M SLURRY USER
INSTRUCTION ENGLISH 71569241 - 02/08
Page 38 of 60
®
from the shaft. Bearings removed can easily be
damaged and undetected until pump is put back in
operation.
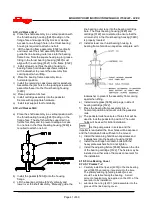
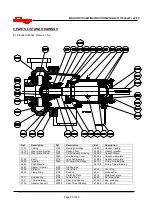
6.8.6 Thrust bearings
a) Lay the shaft [2100] horizontal and support with
wooden ‘V’ Blocks.
b) Remove the thrust bearing clamp ring [2542] from
the thrust bearing housing [3240].
c) Remove the thrust bearing housing [3240].
d) Bend up the locking tab on the bearing lockwasher
[6541] and remove the bearing locknut [3712] and
lockwasher [6541].
e)
Only if necessary remove the thrust bearings [3031]
from the shaft. Bearings removed and reused can
easily be damaged and undetected until pump is put
back in operation.
On frames 5 & 6 there are springs to
preload the thrust bearings. These must be removed
as the bearings are removed.
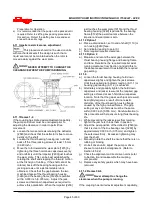
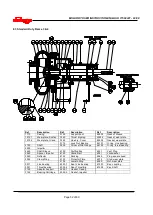
6.8.7 Gland side Wearplates
a) The wearplate [1915] can be removed from the
stuffing box head [4100] if required. The wearplate
is secured to the stuffing box head [4100] with
studs, nuts and washers.
6.8.8 Suction side wearplates
a) The wearplate [1915] can be removed from the
stuffing box head [4100] if required. The wearplate
is secured to the stuffing box head [4100] with
studs, nuts and washers.
6.8.8.1 Standard Duty Pumps
a) Remove the wearplate [1915] from the casing
[1110]. The wearplate is secured to the casing [1110]
with studs, nuts and washers.
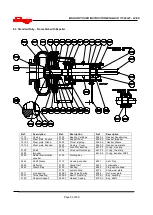
6.8.8.2 Severe Duty Pumps
a) Remove the suction cover [1223] from the casing
[1110].
b) Place the suction cover flat on a table of work
place with the wearplate side down.
c) Unfasten the wearplate from the suction cover
[1223]. The wearplate [1915] is secured to the
suction cover [1223] with studs and enclosed nuts
which have o-rings.
d) Lift the suction cover from the wearplate.
6.9 Examination of parts
Used parts must be inspected before
assembly to ensure the pump will subsequently run
properly.
In particular, fault diagnosis is essential to enhance
pump and plant reliability.
6.9.1 Casing, seal housing and impeller
a) Inspect for excessive wear, pitting, corrosion,
erosion or damage and any sealing surface
irregularities.
b) Replace as necessary.
c) Inspect the impeller [2200] and the wearplates [1915]
and [1915] for excessive wear or damage. Remove
the wearplate from the casing [1110] if necessary.
d) Inspect the casing [1110] and stuffing box head
[4100] for damage or excessive thinning of wall
sections due to wear or corrosion. Clean the internal
surfaces to maintain pump efficiency.
e) Inspect the protector plate [4132] and impeller
spacer [2460] and remove if damaged or worn.
Clean the internal bore of the stuffing box.
6.9.2 Shaft and sleeve [if fitted)
a) Replace sleeve if grooved, pitted or worn.
b) Clean the shaft and inspect for evidence of
corrosion, evidence of cracking, fatigue or mechanical
damage. Remove all burrs or nicks paying particular
attention to the areas under the lip seals. Check that
the shaft is straight within 0.002 inch (0.050 mm).
6.9.3 Gaskets and O-rings
After dismantling, discard and replace.
6.9.4 Bearings
a) It is recommended that bearings are not re-used
after any removal from the shaft.
b) The plain liquid lubricated bearings may be re-
used if both the bearing bush and bearing sleeve
show no sign of wear, grooving or corrosion
attack. (It is recommended that both the bush and
sleeve are replaced at the same time.)
6.9.5 Bearing isolators, labyrinths or lip seals
(if fitted)
a) The lubricant, bearings and bearing housing seals
are to be inspected for contamination and
damage. If oil bath lubrication is utilised, these
provide useful information on operating conditions
within the bearing housing.
b) If bearing damage is not due to normal wear and
the lubricant contains adverse contaminants, the
cause should be corrected before the pump is
returned to service.
c) Labyrinth seals and bearing isolators should be
inspected for damage but are normally non-
wearing parts and can be re-used.
d) Bearing seals are not totally leak free devices.
Oil from these may cause staining adjacent to the
bearings.