5
Battery voltage
Charger output current
Charger output voltage
Battery internal gas pressure
Battery temperature
Battery voltage
Overcharge range
Battery temperature 60 C
120-minute timer
Ni-Cd battery temperature
Charging time
Battery internal
gas pressure
Battery temperature 55 C
dT/dt
Ni-MH battery
temperature
V
Stop current 2A
Li-ion battery
Charger output current
Li-ion battery
Charger output voltage
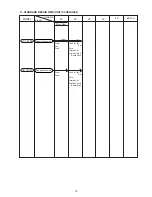
4-1-4. 3-way overcharge protection system
Overcharge protection is ensured by a (A)
2
V system or dT/dt system (for Ni-MH battery), (B) built-in battery
temperature sensor (thermistor) and (C) a timer.
Fig. 7 Relationships of time, voltage, temperature and gas pressure while charging
(A) • : This detects the fall in battery voltage at the end of charging using the value and suspends
charging.
dT/dt : This system is applicable to Ni-MH and SUPER Ni-MH batteries. This detects the variation in
temperature of Ni-MH and SUPER Ni-MH batteries by the value dT/dt at the end of charging and suspends
charging.
(B) • Built-in battery temperature sensor : In the event both the system and the dT/dt system fail to detect
completion of recharging, recharging is automatically stopped when the battery temperature reaches 60
û
C in
the case of the nickel cadmium (Ni-Cd) batteries or 55
û
C in the case of the nickel metal hydride (Ni-MH),
SUPER nickel metal hydride (SUPER Ni-MH) and lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries.
(C) • Timer : Should both the system, dT/dt system and the temperature sensor fail, the timer automatically
stops charging within 120 minutes from the beginning of charging.
(Note 2) The voltage of the battery increases during charging and begins to fall when further charging is not
possible. The system detects the point where the voltage begins to fall, and suspends charging
to protect the battery from overcharging.
(Note 3) The temperature rise during charging of a Ni-MH or SUPER Ni-MH battery is higher than a Ni-Cd
battery, and a sudden temperature rise occurs just before the battery is fully charged. The dT/dt
system detects the point where the temperature rises suddenly and suspends charging to minimize
the temperature rise.
(Note 4) As shown in Fig. 7, the pressure of gas generated after a battery has become fully charged rises
rapidly to cause high temperature and high gas pressure that degrade the effectiveness of the
battery. If charging is allowed to continue, the pressure of the gas will activate the safety valve in the
battery, and the electrolyte will begin leaking.
Содержание UC 18YFL
Страница 26: ......