44
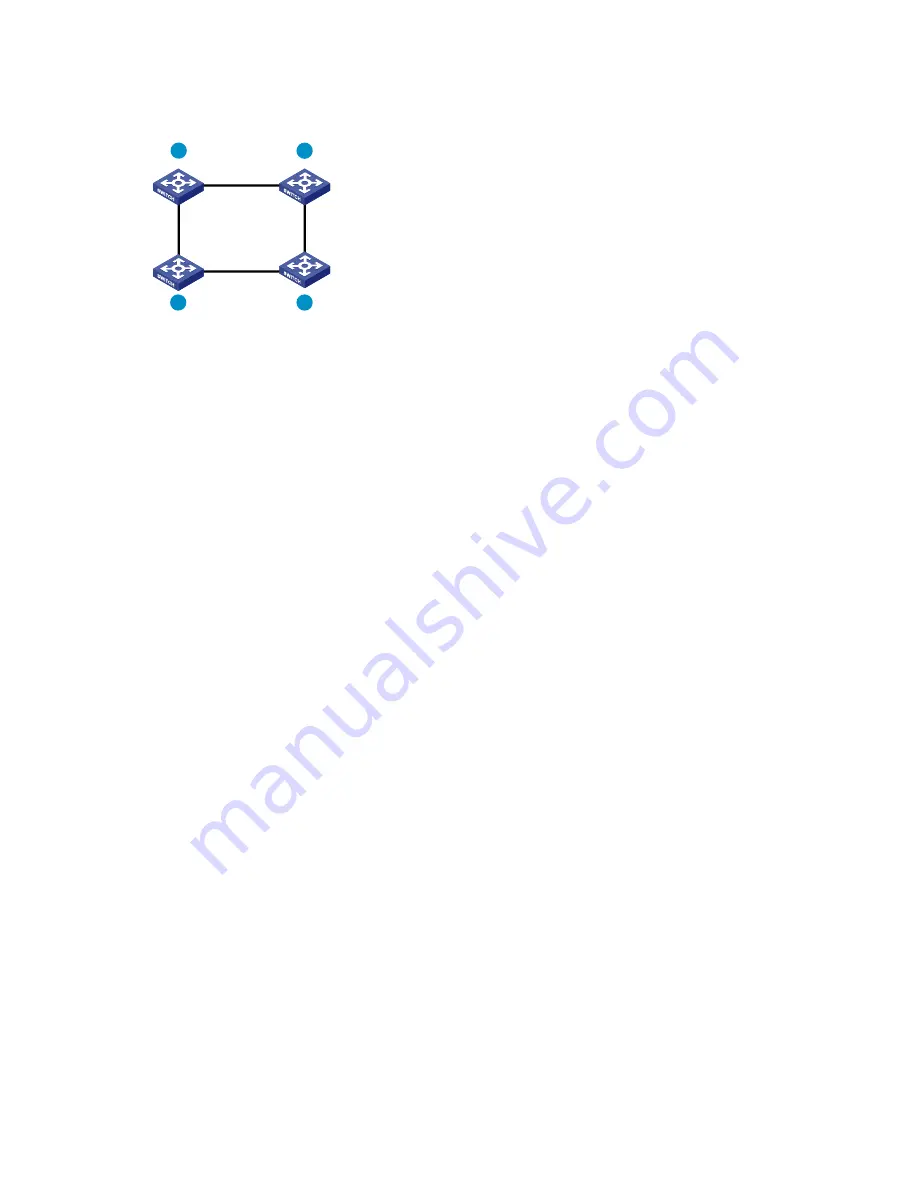
shows the IRF fabric topology.
Figure 47
IRF fabric topology
1
2
3
4
Configuring basic IRF settings
After installing the IRF member switches, power on the switches and log in to each IRF member switch to
configure their member IDs, member priorities, and IRF port bindings. For more information, see the
fundamentals configuration guide for your switch.
Follow these guidelines when you configure the neighboring switches:
Assign the master switch higher member priority than any other switch.
Bind physical ports to IRF port 1 on one switch and to IRF port 2 on the other switch.
To activate the IRF port configuration, execute the
irf-port-configuration active
command.
To verify the basic IRF settings, execute the
display irf configuration
command.
For more information about configuring basic IRF settings, see the IRF configuration guide for your switch.
Connecting the physical IRF ports
Follow your plan in connecting the IRF member switches. Wear an ESD-preventive wrist strap when you
connect the physical IRF ports. For more information about connecting physical IRF ports, see
Pluggable
SFP/SFP+/XFP Transceiver Modules Installation Guide
.
Accessing the IRF fabric to verify the configuration
To verify the basic functionality of the IRF fabric after you finish configuring basic IRF settings and
connecting IRF ports:
1.
Log in to the IRF fabric through the console port of any member switch.
2.
Create a Layer 3 interface, assign it an IP address, and make sure that the IRF fabric and the
remote network management station can reach each other.
3.
Use Telnet, web or SNMP to access the IRF fabric from the network management station.
For more information, see the fundamentals configuration guide for your switch.
4.
Verify that you can manage all member switches as if they were one node.
5.
Display the running status of the IRF fabric by using the commands in






























