17
Technical white paper | HP Z640 Workstation
Performance Considerations
Power Settings
The default “Balanced” and “Power Saver” plans in Windows Power Options may result in power management settings
that may adversely affect performance of your applications. If the workstation is being used for a high demand
application, consider choosing the “High performance” power plan or choose custom settings that better fit your use model.
SSDs used in RAID configurations and TRIM support
TRIM keeps track of files that have been deleted but not erased on the drive to improve performance and help extend the
life of the SSD. As the SSD is used, the controller within the SSD distributes data across the available FLASH on the SSD
until all FLASH is used. After the FLASH has been used up, a block erase is required before subsequent writes can occur.
The TRIM command normally frees up memory prior to being needed for the next write. If the TRIM commands are not
sent to the drive and no unerased FLASH is available for writing, the SSD controller must erase a block of memory prior to
writing. This can slow performance in applications that perform a lot of file write and file delete operations. One example
is in compiling code where the compiler generates many intermediate files that then get deleted.
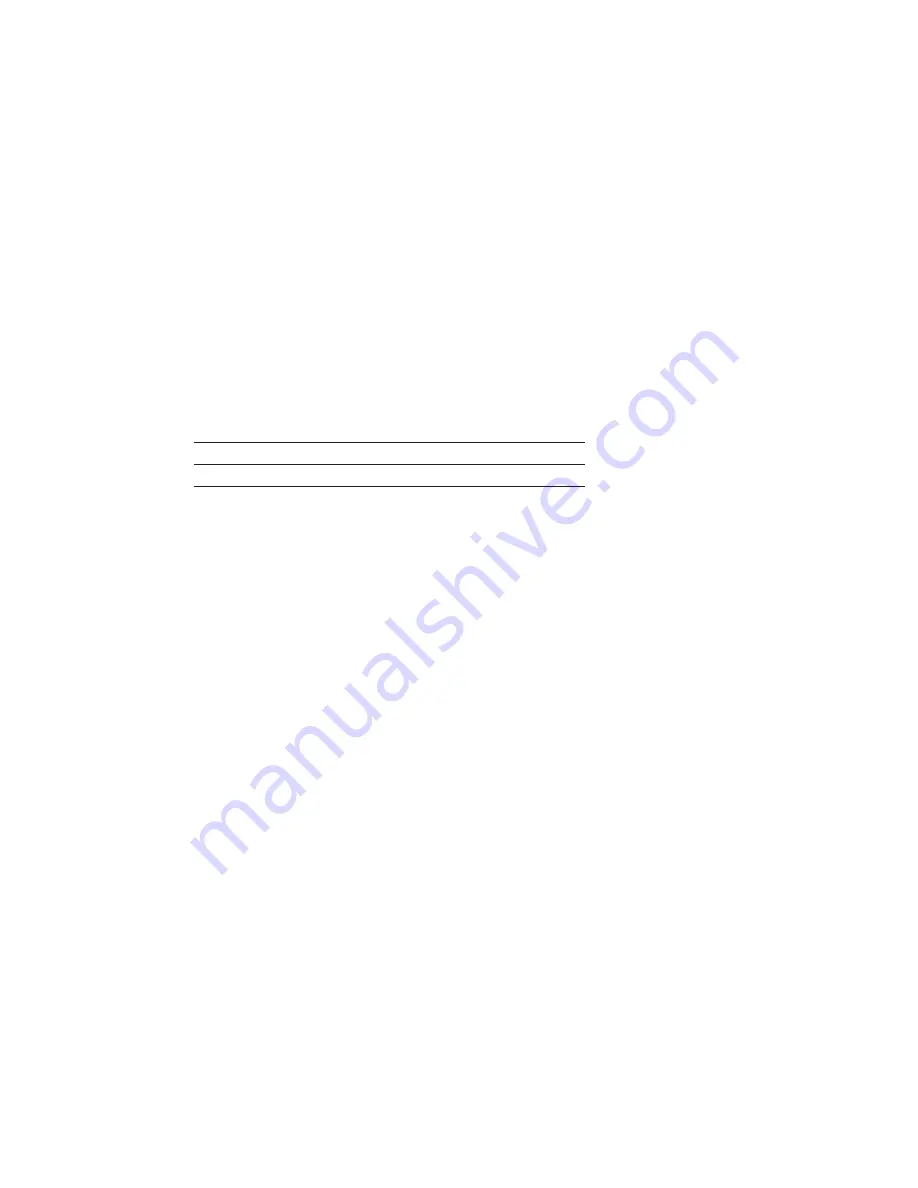
The table below shows which RAID arrays support TRIM:
Controller
TRIM supported
TRIM not supported
SATA
0, 1
sSATA
0, 1, 10
5
Storage Caching Options
HP Workstations ship with default storage cache settings that balance performance with data protection. The balance of
performance and protection can be adjusted by changing one or more of these settings.
Create a backup of your data before attempting to change any storage related settings.
Windows Write-caching policy (Disk Properties in Disk Manager)
Write caching on the device:
DEFAULT: Enabled
Improves performance by enabling write caching on the disk; however, a loss of power may result in loss of data
that has not been committed to the storage media.
Windows write-cache buffer flushing:
DEFAULT: Enabled
When enabled, Windows will periodically instruct the storage device to commit data in the devices cache to the
non-volatile storage media. These periodic commands result in decreased overall system performance.
Note: If Windows write-cache buffer flushing is enabled, Intel® RSTe write-back cache is disabled. To enable write-
back cache on volumes, you must disable Windows write-cache buffer flushing.
A user can choose to disable Windows write-cache buffer flushing to restore system performance, allowing the Intel®
RSTe driver to handle all write-cache buffer flushing.
Intel® RSTe write-back cache [for RAID volumes] (Intel RSTe GUI, Volume Properties)
DEFAULT: Disabled
When enabled, the read and write performance of a RAID or recovery volume is improved. In write-back cache mode,
the RAID controller acknowledges write I/O requests immediately after the data loads into the controller cache. The
application can continue working without waiting for the data to be physically written to the hard drives.
Enabling Intel® RSTe write-back cache will enable Write caching on the device if not already enabled and will disable
Windows write-cache buffer flushing.







































