Design and function
Interfaces for automation
099-007033-EW501
4.1.2022
49
5.7.1 Automation interface
These accessory components can be retrofitted as an option
> see 9 chapter
.
WARNING
No function of the external interrupt equipment (emergency stop switch)!
If the emergency stop circuit has been set up using an external interrupt equipment
connected to the interface for automated welding, the machine must be configured for
this setup. If this is not observed, the power source will ignore the external interrupt
equipment and will not shut down!
• Remove jumper 1 on the corresponding control board (to be done only by qualified service
personnel)!
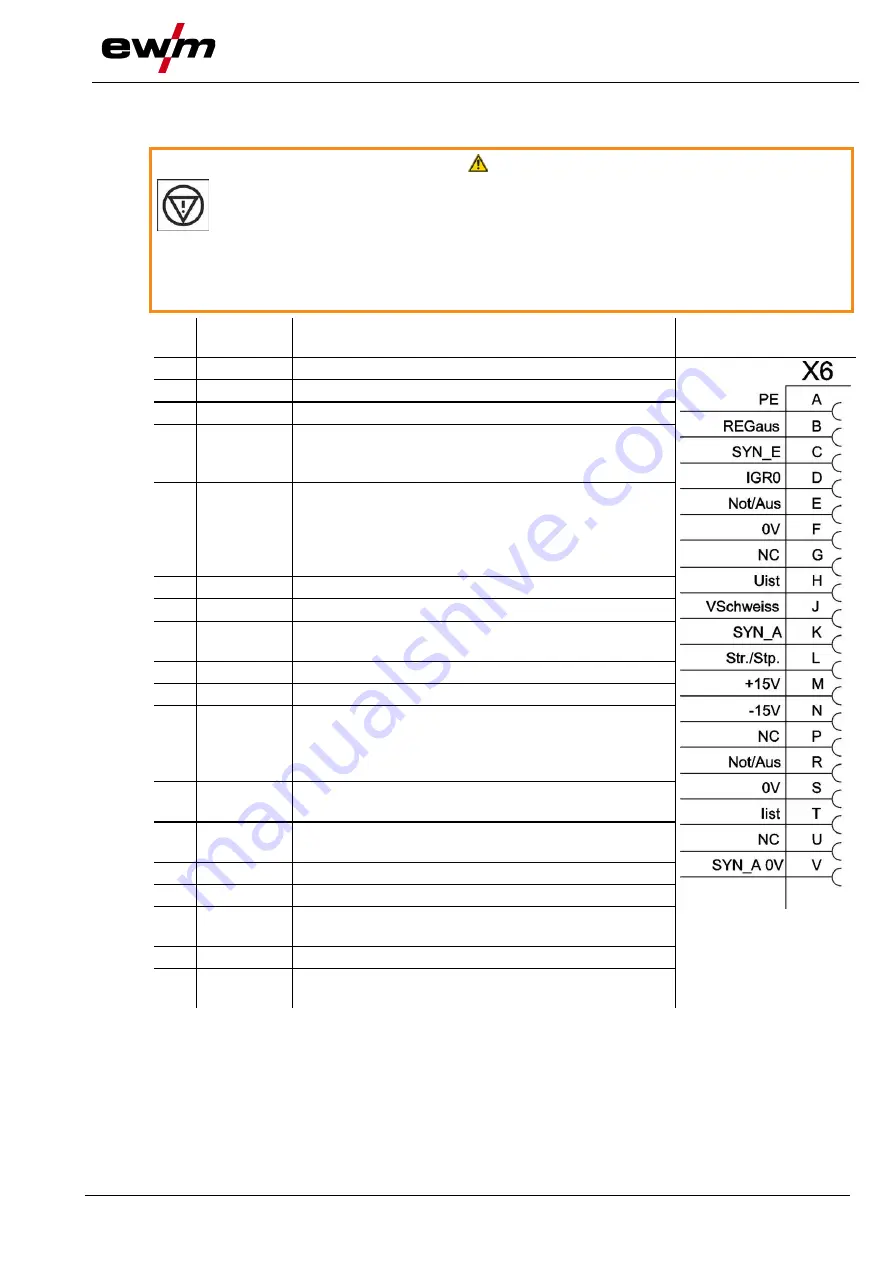
Pin Signal
shape
Designation
Diagram
A
Output
PE
Connection for cable screen
B
Output
REGaus For servicing purposes only
C
Input
SYN_E Synchronisation for master/slave operation
D
Input
(no c.)
IGRO
Current flows signal I>0 (maximum load 20mA
/ 15V)
0V = welding current flowing
E
+
R
Input
Output
Not/Aus Emergency stop for higher level shut-down of
the power source.
To use this function, jumper 1 must be unplugged on
PCB T320/1 in the welding machine. Contact open
=
welding current off
F
Output
0V
Reference potential
G
-
NC
Not assigned
H
Output
Uist
Actual welding voltage, measured on pin F, 0-
10V (0V = 0V, 10V = 100V)
J
Vschweiss
Reserved for special purposes
K
Input
SYN_A Synchronisation for master/slave operation
L
Input
Str/Stp Start / stop welding current, same as torch
trigger.
Only available in non-latched operating mode. +15V =
start, 0V
=
stop
M
Output
+15V
Voltage supply
+15V, max. 75mA
N
Output
-15V
Voltage supply
-15V, max. 25mA
P
-
NC
Not assigned
S
Output
0V
Reference potential
T
Output
Iist
Actual welding current, measured on pin F;
0-10V (0V = 0A, 10V = 1000A)
U
NC
V
Output
SYN_A 0V
Synchronisation for master/slave op-
eration
5.7.2 RINT X12 robot interface
The standard digital interface for mechanised applications
(optional, retrofitting on the machine or external fitting by the customer)
Functions and signals:
• Digital inputs: start/stop, operating modes, JOB and program selection, inching, gas test
• Analogue inputs: control voltages, e.g. for welding performance, welding current, etc.
• Relay outputs: process signal, ready for welding, system composite fault, etc.
















































