60
SERVICING
S-16A CHECKING AIR CIRCULATOR BLOWER
MOTOR (MULTI-SPEED ECM MOTOR)
D
ISCONNECT
ALL
POWER BEFORE SERVICING.
WARNING
1. Remove blower compartment door to gain access to the
circulator blower motor and integrated ignition control.
2. Check for any obstruction that would keep the fan wheel
/ fan motor from turning.
3. Check wiring, the motor has two wiring harnesses, a
main harness and a control harness. The main pin har-
ness has:
White neutral wire connected to the Neutral terminal on
the control board.
Black wire connected to the CIRC H terminal on the con-
trol board.
Red wire connected to the COM terminal, which is a
female spade connection next to the T1 – T4 wires on
the control board.
Green ground wire connected to cabinet ground
The control harness has:
Blue wire connected to T1 on the control board.
Red wire connected to T2 on the control board.
Orange wire connected to T3 on the control board.
Black wire connected to T4 on the control board.
The multi-speed ECM motor requires a line voltage power
supply (black connected to CIRC H and white connected
to neutral on the control board) as well as a signal on
one of the speed taps (T1-T4).
The speed tap voltage is D.C. and can vary depending
on S2 DIP switch selection. The voltage reading from
any one of the speed taps is referenced between the
female COM terminal next to the speed taps on the con-
trol board. From COM to T1 or T2, 6-7 VDC when ener-
gized. From COM to T3, 13-14 VDC when energized.
From COM to T4, 6-7 or 13-14 VDC depending on S2
settings.
S-200 CHECKING DUCT STATIC
The maximum and minimum allowable external static pres-
sures are found in the specification section. These tables
also show the amount of air being delivered at a given static
by a given motor speed.
The furnace motor cannot deliver proper air quantities (CFM)
against statics other than those listed.
Too great of an external static pressure will result in insuffi-
cient air that can cause excessive temperature rise, result-
ing in limit tripping, etc. Whereas not enough static may
result in motor overloading.
To determine proper air movement, proceed as follows:
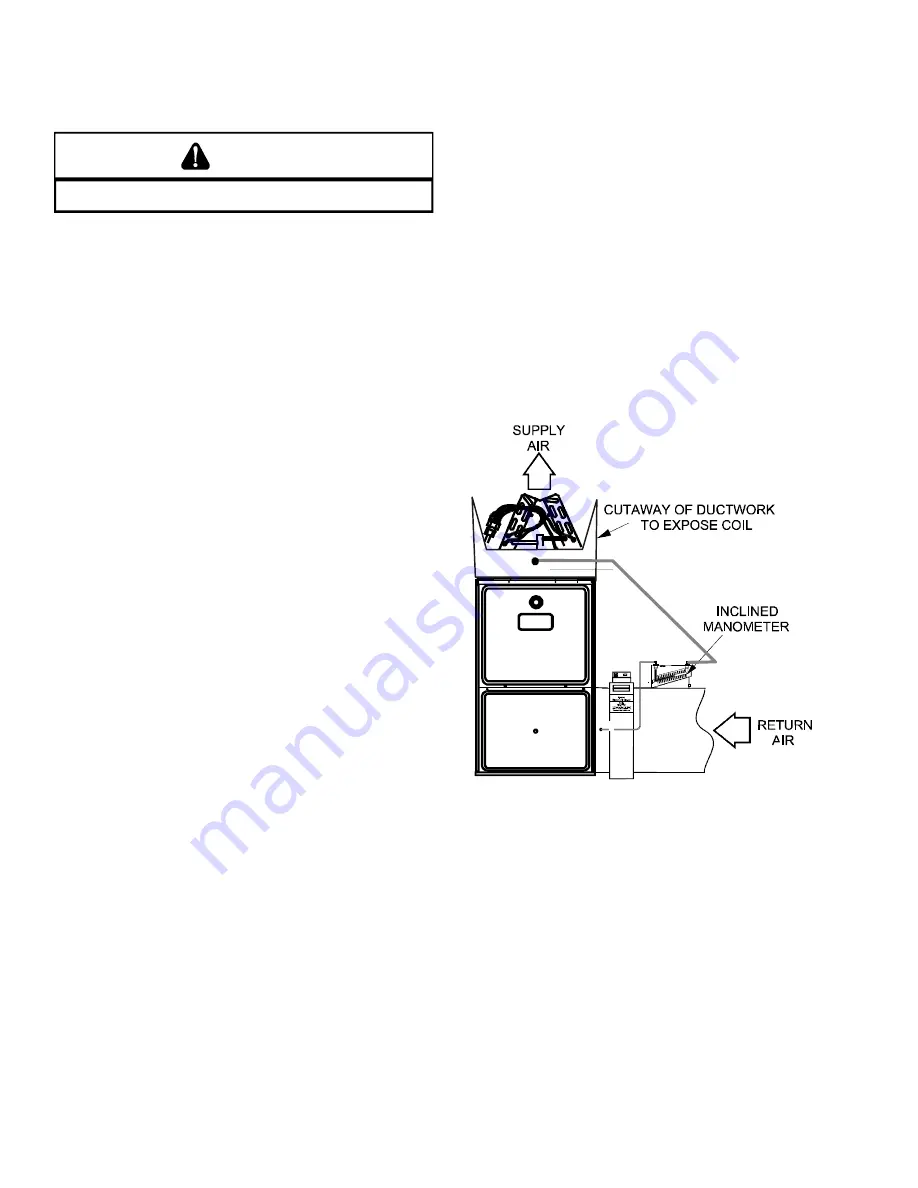
1. With clean filters in the furnace, use a draft gauge (in-
clined manometer) to measure the static pressure of the
return duct at the inlet of the furnace. (Negative Pres-
sure)
2. Measure the static pressure of the supply duct. (Posi-
tive Pressure)
3. Add the two (2) readings together for total external static
pressure.
NOTE:
Both readings may be taken simultaneously and
read directly on the manometer if so desired. If an air condi-
tioner coil or Electronic Air Cleaner is used in conjunction
with the furnace, the readings must also include theses com-
ponents, as shown in the following drawing.
4. Consult proper tables for the quantity of air.
If the total external static pressure exceeds the minimum or
maximum allowable statics, check for closed dampers, reg-
isters, undersized and/or oversized poorly laid out duct work.
Checking Static Pressure
S-201 CHECKING TEMPERATURE RISE
1. Operate furnace with burners firing for approximately ten
minutes. Check BTU input to furnace - do not exceed
input rating stamped on rating plate. Ensure all registers
are open and all duct dampers are in their final (fully or
partially open) position.
2. Place thermometers in the return and supply ducts as
close to the furnace as possible. Thermometers must
not be influenced by radiant heat by being able to “see”
the heat exchanger.





























