Check the Local Status Page
The Neighbors page of the
shows all of the neighbors of a given Meraki AP. Access this page on an online AP and check the to see if
the offline repeater MAC address appears in the table. If it does, the offline repeater is active and within range of the online AP.
Check Mesh Routes
Once a mesh neighbor relationship is confirmed between an offline repeater and its mesh neighbor, the next step is to confirm a mesh route exists. A repeater’s
mesh route table shows the path traffic must take to reach a specific gateway. This path can include multiple hops, meaning there may be intermediate
repeaters which traffic must pass through to reach the gateway. The route from the gateway back to the repeater might not follow the same path, Dashboard
only shows the repeater’s mesh route table.
If a repeater is having mesh connectivity issues, check the mesh route table on that AP's details page (under
Wireless > Monitor > Access points > The
repeater experiencing issues
) in Dashboard. For each route reported, there should be a mesh neighbor one hop away. Since the repeater will communicate
directly with those APs to get online, it is important to ensure that those routes are healthy. After determining which AP is the repeater's first hop, confirm that
the reported mesh neighbor is online, because it is not possible to gather Dashboard data from an offline node.
Repeaters have logic to determine which route to the gateway is best. It is calculated into a metric using a combination of hop count, data rates, RSSI, and loss
rate (FWD and REV rates). A perfect metric has a score of 1179, and APs can dynamically change to use a route with a better metric (if one is available).
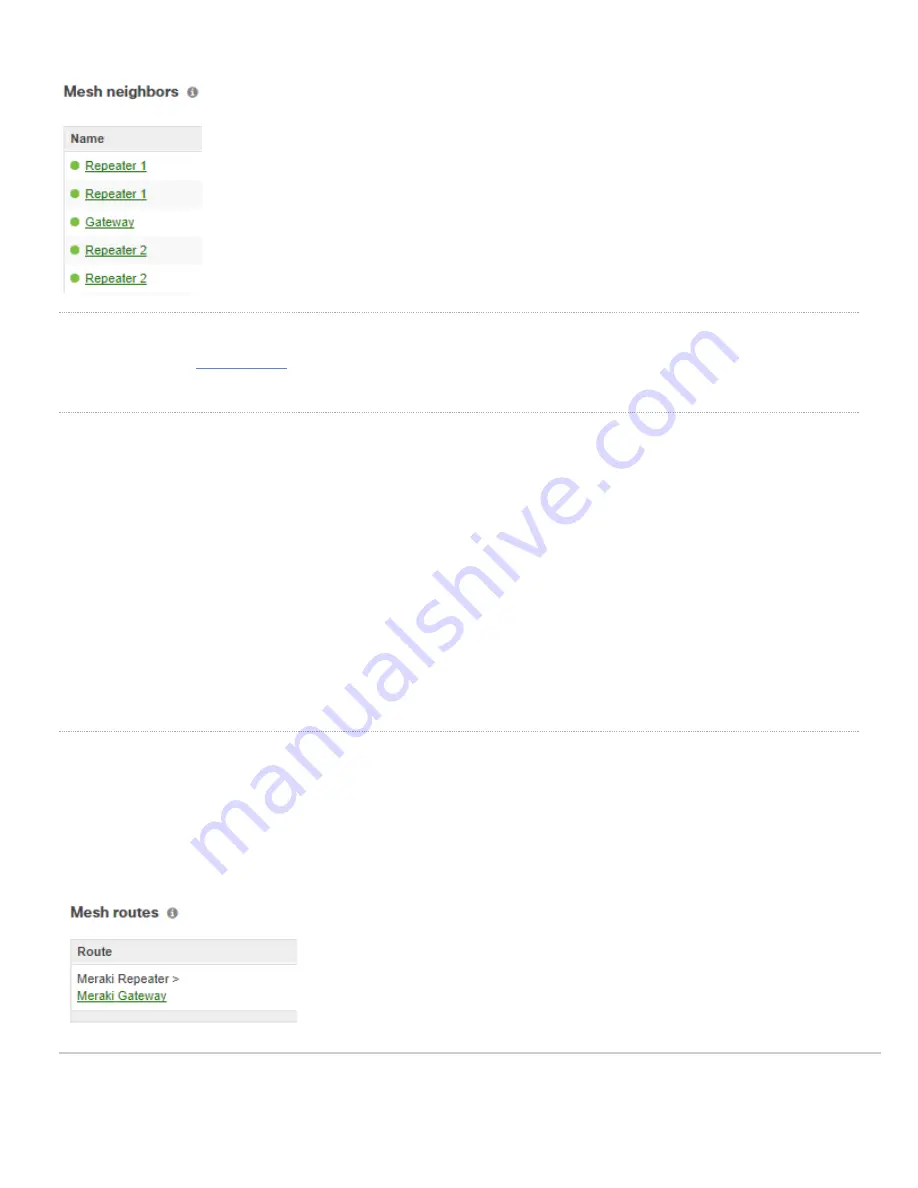
Checking the Mesh Routes Table
Below is an example of a Dashboard mesh route table for repeater “Meraki Repeater”.
Figure 7: The route table on Meraki Repeater can be used to show which network segments are closest.
4

























