9
M
M
o
o
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
o
o
f
f
t
t
h
h
e
e
S
S
t
t
a
a
r
r
s
s
The daily motion of the Sun across the sky is familiar to even the most casual observer. This daily trek is not the
Sun moving as early astronomers thought, but the result of the Earth's rotation. The Earth's rotation also causes the
stars to do the same, scribing out a large circle as the Earth completes one rotation. The size of the circular path a
star follows depends on where it is in the sky. Stars near the celestial equator form the largest circles rising in the
east and setting in the west. Moving toward the north celestial pole, the point around which the stars in the northern
hemisphere appear to rotate, these circles become smaller. Stars in the mid-celestial latitudes rise in the northeast
and set in the northwest. Stars at high celestial latitudes are always above the horizon, and are said to be
circumpolar because they never rise and never set. You will never see the stars complete one circle because the
sunlight during the day washes out the starlight. However, part of this circular motion of stars in this region of the
sky can be seen by setting up a camera on a tripod and opening the shutter for a couple hours. The timed exposure
will reveal semicircles that revolve around the pole. (This description of stellar motions also applies to the southern
hemisphere except all stars south of the celestial equator move around the south celestial pole.)
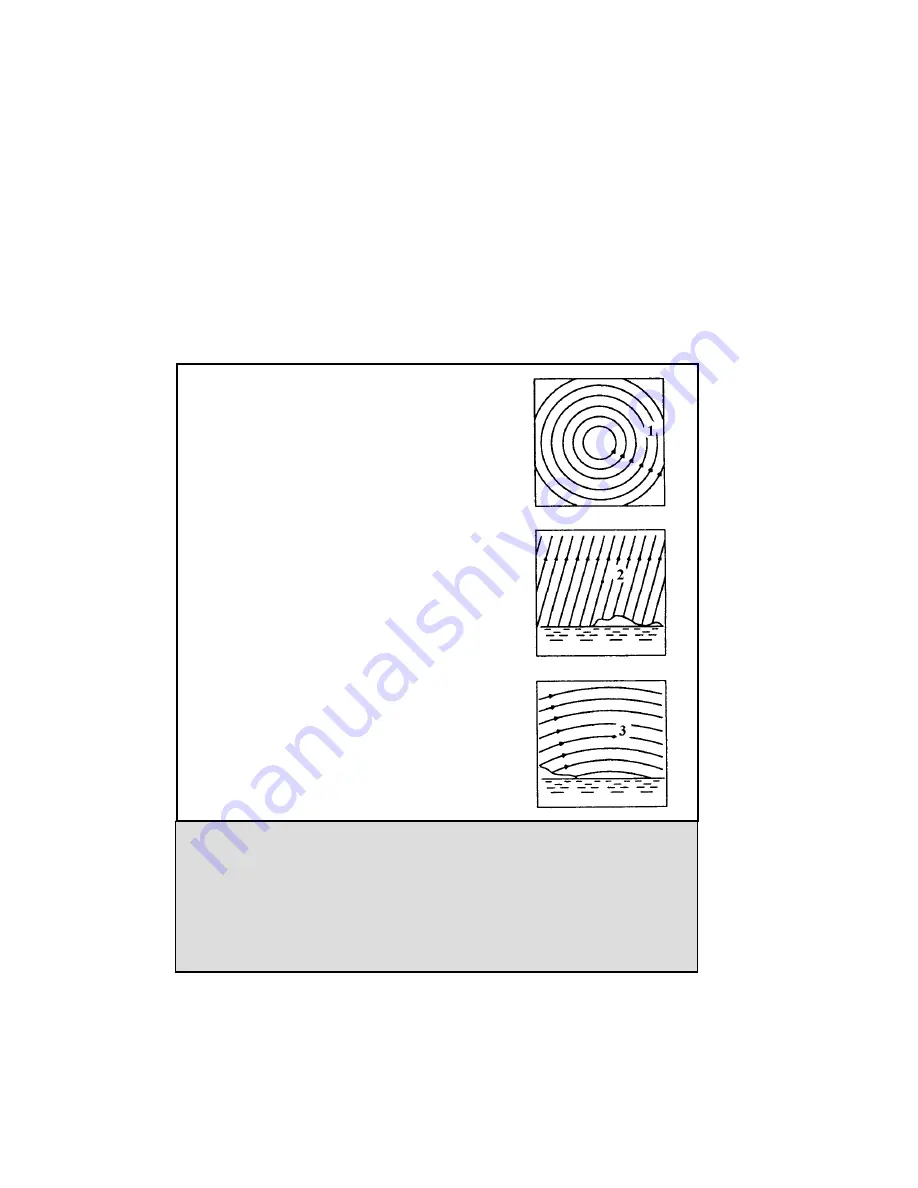
Figure 4-2
All stars appear to rotate around the celestial poles. However, the appearance of
this motion varies depending on where you are looking in the sky. Near the north
celestial pole the stars scribe out recognizable circles centered on the pole (1).
Stars near the celestial equator also follow circular paths around the pole. But, the
complete path is interrupted by the horizon. These appear to rise in the east and
set in the west (2). Looking toward the opposite pole, stars curve or arc in the
opposite direction scribing a circle around the opposite pole (3).
Starts seen near the north celestial
pole
Starts seen near the celestial
equator
Starts seen looking in the opposite
direction of the north celestial pole




























