251
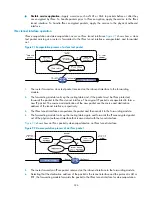
Mirror image ACLs
To ensure that SAs can be set up and the traffic protected by IPsec can be processed correctly at the
remote peer, on the remote peer, create a mirror image ACL rule for each ACL rule created at the local
peer. As shown in
, ACL rules on Router B are mirror images of the rules on Router A. This
ensures that SAs can be created successfully for the traffic between Host A and Host C and the traffic
between Network 1 and Network 2.
Figure 94
Mirror image ACLs
Network 2
2.2.2.0/24
Network 1
1.1.1.0/24
IP network
ACL1: rule permit 1.1.1.1 -> 2.2.2.2
Host A
1.1.1.1
Host B
Host C
2.2.2.2
Host D
Router A
Router B
Eth1/1
Eth1/2
Mirror image ACLs on Eth1/1 of Router A and on Eth1/2 of
Router B
ACL2: rule permit 1.1.1.0/24 -> 2.2.2.0/24
ACL1: rule permit 2.2.2.2 -> 1.1.1.1
ACL2: rule permit 2.2.2.0/24 -> 1.1.1.0/24
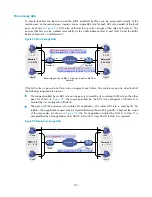
If the ACL rules on peers do not form mirror images of each other, SAs can be set up only when both of
the following requirements are met:
•
The range specified by an ACL rule on one peer is covered by its counterpart ACL rule on the other
peer. As shown in
, the range specified by the ACL rule configured on Router A is
covered by its counterpart on Router B.
•
The peer with the narrower rule initiates SA negotiation. If a wider ACL rule is used by the SA
initiator, the negotiation request may be rejected because the matching traffic is beyond the scope
of the responder. As shown in
, the SA negotiation initiated by Host A to Host C is
accepted but the SA negotiations from Host C to Host B or from Host D to Host A is rejected.
Figure 95
Non-mirror image ACLs