16
EATON
www.eaton.com
Instruction Booklet
IB020003EN
Effective January 2021
AMPGARD RVSS
Reduced Voltage Soft-Starter
User Manual
Figure 6.
Voltage R
amp
Motor Speed %
Motor Cur
rent
% of F
ull L
oad
Current at Full Voltage
Preset Current Limit
Kickstart Current Level
Kickstart Current Mode
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90 100
700
600
500
400
300
200
100
Transition Current
Threshold %
(default 185% - aka UTSD
up-to-speed detection)
Kickstart control mode.
1.5.2 Jog
Jog mode is a fixed applied % voltage. It uses a preset voltage value
to bump the motor, but not initiate a complete start. During a jog,
the RVSS output voltage ramps up to jog voltage level, runs there for
as long as the jog command is present, then ramps down to zero.
Jog is often used during commissioning to establish the minimum
voltage needed on a start to obtain movement of the motor and
connected load. This breakaway voltage value is then set into the
Voltage Ramp with Current Limit control profile as the initial voltage
delivered to the motor on a start.
1.5.3 Emergency bypass (across the line start)
The Ampgard RVSS uses a Bypass contactor as part of the normal
soft start sequence. This contactor can also be used as part of a
temporary emergency operation mode, when the RVSS SCR power
modules cannot be used for a normal start. In that case, moving the
SS2 selector switch from Normal to Bypass before initiating a start
commands the Bypass contactor to close and inhibits the soft-start
electronics operation. Then, when a start is initiated, the starter main
contactor feeds power through the closed Bypass contactor directly
to the motor.
The connected mechanical load must be able to tolerate occasional
across the line starts for Bypass operation to be used. Also, the
normal RVSS soft-start protection features such as Current Limit and
Instantaneous Overcurrent are not active. The starter system must
include an external motor protective relay to provide those features.
1.6 Stopping Modes
1.6.1 Coast stop
Coast Stop is the simplest of the stopping modes. When a stop
command is received, the RVSS will open the main contactor, open
the Bypass contactor, and the motor will coast to a stop, subject
only to the deceleration forces of friction, drag, windage, etc.
AMPGARD RVSS is shipped with Coast stop enabled. See
.
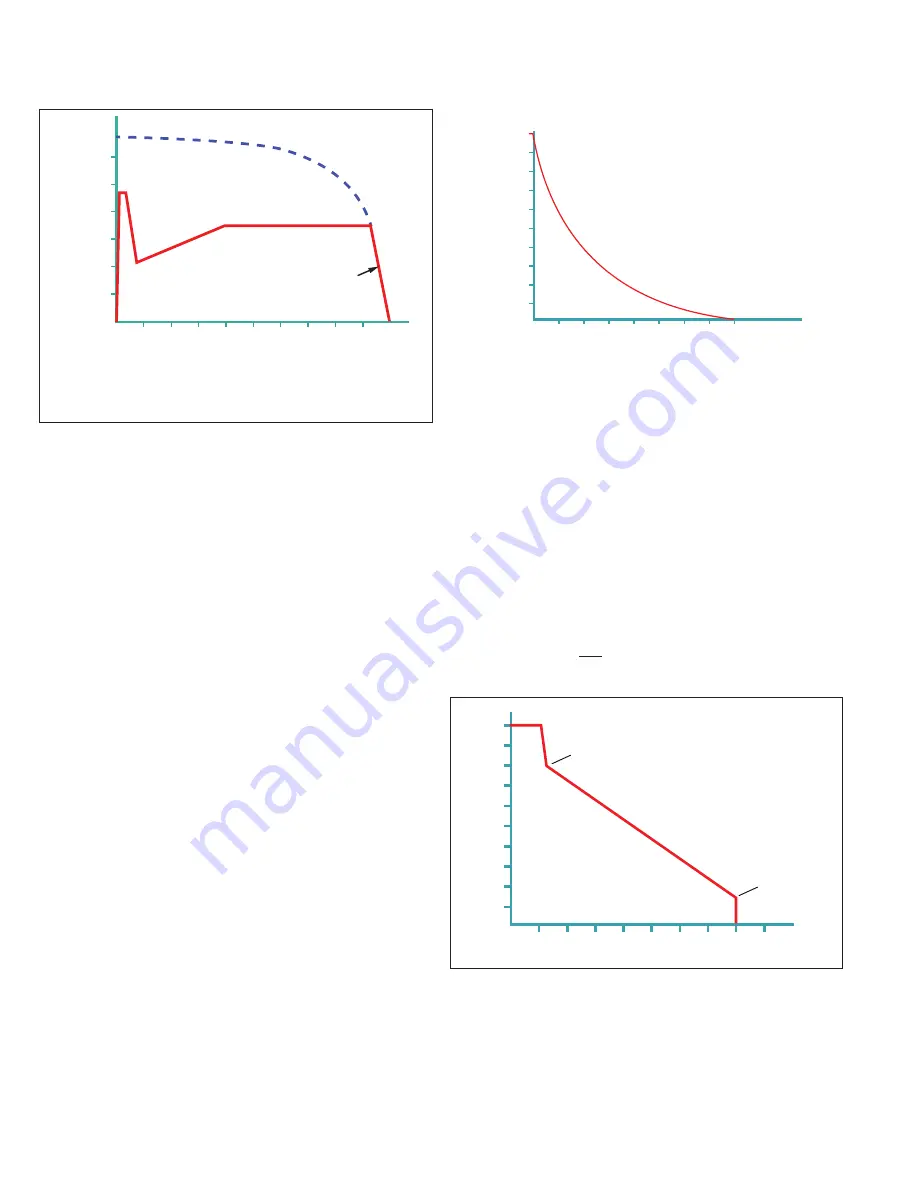
Figure 7.
Stop Time (seconds)
Coasting Stop
Motor Speed %
Coast Stop Mode
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
Coast stop control mode.
1.6.2 Linear Deceleration Voltage Soft-Stop
On some applications where the motor is under constant load, it
may be desirable to control the rate of motor slowing during a stop.
In Linear Deceleration, the RVSS opens the Bypass contactor and
immediately drops the output voltage to a preset initial voltage in a
few cycles. From the initial voltage, the output voltage ramps down
toward a preset final voltage, following a preset ramp rate. This
will have the effect of continuing to provide torque to the motor, in
decreasing amounts, so that it takes longer to come to a stop than
it would during a coast stop. The RVSS can be configured to provide
this controlled stop, following a profile that includes an initial voltage,
a ramp rate, and a final voltage, the point where the RVSS shots off
the SCRs, and the motor coasts to a stop. See
This mode is effective only when the motor is working against a
load. If the motor is unloaded or slightly loaded, it will continue to
rotate as if it were coasting to a stop.
Figure 8.
100%
10%
20%
30%
40%
50%
60%
70%
80%
90%
M
ot
or
Voltage
Time
Pump
Deceleration
Initial Voltage
Pump
Dece
leratio
n Ram
p
Pump
Deceleration
Stop
Linear deceleration voltage soft stop.






























