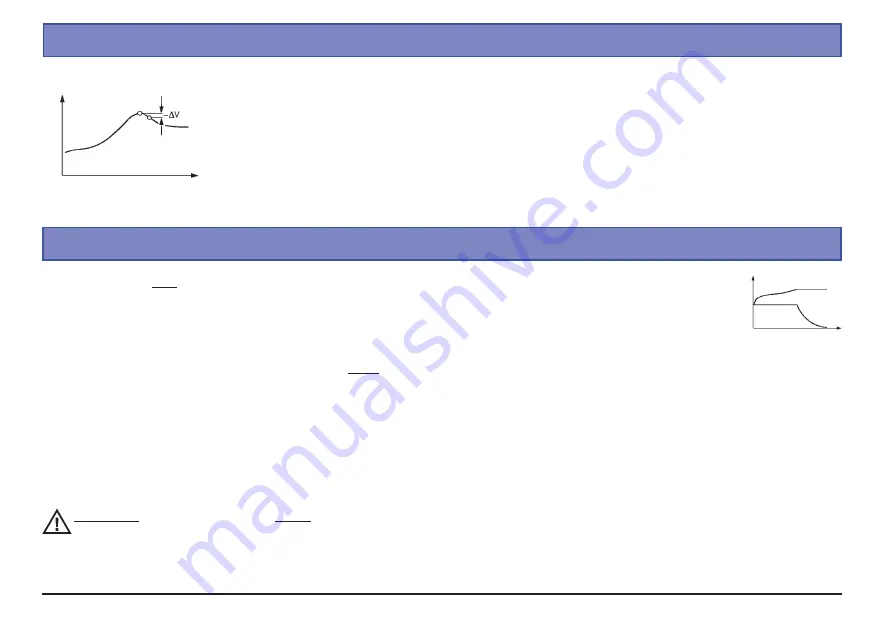
The automatic charge termination circuit (battery full detection) works on the proven Delta Peak principle (also known
as the Delta-V process), which is already in use in millions of chargers. This process analyses the voltage peak of
the charge curve, which indicates with great accuracy when the maximum charge capacity is reached. When the
charge process is started the battery voltage initially rises continuously, but as the pack approaches full capacity it
begins to heat up. This in turn causes the battery voltage to fall slightly (Delta-V). The charger detects and assesses
the voltage decline.It is possible to adjust the sensitivity, or trigger voltage (in mV
per
cell!) of the automatic cut-off
circuit. A practical range of values has proved to be 3 … 20 mV / cell. For most NiMH batteries a value between 5 and
10 mV are found to be ideal, however, RTU batteries
must
set to 5 mV.
12. NiXX charging program
NiXX-Delta-Peak (-
Peak) trigger voltage
13. LiXX charging program
WARNING:
The set battery type must always agree with the battery to be charged; there must never be a discrepancy -
fi re hazard and explosion
hazard!
Never connect a battery with integral charge mechanism to the charger. Batteries should always be placed on a non-infl ammable surface for charging. If
you wish to charge your LiXX batteries as effectively as possible, the balancer plug must be connected to the charger during the charge process.
cell v
oltage
charging time
34
Manual ULTRA QUICK 70
These programs are
only
suitable for charging and discharging LiFePO
4
batteries with a voltage of 3.3 V / Cell and Lithium-Polymer
and Lithium-Manganese batteries with a voltage of 3.7 V / cell. The outstanding feature of Lithium batteries is their much higher
capacity compared to other battery types. However, this important advantage is offset by the need to adopt different handling stra-
tegies: they must be charged and discharged using specifi c methods, otherwise they will be damaged, and can be dangerous. The
directions in these instructions must be observed at all times when handling these batteries. Specifi c information and safety notes
will also be found in the battery manufacturer’s technical information.
The fundamental rule is that Lithium-based batteries may ONLY be charged using special chargers, and the charge program must be set up correctly in
terms of fi nal charge voltage and capacity for the battery type in use. The charge process is fundamentally different to that required for Ni-Cd or Ni-MH
batteries, and is termed a constant current / constant voltage method. The charge current required varies according to the battery capacity, and is set
automatically by the charger. Lithium batteries are usually charged at the 1C rate (1C charge rate = half capacity as charge current. Example: battery
capacity 1500 mAh: 1C charge current = 1500 mA = 1.5 A).
Because some types can be charged with upt to 2C or 4C charging current, the charging current and the capacity of the battery must be set seperately.
When the battery on charge reaches the specifi c fi nal voltage which is appropriate to the battery type, the charger automatically reduces the charge
current in order to prevent the battery exceeding the fi nal permissible voltage. If the battery manufacturer states a charge current lower than the 1C rate,
then the capacity (charge current) must be reduced accordingly.
charge time
current
voltage
















































