CVH8, HVH8, TVH8, VA9, HVA9, TVA9: APPLICATION GUIDELINE & SERVICE MANUAL
Manufacturer reserves the right to change, at any time, specifications and designs without notice and without obligations.
39
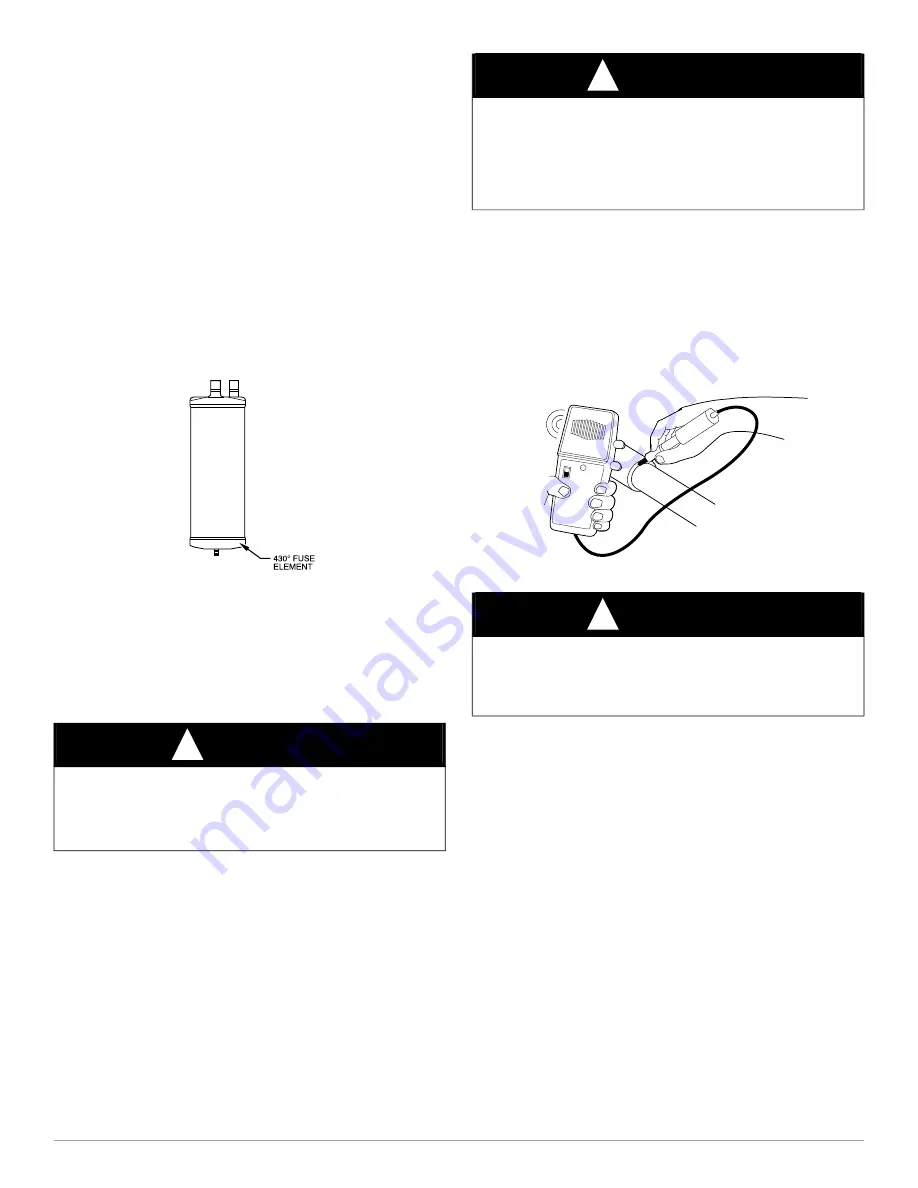
Accumulator
The accumulator is specifically designed to operate with R-410A
or
R22 respectfully; use only factory-authorized components. Under some
light load conditions on indoor coils, liquid refrigerant is present in
suction gas returning to compressor. The accumulator stores liquid and
allows it to boil off into a vapor so it can be safely returned to
compressor. Since a compressor is designed to pump refrigerant in its
gaseous state, introduction of liquid into it could cause severe damage or
total failure of compressor.
The accumulator is a passive device which seldom needs replacing.
Occasionally its internal oil return orifice or bleed hole may become
plugged. Some oil is contained in refrigerant returning to compressor. It
cannot boil off in accumulator with liquid refrigerant. The bleed hole
allows a small amount of oil and refrigerant to enter the return line where
velocity of refrigerant returns it to compressor. If bleed hole plugs, oil is
trapped in accumulator, and compressor will eventually fail from lack of
lubrication. If bleed hole is plugged, accumulator must be changed. The
accumulator has a fusible element located in the bottom end bell. (See
.) This fusible element will melt at 430
_
F//221
_
C and vent the
refrigerant if this temperature is reached either internal or external to the
system. If fuse melts, the accumulator must be replaced.
A88410
Fig. 42 – Accumulator
To change accumulator:
1. Shut off all power to unit.
2. Recover all refrigerant from system.
3. Break vacuum with dry nitrogen. Do not exceed 5 psig.
NOTE:
Coil may be removed for access to accumulator. Refer to
appropriate sections of Service Manual for instructions.
4. Remove accumulator from system with tubing cutter.
5. Tape ends of open tubing.
6. Scratch matching marks on tubing studs and old accumulator.
Scratch matching marks on new accumulator. Unbraze stubs from
old accumulator and braze into new accumulator.
7. Thoroughly rinse any flux residue from joints and paint with
corrosion-resistant coating such as zinc-rich paint.
8. Install factory authorized accumulator into system with copper slip
couplings.
9. Evacuate and charge system.
Pour and measure oil quantity (if any) from old accumulator. If more
than 20 percent of oil charge is trapped in accumulator, add new POE oil
to compressor to make up for this loss.
REFRIGERATION SYSTEM REPAIR
Leak Detection
New installations should be checked for leaks prior to complete
charging. If a system has lost all or most of its charge, system must be
pressurized again to approximately 150 psi minimum and 375 psi
maximum. This can be done by adding refrigerant using normal charging
procedures or by pressurizing system with nitrogen (less expensive than
refrigerant). Nitrogen also leaks faster than refrigerants. Nitrogen
cannot, however, be detected by an electronic leak detector. (See
.)
A95422
Fig. 43 – Electronic Leak Detection
Assuming that a system is pressurized with either all refrigerant or a
mixture of nitrogen and refrigerant, leaks in the system can be found
with an electronic leak detector that is capable of detecting specific
refrigerants.
If system has been operating for some time, first check for a leak
visually. Since refrigerant carries a small quantity of oil, traces of oil at
any joint or connection is an indication that refrigerant is leaking at that
point.
A simple and inexpensive method of testing for leaks is to use soap
bubbles. (See
.) Any solution of water and soap may be used.
Soap solution is applied to all joints and connections in system. A small
pinhole leak is located by tracing bubbles in soap solution around leak. If
the leak is very small, several minutes may pass before a bubble will
form. Popular commercial leak detection solutions give better,
longer-lasting bubbles and more accurate results than plain soapy water.
The bubble solution must be removed from the tubing and fittings after
checking for leaks as some solutions may corrode the metal.
CAUTION
!
PERSONAL INJURY HAZARD
Failure to follow this caution may result in personal injury.
Wear safety glasses, protective clothing, and gloves when handling
refrigerant.
WARNING
!
ELECTRICAL SHOCK HAZARD
Failure to follow this warning could result in personal injury or death.
Before installing, modifying, or servicing system, main electrical
disconnect switch must be in the OFF position. There may be more than
1 disconnect switch. Lock out and tag switch with a suitable warning
label.
WARNING
!
PERSONAL INJURY AND UNIT DAMAGE HAZARD
Failure to follow this warning could result in personal injury or death.
Due to the high pressure of nitrogen, it should never be used without a
pressure regulator on the tank.
BEEP
BEEP


































