4-20
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Chapter 4 Configuring Controller SettingsWireless Device Access
Configuring 802.11n Parameters
Step 4
To specify the aggregation method used for 802.11n packets, follow these steps:
a.
To disable the network, enter this command:
config
{
802.11a
|
802.11b
}
disable network
b.
To specify the aggregation method, enter this command:
config
{
802.11a
|
802.11b
}
11nsupport a-mpdu tx priority {0-7 | all} {enable
|
disable
}
Aggregation is the process of grouping packet data frames together rather than transmitting them
separately. Two aggregation methods are available: Aggregated MAC Protocol Data Unit
(A-MPDU) and Aggregated MAC Service Data Unit (A-MSDU). A-MPDU is performed in the
software whereas A-MSDU is performed in the hardware.
You can specify the aggregation method for various types of traffic from the access point to the
clients.
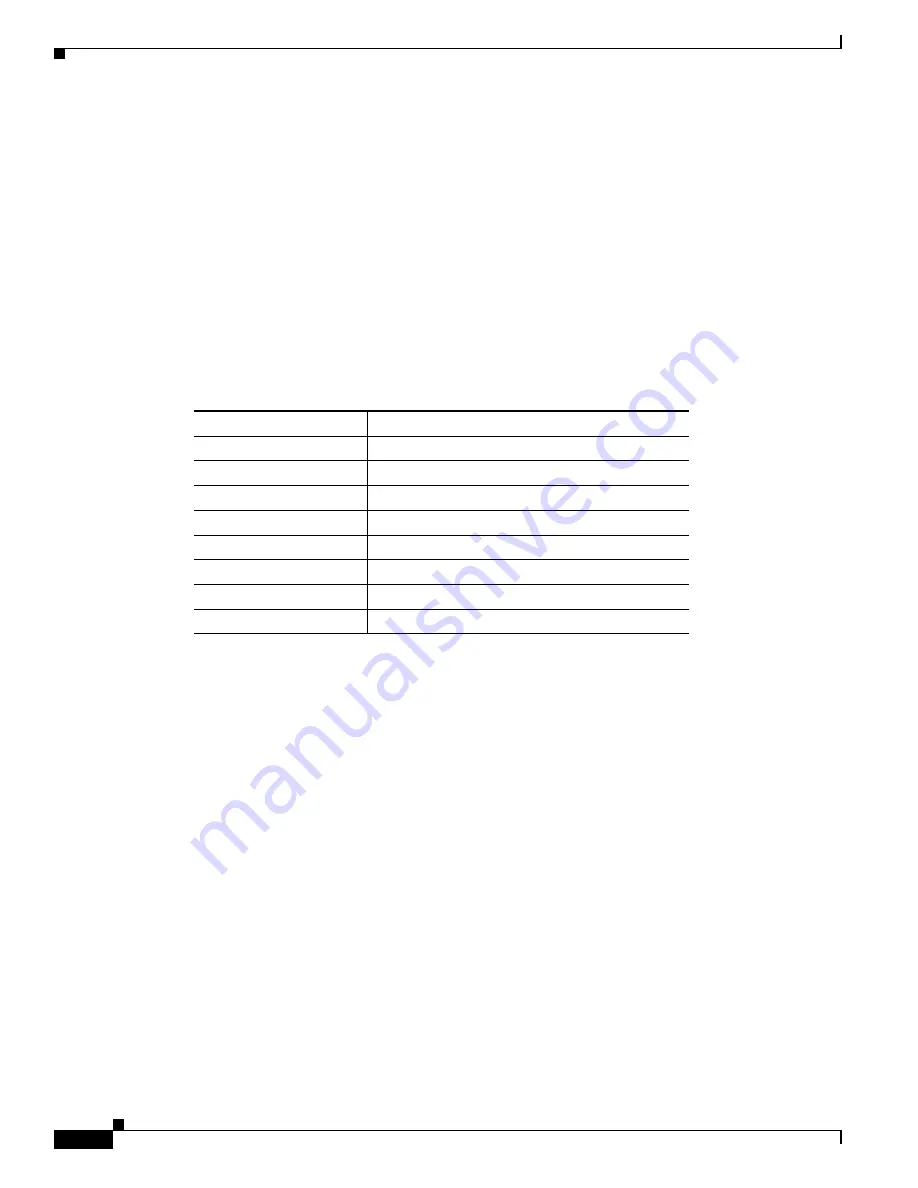
defines the priority levels (0-7) assigned per traffic type.
You can configure each priority level independently, or you can use the
all
parameter to configure
all of the priority levels at once. When you use the
enable
command, the traffic associated with that
priority level uses A-MPDU transmission. When you use the
disable
command, the traffic
associated with that priority level uses A-MSDU transmission. Configure the priority levels to match
the aggregation method used by the clients. By default, only priority level 0 is enabled.
c.
To re-enable the network, enter this command:
config
{
802.11a
|
802.11b
}
enable network
Step 5
To save your changes, enter this command:
save config
Step 6
To view the configuration settings for the 802.11a/n or 802.11b/g/n band, enter this command:
show
{
802.11a
|
802.11b
}
Information similar to the following appears:
802.11a Network............................... Enabled
11nSupport.................................... Enabled
802.11a Low Band........................... Enabled
802.11a Mid Band........................... Enabled
802.11a High Band.......................... Enabled
802.11a Operational Rates
802.11a 6M Rate.............................. Mandatory
802.11a 9M Rate.............................. Supported
802.11a 12M Rate............................. Mandatory
Table 4-1
Traffic Type Priority Levels
User Priority
Traffic Type
0
Best effort
1
Background
2
Spare
3
Excellent effort
4
Controlled load
5
Video, less than 100-ms latency and jitter
6
Voice, less than 10-ms latency and jitter
7
Network control






























