30
To do...
Use the command...
Remarks
Display the one-way DM result on
the specified MEP
display cfd dm one-way history
[
service-instance
instance-id
[
mep
mep-id
] ] [
|
{
begin
|
exclude
|
include
}
regular-expression
]
Available in any view
Display the TST result on the
specified MEP
display cfd tst
[
service-instance
instance-id
[
mep
mep-id
] ] [
|
{
begin
|
exclude
|
include
}
regular-expression
]
Available in any view
Clear the one-way DM result on the
specified MEP
reset cfd dm one-way history
[
service-instance
instance-id
[
mep
mep-id
] ]
Available in user view
Clear the TST result on the
specified MEP
reset cfd tst
[
service-instance
instance-id
[
mep
mep-id
] ]
Available in user view
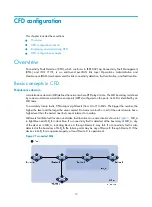
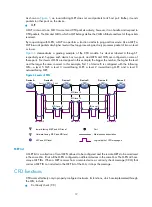
CFD configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in
:
•
The network comprises five devices and is divided into two MDs: MD_A (level 5) and MD_B (level
3). All ports belong to VLAN 100, and the MAs in the two MDs all serve VLAN 100.
•
MD_A has three edge ports: GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 on Device A, GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 on
Device D, and GigabitEthernet 1/0/4 on Device E, and they are all inward-facing MEPs. MD_B has
two edge ports: GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 on Device B and GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 on Device D, and
they are both outward-facing MEPs.
•
In MD_A, Device B is designed to have MIPs when its port is configured with low level MEPs. Port
GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 is configured with MEPs of MD_B, and the MIPs of MD_A can be
configured on this port. You should configure the MIP generation rule of MD_A as explicit.
•
The MIPs of MD_B are designed on Device C, and are configured on all ports. You should configure
the MIP generation rule as default.
•
Configure CC to monitor the connectivity among all the MEPs in MD_A and MD_B. Configure to
use LB to locate link faults, and use the AIS function to suppress the error alarms reported.
•
After the status information of the entire network is obtained, use LT, LM, one-way DM, two-way DM,
and TST to detect link faults.