Viewing Tide Station, Current Station, or Celestial
Information for a Different Date
1
Select
Nav Info
>
Tides & Currents
.
2
Select
Tides
,
Currents
, or
Celestial
.
3
Select an option.
• To view information for a different date, select
Change
Date
>
Manual
, and enter a date.
• To view information for today, select
Change Date
>
Current
.
• If available, to view information for the day after the date
shown, select
Next Day
.
• If available, to view information for the day before the date
shown, select
Previous Day
.
Viewing Information for a Different Tide or Current
Station
1
Select
Nav Info
>
Tides & Currents
.
2
Select
Tides
or
Currents
.
3
Select
Nearby Stations
.
4
Select a station.
Viewing Almanac Information from the Navigation
Chart
1
Select
Charts
>
Navigation Chart
.
2
Select an area on the map.
3
Select
Information
.
4
Select
Tides
,
Currents
, or
Celestial
.
Sonar
When properly connected to an optional Garmin sounder
module and a transducer, your compatible chartplotter can be
used as a fishfinder. There are three different sonar views to
help you view the fish in the area: a full-screen view, a split-
zoom view, and a split frequency view.
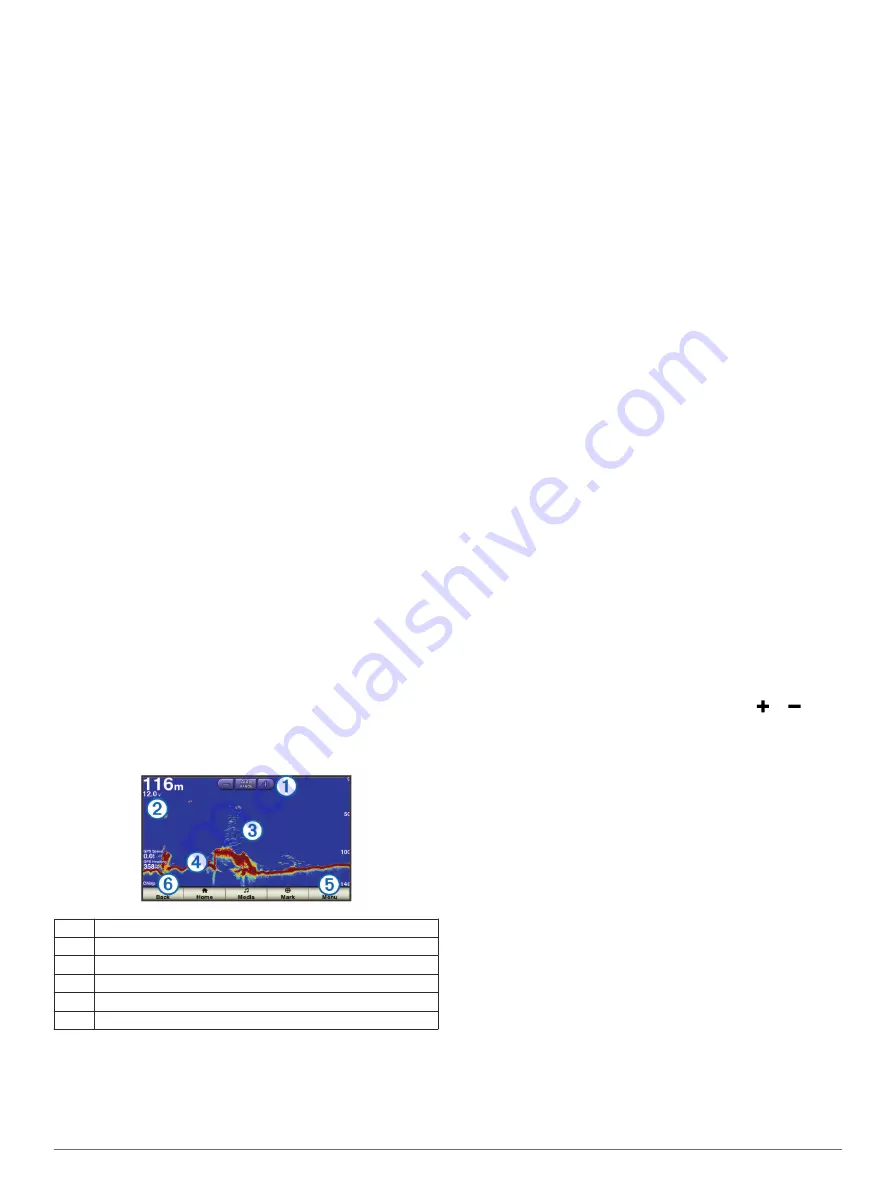
Full-Screen Sonar View
The full-screen sonar view shows a large image of the sonar
readings from a transducer. The range scale along the right side
of the screen shows the depth of detected objects as the screen
scrolls from the right to the left.
Select
Sonar
>
Full Screen
.
À
Range adjustment controls
Á
Position information
Â
Suspended targets or fish
Ã
Bottom of the body of water
Ä
Range or depth of the water
Å
Transducer frequency
Split-Zoom Sonar View
The split-zoom sonar view shows a full-view graph of sonar
readings, and a magnified portion of that graph, on the same
screen.
Select
Sonar
>
Split Zoom
.
Split-Frequency Sonar View
In the split-frequency sonar view, one side of the screen shows
a full-view graph of high frequency sonar data, and the other
side of the screen shows a full-view graph of lower frequency
sonar data.
NOTE:
The split-frequency sonar view requires the use of a
dual-frequency transducer.
Select
Sonar
>
Split Frequency
.
Pausing the Sonar Display
From a Sonar view, select
Menu
>
Pause Sonar
.
Creating a Waypoint on the Sonar Screen
1
From a Sonar view, select
Menu
>
Pause Sonar
.
2
Select the location of the waypoint.
3
Select
Mark
or
New Waypoint
.
Adjusting the Gain on the Sonar Screen
You can control the sensitivity of the sonar receiver. To see
more detail, increase the gain. If the screen is cluttered,
decrease the gain.
1
From a Sonar view, select
Menu
>
Gain
.
2
Select an option:
• To increase or decrease the gain manually, select
Up
or
Down
.
• To allow the chartplotter to adjust the gain automatically,
select an automatic option.
Adjusting the Range of the Depth Scale
You can adjust the range of the depth scale that appears on the
right side of the screen.
1
From a Sonar view, select
Menu
>
Range
.
2
Select an option:
• To allow the chartplotter to adjust the depth scale
automatically, select
Auto
.
• To increase or decrease the range of the depth scale
manually, select
Up
or
Down
.
TIP:
From the sonar screen, you can select or to
manually adjust the range of the depth scale.
Setting the Zoom Level on the Sonar Screen
1
From a Sonar view, select
Menu
>
Zoom
.
2
Select an option:
• To zoom in on the sonar data from the bottom depth,
select
Bottom Lock
.
• To set the depth range of the magnified area manually,
select
Set Zoom
, select
View Up
or
View Down
to set
the depth range of the magnified area, and select
Zoom
In
or
Zoom Out
to increase or decrease the magnification
of the magnified area.
• To set the depth and zoom automatically, select
Set
Zoom
>
Auto
.
Selecting Frequencies
You can indicate which frequencies appear on the sonar screen
when using a dual frequency transducer.
1
From a Sonar view, select
Menu
>
Frequency
.
2
Select an option:
• To sweep each pulse through a range of frequencies to
deliver shallow-water-like target separation at extremely
deep depths and at low frequencies, select
Chirp
. This is
useful mainly for very deep, offshore waters and when
targeting some species of fish.
Sonar
13
















































