172
Although RP 4 and RP 5 are in the same AS (AS 3) and both are MSDP peers of RP 6, because RP
5 has a higher IP address, RP 6 accepts only the SA message from RP 5.
5.
When RP 7 receives the SA message from RP 6:
Because the SA message is from a static RPF peer (RP 6), RP 7 accepts the SA message and
forwards it to other peer (RP 8).
6.
When RP 8 receives the SA message from RP 7:
A BGP or MBGP route exists between two MSDP peers in different ASs. Because the SA message
is from an MSDP peer (RP 7) in a different AS, and the MSDP peer is the next hop on the BGP or
MBGP route to the source-side RP, RP 8 accepts the message and forwards it to its other peer (RP
9).
7.
When RP 9 receives the SA message from RP 8:
Because RP 9 has only one MSDP peer, RP 9 accepts the SA message.
SA messages from paths other than those described previously are not accepted or forwarded by MSDP
peers.
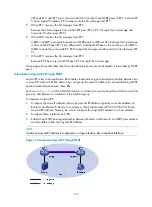
Intra-domain Anycast RP through MSDP
Anycast RP refers to an application that enables load balancing and redundancy backup between two
or more RPs within a PIM-SM domain by configuring the same IP address for, and establishing MSDP
peering relationships between, these RPs.
As shown in
, within a PIM-SM domain, a multicast source sends multicast data to multicast
group G, and Receiver is a member of the multicast group.
To implement Anycast RP:
1.
Configure the same IP address (known as Anycast RP address, typically a private address) on
Router A and Router B. Be sure to configure a 32-bit subnet mask (255.255.255.255) for the
Anycast RP address. Namely, be sure to configure the Anycast RP address to a host address.
2.
Configure these interfaces as C-RPs.
3.
Establish an MSDP peering relationship between Router A and Router B. An MSDP peer address
must be different from the Anycast RP address.
NOTE:
Usually an Anycast RP address is configured on a logic interface, like a loopback interface.
Figure 53
Intra-domain Anycast RP through MSDP