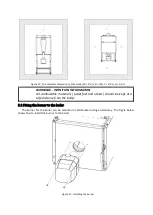
2.2 The principle of operation of individual modules
1.
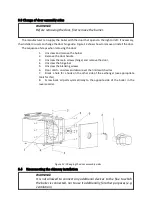
Tray (WZ, WZ + GP , WZO, WZO + GP )
Pellet fuel in the hopper (1) goes by gravity to the feeder (2) . The feeder consists of
a pellet feeding spiral (3) and a supply motor (geared motor) (4) . Pellet is forced by a spiral from
which the flexible tube ± spiro by ( 5 ) goes to the burner, which is an integral part of the heat
exchanger.
Figure 6 - Hopper principle of operation
2.
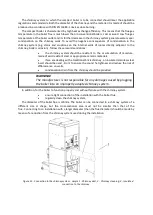
Exchanger
Compact boiler exchanger converts fuel ( pellets ) into thermal energy. The thermal energy is
transferred to the water circuit through the exchanger. The exchanger has the following features:
Exhaust fan - creates negative pressure of exhaust gases in the exchanger This
prevents unwanted smoke escaping through burner or boiler leaks , and ensures a
constant thrust value
Three-pass system - the combustion chamber is the first line (1). Then the
exhaust gases pass through the smoke tubes of the 2nd line (2) to the return chamber
(3). The third line consists of smoke tubes with a simple shape (4), which lead the flue
gases to the flue chamber (5), from where they are discharged by means of an
exhaust fan (6) through the flue (7) to the chimney system.
The filled (colored) areas in Figure 7 show that the boiler waterblock is in direct contact
with the water.