–
Make sure that no bridges or similar can be inserted parallel to the safety
wiring. For example, use the maximum wire cross section or appropriate plastic
wire end sleeves.
–
Use twin wire end sleeves for cross-wiring safety-related inputs and outputs.
A maximum of 10 devices may be cross-wired when cross-wiring inputs and
outputs
è
Manual Assembly, Installation.
–
The safety relay unit and its inputs and outputs must meet the necessary safety
classification of the safety function that is required for the specific case.
–
Connect each of the control inputs to the safety relay unit on 2 channels using
parallel wiring.
–
Only use permitted motor cables for the BR+/BR– connection.
–
If the diagnostic output of the safety sub-function concerned has to be evalu-
ated: connect diagnostic output directly to the safety relay unit. Evaluation
of the diagnostic output is either mandatory or optional depending on which
safety classification is desired.
–
If diagnostic outputs are cross-wired for a device compound: wire diagnostic
outputs as a ring. Run the two ends of the ring to the safety relay unit and
monitor for discrepancies.
7.2
Residual current protective device
WARNING
Risk of injury from electric shock.
This product can cause a DC current in the residual-current conductor in case of
error. In cases where a residual current device (RCD) or a residual current monitor
(RCM) is used to protect against direct or indirect contact, only the type B kind of
RCD or RCM is permitted on the power supply side of this product.
Information on the residual current protective device
è
Manual Assembly, Instal-
lation.
The touch current in the protective earthing conductor can exceed an alternating
current of 3.5 mA or a DC current of 10 mA. Always connect both protective
earthing connections to the mains-side PE connection, the PE pin of [X9A] and
PE earthing screw on the housing. The minimum cross section of the protective
earthing conductor must comply with the local safety regulations for protective
earthing conductors for equipment with high leakage current.
7.3
Mains fuse
The CMMT-AS has no integrated fuse at the mains input or in the DC link circuit.
An external fuse is required at the mains supply of the device. A device compound
coupled in the DC link circuit must be protected by means of a common mains
fuse.
•
Only use line safety switches and fuses that have the relevant approval and
meet the specifications and protection requirements stated below.
Requirements for line safety switches (circuit breakers) and fuses
Fuse/circuit breaker
type
Line safety switch
Class J/CC fuse
Max. permissible rated cur-
rent
[A]
16
25
Restrictions concerning line protection
Short circuit current rating
SCCR of mains fuse
[kA]
Min. 10
Min. 100
Approvals
IEC 60947-2
CE certification
Rated voltage
[V AC]
Min. 240
600
Overvoltage category
III
Pollution degree
2
Characteristic
C
Slow-blowing
Tab. 12: Requirements for line safety switches and fuses
In the case of electricity networks with a SCCR > 10 kA, only class J/CC fuses are
permitted. The line safety switch is used for line protection. The rated current of
the line safety switch must be less than or equal to the acceptable current rating
of the selected conductor cross section. The line safety switch must also take
into account the overload case and must not trip (overload case: up to a 3-fold
increase in the input current for 2 s).
Line protection requirements
Description
Cable cross sec-
tion at [X9A]
Mains fuse [A]
1)
[mm²]
CMMT-AS-
C2-3A-...
CMMT-AS-
C4-3A-...
Minimum fuse protec-
tion
0.75
6
Maximum fuse protec-
tion of an individual
device or a device
compound
1.5
13
2.5
16
1) Specifications according to DIN VDE 0298-4:2013, permissible currents according to EN 60204-1 may
differ (depending on laying method and temperature)
Tab. 13: Line protection requirements
Fuse protection when load circuit is supplied with DC power
The CMMT-AS allows the load circuit to be supplied with DC power. With DC
power, external fuse protection is once again required in the form of short circuit
protection and line protection. The fuse that is used must be capable of reliably
disconnecting the maximum DC supply voltage that could occur and the potential
short circuit current (SCCR
DC
).
Maximum fuse protection: 16 A
If fuse protection is to be avoided on the DC side, check whether the fuse protec-
tion could alternatively be installed on the AC side upstream of the DC fixed power
supply.
7.4
Permissible and impermissible mains types of system earthing
Information on allowed and prohibited mains types of system earthing and neces-
sary measures for use in IT networks
è
Manual Assembly, Installation.
Leakage currents in IT systems
High-frequency leakage currents to protective earthing (PE) may be encountered
even in IT systems (IT = Isolé Terre) during operation of the servo drive. The
leakage currents flow to the PE through the coupling capacitances of the motor
cable and the motor and back to the servo drive through the coupling capacitance
of the isolating transformer via the load supply. The coupling capacitances can be
minimised by selection of a suitable isolating transformer and keeping the motor
cable as short as possible.
WARNING
Risk of injury from electric shock.
The servo drive generates high-frequency leakage currents, which can lead to
dangerous contact currents on the external conductors and the neutral conductor
of the IT system. Touching the mains conductor or the neutral conductor can result
in serious injuries or death.
• Before working on the IT systems, disconnect the servo drive from the mains.
7.5
Connection of the mains side PE conductor
All PE conductors must always be connected prior to commissioning for safety
reasons. Observe the regulations of EN 60204-1 when implementing protective
earthing.
Always connect PE connection on the mains side (PE rail in the control cabinet) at
the following positions:
–
PE pin of the connection [X9A]
–
PE connection (earthing screw) next to the upper slot of the cooling element
The cross section of the PE conductors must be at least equal to the cross section
of the mains conductor L at [X9A]. Wire individually wired devices in a star shape.
Observe the requirements for cross-wiring for cross-wired devices. Recommenda-
tion: use copper earthing strap (advantageous for EMC).
1. Equip PE conductors for the earthing screw with a suitable cable lug.
2. Tighten earthing screw with a TORX screwdriver of size T20 (tightening torque
1.8 Nm
±
15 %).
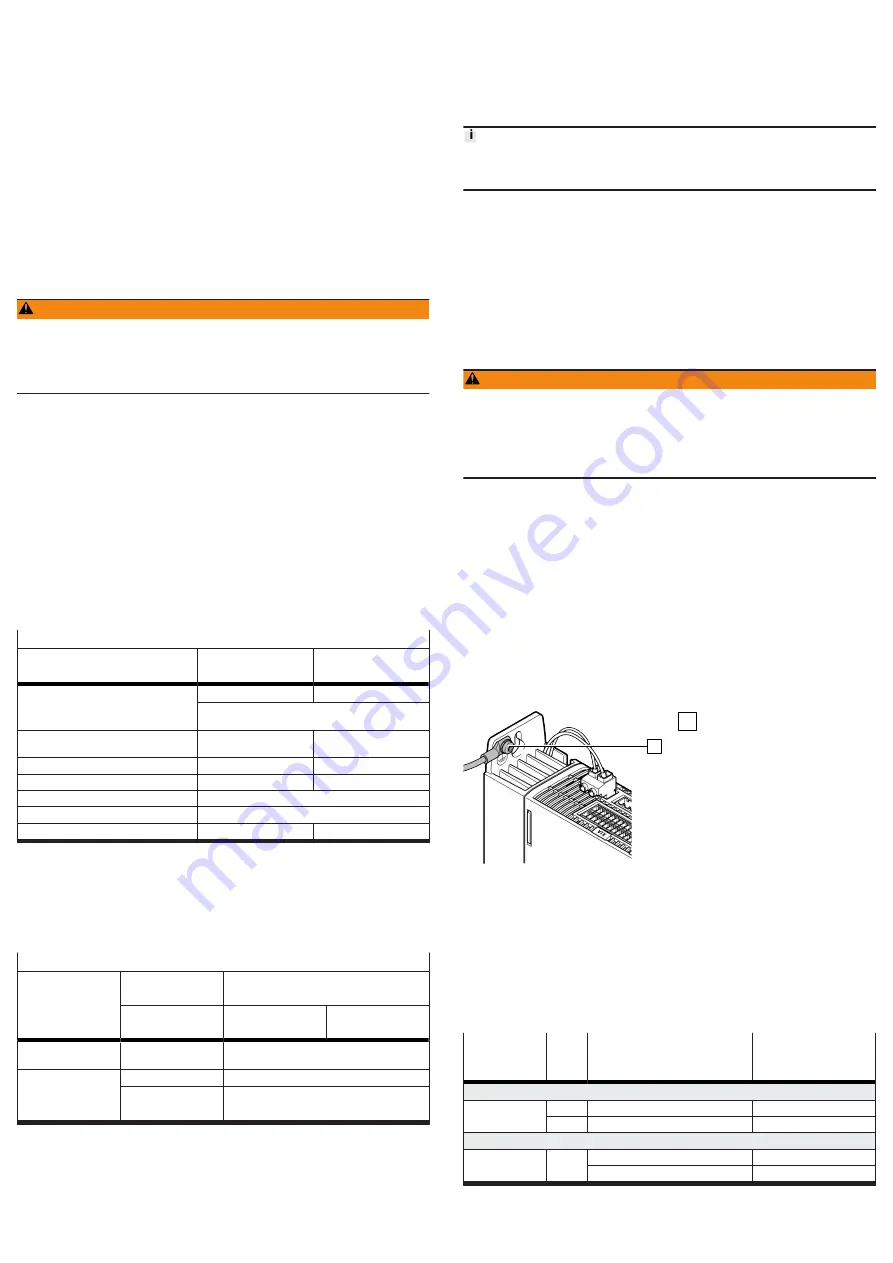
1
Fig. 5: PE connection (earthing screw)
1
PE connection (earthing screw)
7.6
Information on EMC-compliant installation
A mains filter is integrated into the device. The mains filter fulfils the following
tasks:
–
Guarantees the device’s immunity to interference
–
Limits the conducted emissions of the device
The device fulfills the requirements of the relevant product standard EN 61800-3
with suitable installation and wiring of all connecting cables.
The category that the device fulfils is dependent on the filter measures used and
the motor cable length. The integrated mains filter is designed so the device fulfils
the following categories when operated as an individual device:
CMMT-AS...
PWM
[kHz]
required measures
Max. permissible
motor cable length
[m]
Category C2: operation in the first environment (residential area)
-C2-3A
-C4-3A
8
Line choke
15
16
Line choke and snap ferrite
10
Category C3: operation in the second environment (industrial area)
-C2-3A
-C4-3A
8, 16
– (none)
25
External mains filter
50
Tab. 14: Category according to the pulse-width modulation frequency and the
cable length


































