92
[DeviceD-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] port link-type trunk
[DeviceD-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan all
[DeviceD-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] qos trust dot1p
[DeviceD-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
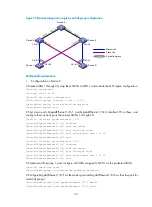
# Create RRPP domain 1, configure VLAN 4092 as the primary VLAN of RPPP domain 1, and configure
the VLANs mapped to MSTIs 0 through 32 as the protected VLANs of RRPP domain 1.
[DeviceD] rrpp domain 1
[DeviceD-rrpp-domain1] control-vlan 4092
[DeviceD-rrpp-domain1] protected-vlan reference-instance 0 to 32
# Configure Device D as a transit node of the primary ring Ring 1, with GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 as the
primary port and GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 as the secondary port, and enable Ring 1.
[DeviceD-rrpp-domain1] ring 1 node-mode transit primary-port gigabitethernet 1/0/1
secondary-port gigabitethernet 1/0/2 level 0
[DeviceD-rrpp-domain1] ring 1 enable
[DeviceD-rrpp-domain1] quit
# Enable the RRPP protocol.
[DeviceD] rrpp enable
5.
Verification
Use the
display
command to view RRPP configuration and operational information on Device A and
Device D.
Troubleshooting
Symptom
When the link state is normal, the master node cannot receive Hello packets, and the master node
unblocks the secondary port.
Analysis
The following reasons may apply:
•
RRPP is not enabled on some nodes in the RRPP ring.
•
The domain ID or primary control VLAN ID is not the same for the nodes in the same RRPP ring.
•
Some ports are abnormal.
Solution
•
Use the
display rrpp brief
command to check whether RRPP is enabled for all nodes. If not, use the
rrpp enable
command and the
ring enable
command to enable RRPP and RRPP rings for all nodes.
•
Use the
display rrpp brief
command to check whether the domain ID and primary control VLAN ID
are the same for all nodes. If not, set the same domain ID and primary control VLAN ID for the
nodes.
•
Use the
display rrpp verbose
command to check the link state of each port in each ring.
•
Use the
debugging rrpp
command on each node to check whether a port receives or transmits
Hello packets. If not, Hello packets are lost.