Battery Maintenance
2240 SRM 1
(77
F)
. See Figure 15. NEVER charge a battery at a
rate that will raise the electrolyte temperature above
49 C (120
F)
. Never let a battery stay discharged for
long periods.
Types of Battery Charges
1.
NORMAL CHARGE. This charge is usually
given to a battery that is discharged from nor-
mal operation. This is often an 8-hour charge.
Many customers charge the battery at regular
intervals that depend on use. This procedure will
keep the battery correctly charged if the battery
is not discharged below the limit. Always use a
hydrometer to check the battery if the battery is
charged at regular intervals. Frequent charging
of a battery that has a 2/3 or more charge can
decrease the life of the battery.
2.
EQUALIZING CHARGE. This charge is at a low
rate and balances the charge in all the cells. The
equalizing charge is usually given approximately
once a month. It is a charge at a slow rate for 3
to 6 hours in addition to the regular charging cy-
cle. Do not give an equalizing charge more than
once a week. The most accurate specific gravity
measurements for a charged battery will be after
an equalizing charge. If the specific gravity dif-
ference is more than 0.020 between cells of the
battery after an equalizing charge, there can be
a damaged cell. Consult your battery dealer.
NOTE:
Many customers have battery chargers that
can follow a program to automatically charge a
battery according to recommendations of the battery
manufacturer.
Use the recommendations of the
battery manufacturer for charging the battery.
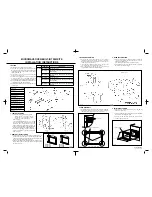
The discharge limits and the limits for the specific
gravity before the battery must be charged again are
shown in Figure 17. NEVER discharge a battery be-
low the limits shown in Figure 18. Discharging a bat-
tery beyond the design limits will decrease the ser-
vice life of the battery.
NOTE:
Sometimes the capacity of a battery is not
enough to complete a work period. Check for the fol-
lowing conditions:
• The battery is too small for the job.
• The battery is not fully charged.
• The battery charger is not operating correctly.
• The battery is near the end of its service life.
Figure 17. Specific Gravity Versus Percent
Discharge
Figure 18. Specific Gravity Compared to
Charging Time
12