247
The BGP AS number substitution function allows physically dispersed CEs to use the same AS number.
The function is a BGP outbound policy and functions on routes to be advertised.
With the BGP AS number substitution function, when a PE advertises a route to a CE of the specified peer,
if an AS number identical to that of the CE exist in the AS_PATH of the route, it will be replaced with that
of the PE.
After you enable the BGP AS number substitution function, the PE re-advertises all routing information to
the connected CEs in the peer group, performing BGP AS number substitution based on the previous
principle.
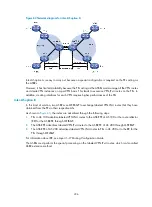
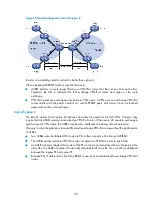
Figure 75
Application of BGP AS number substitution and SoO
, both CE 1 and CE 2 use the AS number of 800. AS number substitution is enabled on PE
2 for CE 2. Before advertising updates received from CE 1 to CE 2, PE 2 finds that an AS number in the
AS_PATH is the same as that of CE 2 and hence substitutes its own AS number 100 for the AS number.
In this way, CE 2 can normally receive the routing information from CE 1.
However, the AS number substitution function also introduces a routing loop in Site 2 because route
updates originated from CE3 can be advertised back to Site 2 through PE 2 and CE2. To remove the
routing loop, you can configure a routing policy on PE2 to add the SoO attribute to route updates
received from CE 2 and CE 3 so that PE 2 will not advertise route updates from CE 3 to CE 2.
MPLS L3VPN configuration task list
Task Remarks
By configuring basic MPLS L3VPN, you can construct
simple VPN networks over an MPLS backbone.
To deploy special MPLS L3VPN networks, such as
inter-AS VPN and nested VPN, you also need to
perform some specific configurations in addition to the
basic MPLS L3VPN configuration. See the related
sections for details.
Configuring BGP AS number substitution and SoO
Configuring basic MPLS L3VPN
The key task in MPLS L3VPN configuration is to manage the advertisement of VPN routes on the MPLS
backbone, including PE-CE route exchange and PE-PE route exchange.