11
English
䡬
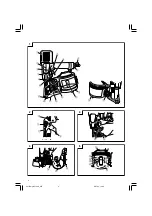
Place the nailer vertically over the location into which
the nail is to be driven.
䡬
Do not drive nails directly into C-beam steel or attach
wire mesh laths, galvanized steel etc. directly onto it.
䡬
Do not use the nailer on roofs or ceilings.
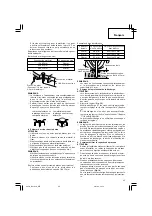
[Selecting hardened nails for steel plating]
CAUTION
Make sure that the length of the hardened nails
designed for use with steel plating is of the correct
thickness for the C-beam steel.
If the nail is too long for the material, the nail cannot
be driven enough into the C-beam steel and it may
result in bent nails, personal injury or accident.
Refer to the following figure to select the correct nail
length.
[Selecting Nail Length]
NOTE:
䡬
Holding power will be greatly decreased if nails are
driven too hard into steel plating, adjust the driving
depth of the nail by the adjuster.
䡬
There are cases in which the nails will not be driven
in sufficiently depending on a combination of the
hardness and thickness of the C-beam or material.
4. Driving nails into concrete
CAUTION
䡬
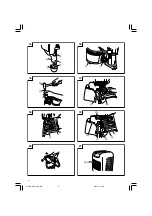
Use hardened nails designed for use with concrete.
䡬
Place the nailer vertically over the location into which
the nail is to be driven.
䡬
Do not drive nails directly into concrete or attach
metal plates directly onto it.
䡬
Do not drive nails into the edge of concrete.
䡬
Do not use the nailer in locations from which other
items are suspended (suspended pipes, etc.).
NOTE:
Only use the nailer on concrete that has not yet set,
soon after it has been poured.
Using the nailer on hardened concrete may result in
bent nails and nails being insufficiently driven in.
[Selecting hardened nails for use with concrete]
Select nails with a concrete intrusion depth of between
10 to 15 mm.
Reference Examples
NOTE:
The nails will not be driven in sufficiently if the
concrete intrusion depth is deeper than 15 mm.
5. Adjusting the nail-driving depth
CAUTION
When making adjustments, be sure remove your
finger from the trigger. When making adjustments,
be sure that the nail outlet is not facing downward
and that body parts or other people are not in the
path of the nail outlet.
䡬
Adjusting the adjuster (
Fig. 12
)
Carry out test driving. If the nails are too deep, turn
the adjuster to the shallow side (
mark).
If the nail depth is too shallow, turn the adjuster to
the deep side (
mark) (See
Fig. 12, 13
).
Depth is changed 1 mm with each rotation of the
adjuster.
NOTE:
䡬
When adjusting the adjuster, it does not rotate more
than 3 mm from the deepest point where a nail goes
down. Do not rotate the adjuster by force beyond
that point.
䡬
The nail-driving depth can also be adjusted by
changing the air pressure used. Carry this out together
with movement of the adjuster. Using a high air
pressure that does not match the nail-driving
resistance will shorten the life of this nailer.
6. How to use nosecap
CAUTION
Remove the hose from the nailer and release the
compressed air before installing or removing the
nosecap to prevent accidental nail ejection.
䡬
Attach the nose cap on the tip of the push lever when
you wish to protect the surface of wood, etc., from
scratches.
(1) Attaching and detaching nose cap
The nose cap can be attached by simply pressing it
into the push lever.
Press it in until a convex part inside the nose cap
enters into a hole of the push lever. (
Fig.14
)
For removal, insert a thin rod such as a screw driver
into the gap on the back of the push lever, and then
pull it out.
C-beam Steel
(Thickness: 1.6 mm to a
maximum of 3.2 mm)
Material Thickness
Approximately
10 to 35 mm
The external material
and steel plating is not
deformed.
The external material
and steel plating is
deformed.
Material Thickness
Nail Length
15 to 45 mm
50 mm
22 to 47 mm
57 mm
30 to 55 mm
65 mm
Length of Nails
to be Used
Wood Thickness
Concrete Intrusion
Depth 10 to 15 mm
Wood
Length of Nails
Concrete
Thickness
to be Used
Intrusion Depth
35 mm
50 mm
Approx. 15 mm
45 mm
57 mm
Approx. 12 mm
50 mm
65 mm
Approx. 15 mm
01Eng_NV100H_WE
3/27/12, 14:05
11