RABO
®
Rotary Gas Meter
05 Elster Instromet
7. Decommissioning and Removal
a) Always follow your company’s procedures, and local codes
and ordinances.
b) Slowly open bypass valve.
c) Slowly close the meter’s outlet valve, then the inlet valve.
d) Slowly, completely depressurize the meter piping.
!
WARNING
Failure to depressurize the meter prior to removing meter
and/or components could result in personal injury and/or
property damage.
e) Drain oil from the index end case cover and dispose of the oil
in accordance with applicable regulations.
f) If removing the meter from the piping system, loosen flange
bolts. Ensure meter is properly supported before removing
bolts completely.
8. Inspection and Maintenance
It is recommended to inspect Elster RABO meters periodically to
help ensure accurate performance over a long period of time.
Maintenance intervals can be derived from inspection criteria.
Routine inspections should include:
a) Checking to ensure the meter is level in all planes
b) Listening for abnormal sounds in the meter
c) Checking oil level and clarity — oil should be red and clear
d) Checking index movement if gas is flowing
e) Checking for leaks
f) Testing the meter’s differential pressure
Routine maintenance should include:
a) Changing the oil if the color becomes dark
b) Adding oil if the color is red and clear, but below the
recommended level
9. Testing
Elster RABO meters should be tested in accordance with applicable
governing standards. The accuracy of a meter can only be
determined by comparing results to a traceable reference, typically
a sonic nozzle, bell, piston or transfer prover. Accuracy may be
done on site using transfer provers, and typically requires removal
for testing with other technologies.
Differential pressure testing is a method of determining whether
the performance of a rotary meter may have changed over time,
and can be done on site while the meter is operating under
pressure. Baseline data must be captured during initial start-up to
which future data can be compared.
a) Proving
When testing a meter on a prover, the meter temperature,
pressure and volume are necessary inputs for the proving
device. The meter temperature is obtained by a temperature
probe installed near the inlet of the meter. A thermowell
can be installed in the meter run piping or on the meter
itself to facilitate installation of the temperature probe.
The meter pressure should come from the meter differential
pressure taps.
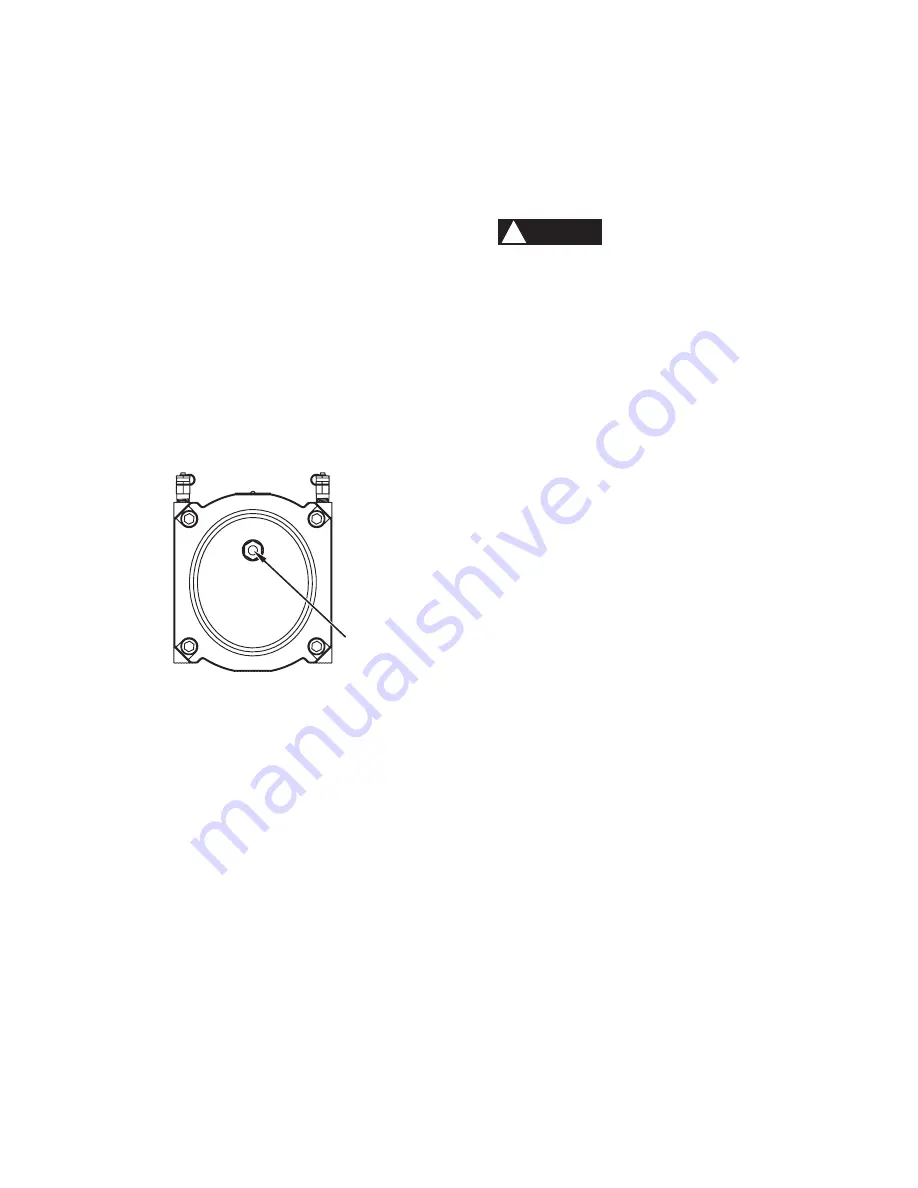
Figure 8. Back of meter
6. Start-up/Commissioning
After the meter has been properly installed, it is important to use
extreme care during start-up to mitigate adverse conditions that
can damage the meter.
a) Ensure that the maximum operating pressure of the meter
will not be exceeded.
b) Always follow your company’s procedures, and local codes
and ordinances.
c) With the meter run’s inlet and outlet valves closed, open the
bypass valve and pressurize the piping system.
d) With the meter outlet valve closed, slowly open the meter
inlet valve not to exceed 5 psig per second until pressure
is equalized throughout the meter piping system. Rapid
pressurization can cause an over-speed condition and
can damage the meter. Damage will not be covered
under warranty. When the meter piping system pressure is
stabilized, open the inlet valve completely.
e) Slowly open the meter’s outlet valve until the meter starts to
operate at low speed. Meter speed can be seen through the
view port located on the back of the meter [Figure 8].
f) Operate the meter at low flow for 1 to 2 minutes to verify
proper operation. If the index does not start registration, or
if you hear knocking or scraping sounds coming from the
meter, stop the flow and follow appropriate decommissioning
procedures before removing the meter from the line.
g) If operation is satisfactory, gradually open the meter’s outlet
valve to the full open position.
h) Slowly close the bypass valve.
i) Check the meter connections for leaks using common
industry practices.
j) Clock the meter (see Index section 11c) to confirm the flow rate
is not exceeding the maximum capacity of the meter.
k) Perform and record the meter’s differential pressure (see
Testing section 9b).
VIEW PORT
(DO NOT REMOVE)












