booting and data storage.