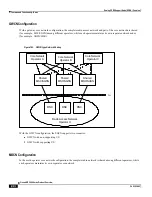
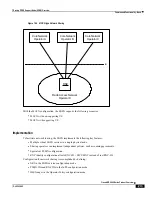
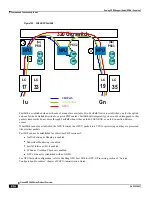
Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN) Overview
Features and Functionality - Basic ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series Product Overview ▄
OL-22938-02
Operator Policy
The non-standard operator policy feature is unique to the ASR 5000 SGSN. This feature empowers the carrier with
unusual and flexible control to manage functions that aren‘t typically used in all applications and to determine the
granularity of the implementation of any operator policy: to groups of incoming calls or to simply one single incoming
call.
What an Operator Policy Can Do
An SGSN operator policy enables the operator to define a policy with rules governing the services, facilities and
privileges available to subscribers depending on factors such as:
roaming agreements between operators,
subscription restrictions for visiting or roaming subscribers, and/or
provisioning of defaults to over-ride standard behavior.
These policies can override standard behaviors and provide mechanisms for an operator to circumvent the limitations of
other infrastructure elements such as DNS servers and HLRs. By configuring an operator policy, the operator fine-tunes
any desired restrictions or limitations needed to control call handling and this can be done for a group of callers within a
defined IMSI range or per subscriber.
For example, on APN resolution, DNS servers can be configured to return a list of IP addresses of GGSNs. However,
this only allows the implementation of an equal-weight round-robin scheme for distribution of load. The operator policy
configuration can provide finer control.
In another example, it is not unusual for a blanket configuration to be implemented for all subscriber profiles stored in
the HLR. This results in a waste of resources, such as the allocation of the default highest QoS setting for all
subscribers. The operator policy provides the opportunity to address such issues by allowing fine-tuning of certain
aspects of profiles fetched from HLRs and if desired overwrite QoS settings received from HLR.
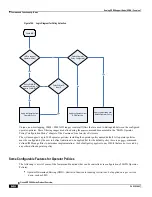
How the Operator Policies Work
The specific operator policy that is applied is selected on the basis of the subscribers IMSI at attach time, and optionally
the PLMN ID selected by the subscriber or the RAN node‘s PLMN ID.
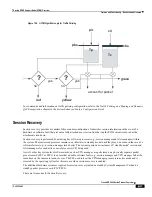
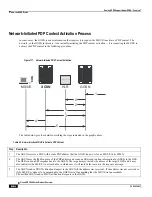
The following flow diagram maps out the logic for applying operator policies.
Содержание ASR 5000 Series
Страница 1: ......
Страница 26: ......
Страница 48: ...New In Release 10 0 SCM Features Cisco ASR 5000 Series Product Overview OL 22938 02 ...
Страница 50: ......
Страница 58: ......
Страница 67: ...Product Service and Feature Licenses Default Licenses Cisco ASR 5000 Series Product Overview OL 22938 02 ...
Страница 68: ......
Страница 126: ......
Страница 138: ......
Страница 146: ......
Страница 218: ......
Страница 236: ......
Страница 356: ......
Страница 374: ......
Страница 422: ......
Страница 496: ......
Страница 572: ......
Страница 654: ......
Страница 700: ......
Страница 726: ......
Страница 784: ......
Страница 816: ......
Страница 839: ...Network Address Translation Overview How NAT Works Cisco ASR 5000 Series Product Overview OL 22938 02 ...
Страница 841: ...Network Address Translation Overview How NAT Works Cisco ASR 5000 Series Product Overview OL 22938 02 ...
Страница 844: ......
Страница 906: ......
Страница 926: ......
Страница 942: ......
Страница 943: ...Cisco ASR 5000 Series Product Overview OL 22938 02 Chapter 30 Technical Specifications ...
Страница 966: ......
Страница 967: ...Cisco ASR 5000 Series Product Overview OL 22938 02 Chapter 31 Safety Electrical and Environmental Certifications ...
Страница 972: ......