5.2 OPEN CIRCUITS
(1) Opens are caused when one or both. Conductors of a pair are disconnected or broken.
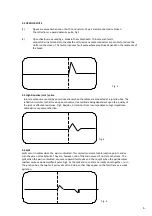
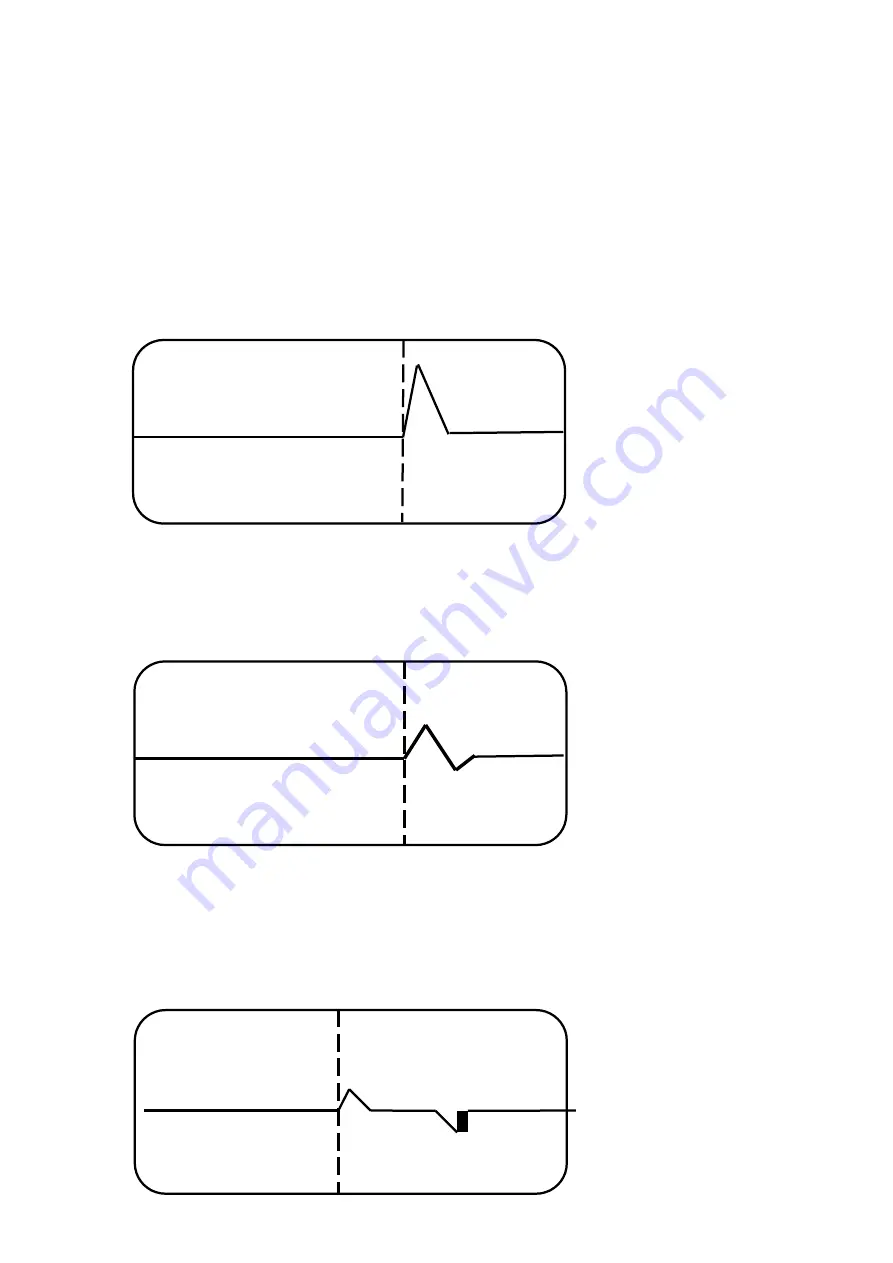
The reflection is upward polarity pulse, Fig.2
(2)
Open sheaths are caused by a break in the cable sheath. To locate such faults,
connect the line terminals to the sheath and to as many cable conductors as possible to reduce the
clutter on the screen. This fault produces a fault pulse whose amplitude depends on the resistance of
the break
.
Fig. 2
5.3 High Resistive joint / splice
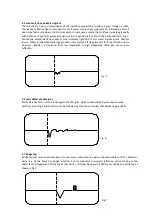
Joints or splices are caused by poor connections when the cables are connected at a junction box. The
reflection is similar to that for an open conductor, its amplitude being dependent upon the quality of
the joint or effective resistance. Fig 3. Besides, A transition from low impedance to high impedance
cable also cause same reflection.
Fig. 3
5.4 Split
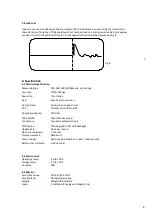
Splits occur in cables when the pair is untwisted. This normally occurs at cable junction points, and as
such they are not really faults. They are, however, one of the main causes of clutter on the trace. The
split, when the pair is untwisted, causes an upward fault pulse and the re-split, when the pair becomes
twisted, causes a downward fault pulse Fig 4. As the split and re-split are normally close together, i.e. in
the junction box, the two fault pulses almost coincide, so that they appear on the fault trace as a weak
agitation.
Fig. 4
6.