English
14
1. Rectilinear cutting
When cutting on a straight line, first draw
a marking gauge line and advance the saw
along that line. Using the auxiliary straight
guide (sold separately) will make it possible
to cut accurately on a straight line. Attach
the guide by passing it through the
attachment hole on the base and tightening
the M5 knob bolt. (Fig. 7)
2. Sawing curved lines
When sawing a small circular arc, reduce
the feeding speed of the machine. If the
machine is fed too fast, it could cause the
blade to break.
3. Cutting a circle or a circular arc
In this case it will be helpful to use the
auxiliary circular guide and guide center
(sold separately) (Fig. 8).
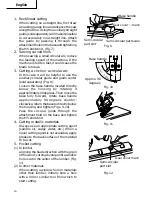
Loosen the base handle located directly
below the housing by rotating it
approximately 90 degrees. Then move the
base fully forward, rotate base handle
approximately 90 degrees counter-
clockwise, return the base to directly below
the housing and tighten (Figs. 9, 10).
Pass the circular guide through the
attachment hold on the base and tighten
the M5 knob bolt.
4. Cutting metallic materials
Always use an appropriate cutting agent
(spindle oil, soapy water, etc.) When a
liquid cutting agent is not available, apply
grease to the back surface of the material
to be cut.
5. Pocket cutting
(1) In lumber
Aligning the blade direction with the grain
of the wood, cut step by step until a window
hole is cut in the center of the lumber. (Fig.
11)
(2) In other materials
When cutting a window hole in materials
other than lumber, initially bore a hole
with a drill or similar tool from which to
start cutting.
Fig. 10
Base handle
Approx. 90
degrees
Tighten
Loosen
Fig. 11
Gear cover mark
Semi-circular
part slot
Fig. 12
Fig. 9
Semi-circular part scale
Semi-circular
part slot
Base handle
Gear cover
-mark