258
192.168.99.0/24 BGP 255 1 10.220.2.16 Eth1/1
BGP Routing table Status : <Inactive>
Summary Count : 0
The output shows that Router D has learned routes to 192.168.64.0/24, 192.168.74.0/24, and
192.168.99.0/24 through BGP.
After the above configurations, ping the hosts on networks 192.168.64.0/24,
192.168.74.0/24, and 192.168.99.0/24 from Router D. The ping operations succeed.
5.
Configure route summarization on Router C to summarize 192.168.64.0/24,
192.168.74.0/24, and 192.168.99.0/24 into a single route 192.168.64.0/18 and disable
advertisement of the more specific routes.
[RouterC-bgp-ipv4] aggregate 192.168.64.0 18 detail-suppressed
[RouterC-bgp-ipv4] quit
[RouterC-bgp] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display IP routing table information on Router C.
[RouterC] display ip routing-table | include 192.168
192.168.64.0/18 BGP 130 0 127.0.0.1 NULL0
192.168.64.0/24 OSPF 150 1 172.17.100.1 Eth1/1
192.168.74.0/24 OSPF 150 1 172.17.100.1 Eth1/1
192.168.99.0/24 OSPF 150 1 172.17.100.1 Eth1/1
The output shows that Router C has a summary route 192.168.64.0/18 with the output interface Null0.
# Display the IP routing table information on Router D.
[RouterD] display ip routing-table protocol bgp
Summary Count : 1
BGP Routing table Status : <Active>
Summary Count : 1
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
192.168.64.0/18 BGP 255 0 10.220.2.16 Eth1/1
BGP Routing table Status : <Inactive>
Summary Count : 0
The output shows that Router D has only one route 192.168.64.0/18 to AS 65106.
After the above configurations, ping the hosts on subnets 192.168.64.0/24, 192.168.74.0/24 and
192.168.99.0/24 from Router D. The ping operations succeed.
BGP load balancing configuration example
Network requirements
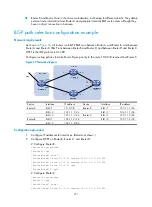
As shown in
, run EBGP between Router A and Router B and between Router A and Router C.
Run IBGP between Router B and Router C. Configure load balancing over the two EBGP links on Router
A.