197
Configuring DDNS
Overview
Although DNS allows you to access nodes in networks using their domain names, it provides only the
static mappings between domain names and IP addresses. When you use the domain name to access
a node whose IP address has changed, your access fails because DNS leads you to the IP address that
is no longer where the node resides.
Dynamic Domain Name System (DDNS) can dynamically update the mappings between domain names
and IP addresses for DNS servers to direct you to the latest IP address corresponding to a domain name.
DDNS can only dynamically update the mappings between domain names and IPv4 addresses but not
IPv6 addresses.
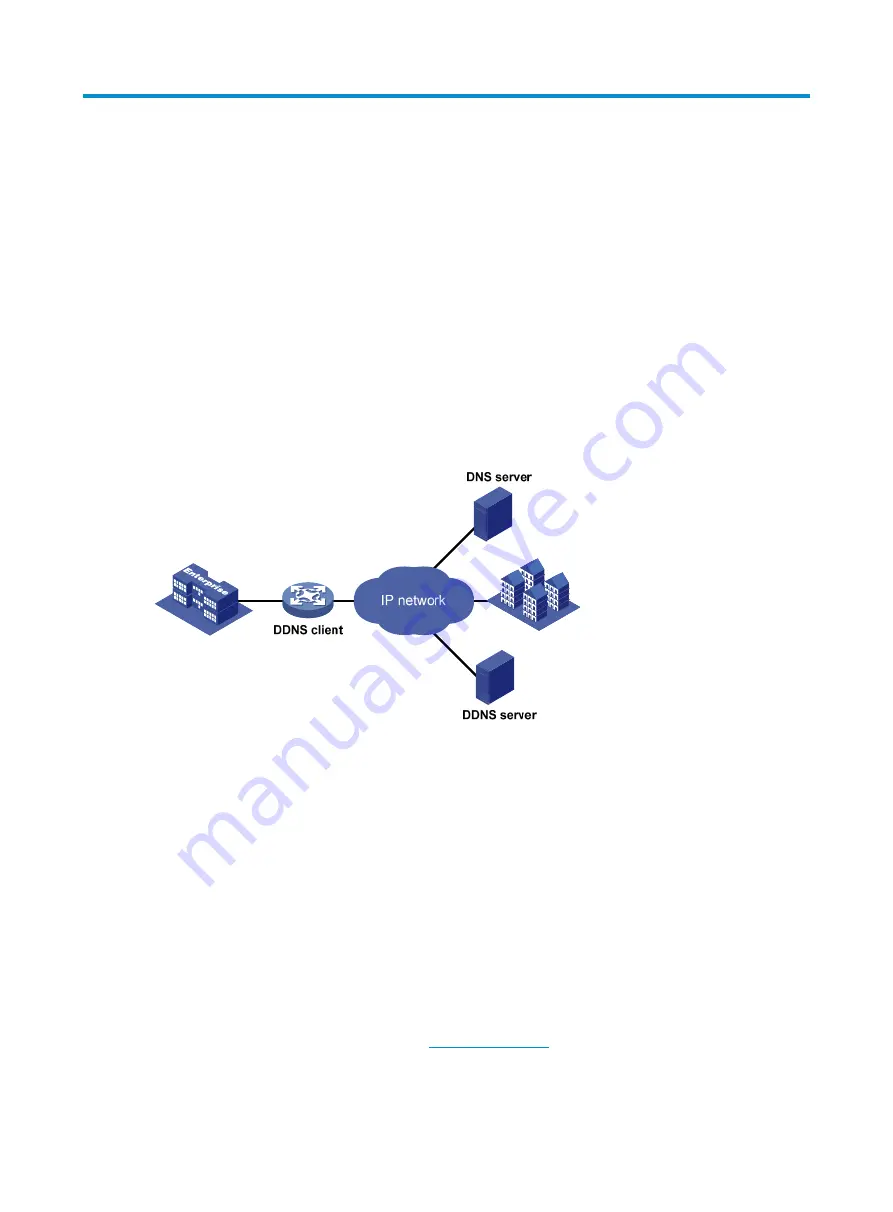
Figure 205
DDNS networking application
As shown in
, DDNS works on the client-server model comprising the DDNS client and the
DDNS server.
•
DDNS client
—A device that needs to update the mapping between the domain name and the IP
address dynamically on a DNS server. An Internet user usually uses the domain name to access an
application layer server such as an HTTP and FTP server. When its IP address changes, the
application layer server runs as a DDNS client that sends a request to the DDNS server for updating
the mapping between the domain name and the IP address.
•
DDNS server
—Informs the DNS server of latest mappings. When receiving the mapping update
request from a DDNS client, the DDNS server tells the DNS server to re-map between the domain
name and IP address of the DDNS client. Therefore, the Internet users can use the same domain
name to access the DDNS client even if the IP address of the DDNS client has changed.
The DDNS update process does not have a unified standard and depends on the DDNS server that the
DDNS client contacts. The well-known DDNS service providers include www.3322.org, www.oray.cn
(also known as the PeanutHull server), and
www.dyndns.com.
The device can act as a DDNS client to dynamically update the latest mapping between its domain name
and IP address on the DNS server through a DDNS server at www.3322.org or www.oray.cn for
example.
Содержание MSR SERIES
Страница 17: ...xv Documents 835 Websites 835 Conventions 836 Index 838 ...
Страница 20: ...3 Figure 3 Initial page of the Web interface ...
Страница 42: ...25 Figure 13 Firefox Web browser setting ...
Страница 59: ...42 Figure 27 Checking the basic service configuration ...
Страница 73: ...56 Figure 35 Sample interface statistics ...
Страница 156: ...139 Figure 139 Rebooting the 3G modem ...
Страница 168: ...151 Figure 152 Configuring Web server 2 ...
Страница 174: ...157 Figure 158 Configure the URL filtering function ...
Страница 187: ...170 Upon detecting the Land or Smurf attack on Ethernet 0 2 Router outputs an alarm log and drops the attack packet ...
Страница 242: ...225 Figure 233 Enabling the DHCP client on interface Ethernet 0 1 ...
Страница 247: ...230 Figure 236 The page for configuring an advanced IPv4 ACL ...
Страница 255: ...238 Figure 241 Advanced limit setting ...
Страница 298: ...281 e Click Apply 2 Configure Router B in the same way Router A is configured ...
Страница 354: ...337 Figure 339 Configuring a login control rule so Host B cannot access Router through the Web ...
Страница 400: ...383 Figure 387 Verifying the configuration ...
Страница 405: ...388 ...
Страница 523: ...506 Figure 530 Ping configuration page ...
Страница 538: ...521 a Click Device A on the topology diagram b Click Ethernet 0 2 on the panel diagram c Click Port Guard ...
Страница 744: ...727 Verifying the configuration In the case that the IP network is unavailable calls can be made over PSTN ...
Страница 775: ...758 Figure 785 Configuring a jump node ...
Страница 791: ...774 Figure 801 Configuring a jump node ...